
Dehydroalanine is a dehydroamino acid. It does not exist in its free form, but it occurs naturally as a residue found in peptides of microbial origin. As an amino acid residue, it is unusual because it has an unsaturated backbone.
Nitrilase enzymes catalyse the hydrolysis of nitriles to carboxylic acids and ammonia, without the formation of "free" amide intermediates. Nitrilases are involved in natural product biosynthesis and post translational modifications in plants, animals, fungi and certain prokaryotes. Nitrilases can also be used as catalysts in preparative organic chemistry. Among others, nitrilases have been used for the resolution of racemic mixtures. Nitrilase should not be confused with nitrile hydratase which hydrolyses nitriles to amides. Nitrile hydratases are almost invariably co-expressed with an amidase, which converts the amide to the carboxylic acid. Consequently, it can sometimes be difficult to distinguish nitrilase activity from nitrile hydratase plus amidase activity.
Glutamine synthetase (GS) is an enzyme that plays an essential role in the metabolism of nitrogen by catalyzing the condensation of glutamate and ammonia to form glutamine:

Histidine ammonia-lyase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HAL gene. It converts histidine into ammonia and urocanic acid. Its systematic name is L-histidine ammonia-lyase (urocanate-forming).

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.
Serine dehydratase or L-serine ammonia lyase (SDH) is in the β-family of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent (PLP) enzymes. SDH is found widely in nature, but its structural and properties vary among species. SDH is found in yeast, bacteria, and the cytoplasm of mammalian hepatocytes. SDH catalyzes is the deamination of L-serine to yield pyruvate, with the release of ammonia.
The enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.1, CTH or CSE; also cystathionase; systematic name L-cystathionine cysteine-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming)) breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, 2-oxobutanoate (α-ketobutyrate), and ammonia:

The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.
In enzymology, a methylaspartate mutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cystathionine beta-lyase, also commonly referred to as CBL or β-cystathionase, is an enzyme that primarily catalyzes the following α,β-elimination reaction
The enzyme ethanolamine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.7) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme Glucosaminate ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.9) catalyzes the chemical reaction
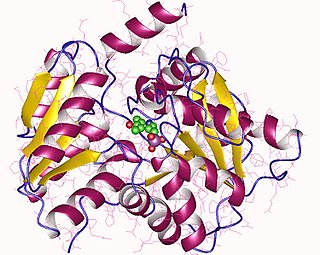
The enzyme L-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.17) catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme phenylalanine ammonia lyase (EC 4.3.1.24) catalyzes the conversion of L-phenylalanine to ammonia and trans-cinnamic acid.:
The enzyme threo-3-hydroxyaspartate ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.16) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Threonine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.19, systematic name L-threonine ammonia-lyase (2-oxobutanoate-forming), also commonly referred to as threonine deaminase or threonine dehydratase, is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of L-threonine into α-ketobutyrate and ammonia:

Isocitrate lyase, or ICL, is an enzyme in the glyoxylate cycle that catalyzes the cleavage of isocitrate to succinate and glyoxylate. Together with malate synthase, it bypasses the two decarboxylation steps of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and is used by bacteria, fungi, and plants.
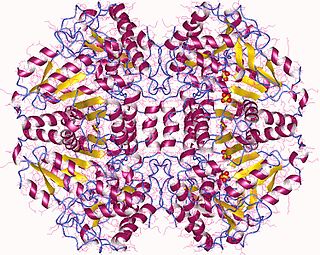
The enzyme tryptophanase (EC 4.1.99.1) catalyzes the chemical reaction
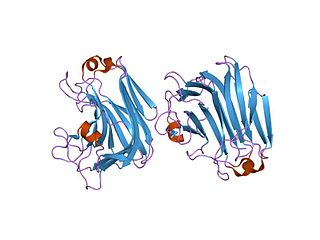
The enzyme mannuronate-specific alginate lyase catalyzes the degradation of alginate into various monosaccharide and polysaccharide products:
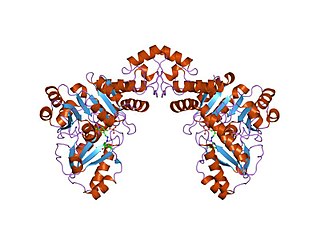
In molecular biology, the Cys/Met metabolism PLP-dependent enzyme family is a family of proteins including enzymes involved in cysteine and methionine metabolism which use PLP (pyridoxal-5'-phosphate) as a cofactor.

















