
The Croatian Spring, or Maspok, was a political conflict that took place from 1967 to 1971 in the Socialist Republic of Croatia, at the time part of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. As one of six republics comprising Yugoslavia at the time, Croatia was ruled by the League of Communists of Croatia (SKH), nominally independent from the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ), led by President Josip Broz Tito. The 1960s in Yugoslavia were marked by a series of reforms aimed at improving the economic situation in the country and increasingly politicised efforts by the leadership of the republics to protect the economic interests of their respective republics. As part of this, political conflict occurred in Croatia when reformers within the SKH, generally aligned with the Croatian cultural society Matica hrvatska, came into conflict with conservatives.

League of Communists of Croatia was the Croatian branch of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ). It came into power in 1945. Until 1952, it was known as Communist Party of Croatia. In the early 1990s, it underwent several renames and lost power.

The League of Communists of Yugoslavia, known until 1952 as the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, was the founding and ruling party of SFR Yugoslavia. It was formed in 1919 as the main communist opposition party in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes and after its initial successes in the elections, it was proscribed by the royal government and was at times harshly and violently suppressed. It remained an illegal underground group until World War II when, after the invasion of Yugoslavia in 1941, the military arm of the party, the Yugoslav Partisans, became embroiled in a bloody civil war and defeated the Axis powers and their local auxiliaries. After the liberation from foreign occupation in 1945, the party consolidated its power and established a one-party state, which existed until 1990, two years prior to the breakup of Yugoslavia.
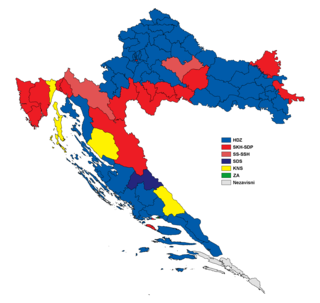
Parliamentary elections were held in the Socialist Republic of Croatia between 22 and 23 April 1990; the second round of voting occurred on 6–7 May. These were the first free, multi-party elections held in Croatia since 1938, and the first such elections for the Croatian Parliament since 1913. Voters elected candidates for 356 seats in the tri-cameral parliament; the turnout in the first round ranged between 76.56% and 84.54% for various parliamentary chambers. In the second round, the turnout was 74.82%. The Croatian Democratic Union (HDZ) won 205 seats, ousted the League of Communists of Croatia – Party of Democratic Reform (SKH-SDP) from power and ended 45 years of communist rule in Croatia. The new parliament convened for the first time on 30 May, elected Franjo Tuđman as President of the Croatian Presidency and soon after renamed the office to President of Croatia.
Stipe Šuvar was a Croatian politician and sociologist who was regarded to have been one of the most influential communist politicians in the League of Communists of Croatia in Socialist Republic of Croatia during Yugoslavia and later in modern Croatia.

The League of Communists of Serbia, founded as the Communist Party of Serbia in 1945, was the Serbian branch of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia, the sole legal party of Yugoslavia from 1945 to 1990. It changed its name from KPS to SKS in 1952. Under a new constitution ratified in 1974, greater power was devolved to the various republic level branches. In the late 1980s, the party was taken over by a faction endorsing Slobodan Milošević to become leader of the party. Milošević appeased nationalists in Serbia by promising to reduce the level of autonomy within the autonomous provinces of Kosovo and Vojvodina. This policy increased ethnic tensions with the other republics and nationalities. During the early 1990s, the growing ethnic tensions between the republics of Yugoslavia led to the breakup of the federal party.

The Socialist Republic of Serbia, previously known as the People's Republic of Serbia, was one of the six constituent republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in what is now the modern day states of Serbia and the disputed territory of Kosovo. Its formation was initiated in 1941, and achieved in 1944–1946, when it was established as a federated republic within Yugoslavia. In that form, it lasted until the constitutional reforms from 1990 to 1992, when it was reconstituted, as the Republic of Serbia within the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. It was the largest constituent republic of Yugoslavia, in terms of population and territory. Its capital, Belgrade, was also the federal capital of Yugoslavia.

League of Communist Youth of Yugoslavia, commonly known in English as the Young Communist League of Yugoslavia, or simply Communist Youth, was the youth wing of the Communist Party of Yugoslavia from 1919 to 1948. Although it was banned just two years after its establishment and at times ruthlessly prosecuted, it continued to work clandestinely and was an influential organization among revolutionary youth in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, and consequently became a major organizer of Partisan resistance to Axis occupation and local Quisling forces. After World War II, SKOJ became a part of a wider organization of Yugoslav youth, the People's Youth of Yugoslavia, which later became the League of Socialist Youth of Yugoslavia.
Borislav Mikelić was a Serbian businessman and politician. He was of Croatian Serb background.

The Socialist Alliance of Working People of Yugoslavia or SSRNJ, known before 1953 as the People's Front, was the largest and most influential mass organization in SFR Yugoslavia from August 1945 through 1990. By 1990, its membership was thirteen million individuals, including most of the adult population of the country. Together with the League of Communists of Serbia, it merged in July 1990 to form the Socialist Party of Serbia.

Yugoslavism, Yugoslavdom, or Yugoslav nationalism is an ideology supporting the notion that the South Slavs, namely the Bosniaks, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes, but also Bulgarians, belong to a single Yugoslav nation separated by diverging historical circumstances, forms of speech, and religious divides. During the interwar period, Yugoslavism became predominant in, and then the official ideology of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. There were two major forms of Yugoslavism in the period: the regime favoured integral Yugoslavism promoting unitarism, centralisation, and unification of the country's ethnic groups into a single Yugoslav nation, by coercion if necessary. The approach was also applied to languages spoken in the Kingdom. The main alternative was federalist Yugoslavism which advocated the autonomy of the historical lands in the form of a federation and gradual unification without outside pressure. Both agreed on the concept of National Oneness developed as an expression of the strategic alliance of South Slavs in Austria-Hungary in the early 20th century. The concept was meant as a notion that the South Slavs belong to a single "race", were of "one blood", and had shared language. It was considered neutral regarding the choice of centralism or federalism.

The League of Socialist Youth of Yugoslavia (SSOJ) was the youth movement, member organisation of the Socialist Alliance of Working People of Yugoslavia (SSRNJ). Membership stood at more than 3.6 million individuals in 1983.
In the Socialist Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, which was at the time one of the two socialist autonomous provinces of the Socialist Republic of Serbia and one of the federal units of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, a single-party system was in place. During this time there were six heads of state, all from the ranks of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ). The federal party was organized into six sub-organizations - the republic parties, one for each of the six federal republics. Vojvodinian politicians and presidents of the presidency of the period were members of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia through their membership in the League of Communists of Vojvodina (SKV), the Vojvodinian part of the federal party.
In the Socialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo, which was at the time one of the two socialist autonomous provinces of the Socialist Republic of Serbia and one of the federal units of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, a single-party system was in place. During this time there were eight heads of state, all from the ranks of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ). The federal party was organized into six sub-organizations - the republic parties, one for each of the six federal republics. Kosovan politicians and presidents of the presidency of the period were members of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia through their membership in the League of Communists of Kosovo (SKK), the Kosovan part of the federal party.

The Organization of the League of Communists in the Yugoslav People's Army was the branch of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ) for members of the Yugoslav People's Army.

The 14th (Extraordinary) Congress of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia was held from 20 to 22 January 1990, in the Belgrade Sava Centar. The highest organ of both the government and the party, it was the last Congress of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia. It was attended by delegates from all the republics and provinces, as well as a party delegation from the Yugoslav People's Army. The meeting was chaired by President of the Presidency of the Central Committee Milan Pančevski from Macedonia.
Two members of the Presidency of the Central Committee of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ) for the Socialist Republic of Montenegro existed from the 11th Congress in 1978 to the dissolution of the SKJ at the 14th Congress in 1990.
A member of the Presidency of the Central Committee of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ) for the Socialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo existed from the 11th Congress in 1978 to the dissolution of the SKJ at the 14th Congress in 1990.

The Communist Party of Yugoslavia held its 6th Congress in Zagreb on 2–7 November 1952. It was attended by 2,022 delegates representing 779,382 party members. The 6th Congress sought to discuss new policies, first of all in reaction to the Yugoslav–Soviet split and Yugoslav rapprochement with the United States. The congress is considered the peak of liberalisation of Yugoslav political life in the 1950s. The Congress also renamed the party the League of Communists of Yugoslavia.
The 12th Congress of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia was held from 26 to 29 June 1982, in the Belgrade Sava Centar. The highest organ of both the government and the party, it was the first Congress of League of Communists of Yugoslavia convened since Josip Broz Tito's death in 1980. It was attended by delegates from all the republics and provinces, as well as a party delegation from the Yugoslav People's Army.














