
The semipalmated sandpiper is a very small shorebird. The genus name is from Ancient Greek kalidris or skalidris, a term used by Aristotle for some grey-coloured waterside birds. The specific pusilla is Latin for "very small".

The little bunting is a passerine bird belonging to the bunting family (Emberizidae).

Wilson's warbler is a small New World warbler. It is greenish above and yellow below, with rounded wings and a long, slim tail. The male has a black crown patch; depending on the subspecies, that mark is reduced or absent in the female. It breeds across Canada and south through the western United States, and winters from Mexico south through much of Central America. It is a very rare vagrant to western Europe.

Kogia is a genus of toothed whales within the superfamily Physeteroidea comprising two extant and two extinct species from the Neogene:
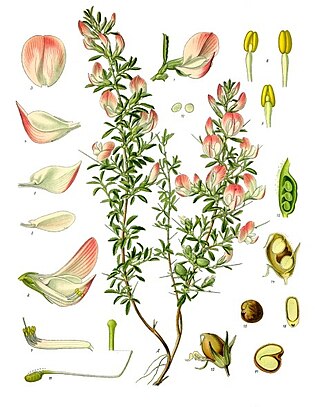
Ononis is a large genus of perennial herbs and shrubs from the legume family Fabaceae. The members of this genus are often called restharrows as some species grow as weeds on arable lands whose tough stems would stop the harrow. They are natively distributed in Europe.

The brown thornbill is a passerine bird usually found in eastern and south-eastern Australia, including Tasmania. It can grow up to 10 cm (3.9 in) long, and feeds on insects. It is brown, grey and white. The species has five subspecies.
The least big-eared bat is a bat species of the family Phyllostomidae, found in northwestern Brazil and eastern Colombia. It is the only species within its genus.

Bettongs, species of the genus Bettongia, are potoroine marsupials once common in Australia. They are important ecosystem engineers displaced during the colonisation of the continent, and are vulnerable to threatening factors such as altered fire regimes, land clearing, pastoralism and introduced predatory species such as the fox and cat.

Vampyressa is a genus of bats in the family Phyllostomidae, the leaf-nosed bats. They are known commonly as the yellow-eared bats or yellow-eared vampire bats.

The steppe pika is a small mammal of the pika family, Ochotonidae. It is found in the steppes of southern Russia and northern Kazakhstan.
Micromonas is a genus of green algae in the family Mamiellaceae.

Tithonia is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Heliantheae within the family Asteraceae.

Rhipidoglossum is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It contains about 20-30 species, all from sub-Saharan Africa.
Malva pusilla, also known as Malva rotundifolia, the low mallow, small mallow, or the round-leaved mallow, is an annual and biennial herb species of the Mallow genus Malva in the family of Malvaceae. Malva is a genus that consists of about 30 species of plants. This genus consists of plants named mallows. Mallows grow in many regions, including temperate, subtropical, and tropical areas.

Solemya is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Solemyidae, the awning clams. Solemya is the type genus of the family Solemyidae.

Klasea pusilla, is a species in the genus Klasea. It is a native of the Eastern Mediterranean.

Enoicyla pusilla also known as the land caddis and the terrestrial caddis is a species of caddisfly in the family Limnephilidae. The genus Enoicyla is unique among caddisflies because the larvae are terrestrial, living in leaf litter.

Kogia pusilla is an extinct species of sperm whale from the Middle Pliocene of Italy related to the modern day dwarf sperm whale and pygmy sperm whale. It is known from a single skull discovered in 1877, and was considered a species of beaked whale until 1997. The skull shares many characteristics with other sperm whales, and is comparable in size to that of the dwarf sperm whale. Like the modern Kogia, it probably hunted squid in the twilight zone, and frequented continental slopes. The environment it inhabited was likely a calm, nearshore area with a combination sandy and hard-rock seafloor. K. pusilla likely died out due to the ice ages at the end of the Pliocene.

Calogaya pusilla is a species of saxicolous (rock-dwelling), crustose lichen in the family Teloschistaceae. It was originally formally described in 1852 by Italian lichenologist Abramo Bartolommeo Massalongo, who placed it in genus Physcia. The type specimen was collected in Veneto, Italy. It has undergone several changes of genus in its taxonomic history, including transfers to Caloplaca, Placodium, and Teloschistes. In 2013, it was placed in the newly circumscribed genus Calogaya.
















