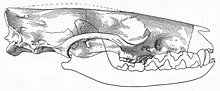
Creodonta is a former order of extinct carnivorous placental mammals that lived from the early Paleocene to the late Miocene epochs in North America, Europe, Asia and Africa. Originally thought to be a single group of animals ancestral to the modern Carnivora, this order is now usually considered a polyphyletic assemblage of two different groups, the Oxyaenids and the Hyenodonts, not a natural group. Oxyaenids are first known from the Palaeocene of North America, while hyaenodonts hail from the Palaeocene of Africa.

Viverravidae is an extinct monophyletic family of mammals from extinct superfamily Viverravoidea within the clade Carnivoramorpha, that lived from the early Palaeocene to the late Eocene in North America, Europe and Asia. They were once thought to be the earliest carnivorans and ancestral to extant ones, but now are placed outside the order Carnivora based on cranial morphology as relatives to extant carnivorans.

Miacidae is a former paraphyletic family of extinct primitive placental mammals that lived in North America, Europe and Asia during the Paleocene and Eocene epochs, about 65-33,9 million years ago. These mammals were basal to order Carnivora, the crown-group within the Carnivoraformes.

Miacis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from early to middle Eocene.

Carnivoramorpha is a clade of placental mammals that includes the modern order Carnivora and its extinct stem-relatives.

Vulpavus is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from early to middle Eocene.

Miocyon is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from early to late Eocene.

Oodectes is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from early to middle Eocene.

Palaearctonyx is an extinct genus of omnivorous placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from early to middle Eocene.
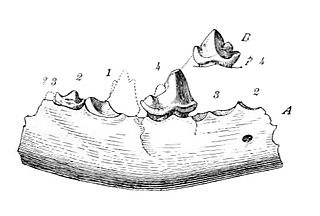
Prodaphaenus is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America during the middle Eocene.

Tapocyon is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America during the middle Eocene. Tapocyon was about the size of a coyote and is believed to have been a good climber that spent a lot of time in trees.

Uintacyon is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from early to middle Eocene.

Vassacyon is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America and Europe from late Paleocene to early Eocene. It is considered the largest of the early Eocene mammals.

Bryanictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America, from the early to late Paleocene.

Didymictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America and Europe from the late Paleocene to middle Eocene.
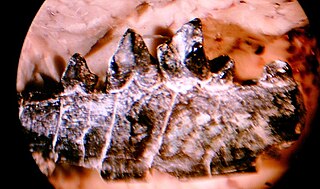
Ictidopappus is an extinct genus of mammals from extinct subfamily Ictidopappinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during the early Paleocene.
Intyrictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during early Paleocene.
Pristinictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during middle Paleocene.
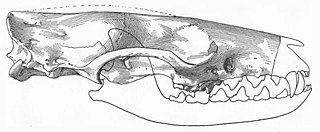
Viverravus is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Viverravinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America, Europe and Asia from the middle Paleocene to middle Eocene.

Protictis is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America from early Paleocene to middle Eocene.