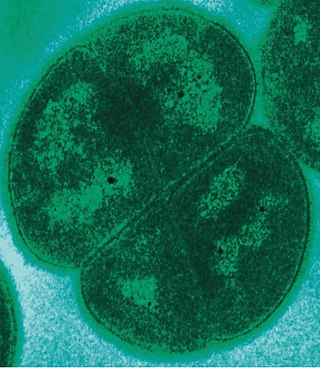
Deinococcus radiodurans is a bacterium, an extremophile and one of the most radiation-resistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and therefore is known as a polyextremophile. The Guinness Book Of World Records listed it in January 1998 as the world's most radiation-resistant bacterium or lifeform. However the archaea Thermococcus gammatolerans is actually the most resistant organism to radiation.

Deinococcus is in the monotypic family Deinococcaceae, and one genus of three in the order Deinococcales of the bacterial phylum Deinococcota highly resistant to environmental hazards. These bacteria have thick cell walls that give them Gram-positive stains, but they also include a second membrane and are therefore closer in structure to Gram-negative bacteria. Deinococcus survive when their DNA is exposed to high doses of gamma and UV radiation. Whereas other bacteria change their structure in the presence of radiation, such as by forming endospores, Deinococcus tolerate it without changing their cellular form and do not retreat into a hardened structure. They are also characterized by the presence of the carotenoid pigment deinoxanthin that give them their pink color. They are usually isolated according to these two criteria. In August 2020, scientists reported that bacteria from Earth, particularly Deinococcus bacteria, were found to survive for three years in outer space, based on studies conducted on the International Space Station. These findings support the notion of panspermia, the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed in various ways, including space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids or contaminated spacecraft.
Deinococcus frigens is a species of low temperature and drought-tolerating, UV-resistant bacteria from Antarctica. It is Gram-positive, non-motile and coccoid-shaped. Its type strain is AA-692. Individual Deinococcus frigens range in size from 0.9-2.0 μm and colonies appear orange or pink in color. Liquid-grown cells viewed using phase-contrast light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy on agar-coated slides show that isolated D. frigens appear to produce buds. Comparison of the genomes of Deiococcus radiodurans and D. frigens have predicted that no flagellar assembly exists in D. frigens.
Deinococcus marmoris is a Gram-positive bacterium isolated from Antarctica. As a species of the genus Deinococcus, the bacterium is UV-tolerant and able to withstand low temperatures.
Streptomyces radiopugnans is a halotolerant and radiation resistant bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from radiation polluted soil from the Xinjiang Province in China.
Microbacterium agarici is a Gram-positive and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from the mushroom Agaricus blazei in Taiwan.
Microbacterium barkeri is a bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from domestic sewage and from smear from a cheeses. Microbacterium barkeri has the ability to degrade polyvinyl alcohol.
Microbacterium ginsengisoli is a Gram-positive, heterotrophic, strictly aerobic bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from soil from a ginseng field in Daejeon, South Korea.

Microbacterium gubbeenense is a Gram-positive, facultatively anaerobic, non-spore-forming and non-motile bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from the surface of a smear-ripened cheese in Ireland.
Microbacterium halotolerans is a Gram-positive, halophilic aerobic, non-spore-forming and non-motile bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from hypersaline soil in China.
Microbacterium kitamiense is a heterotrophic, strictly aerobic, mesophilic and non-motile bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from waste water from a sugar-beet factory in Kitami in Japan. Microbacterium kitamiense produces polysaccharide. Microbacterium kitamiense has a high GC-content.
Microbacterium lacus is a bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from sediments from the Shinji lake from the Shimane Prefecture in Japan. Microbacterium lacus has the ability to degrade sulfadiazine.
Microbacterium lindanitolerans is a Gram-positive, aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from soil which was contaminated with hexachlorocyclohexane in India.
Microbacterium marinilacus is a Gram-positive bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from the Sano Marine Lake in the Republic of Palau.
Microbacterium natoriense is a Gram-positive and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from soil from Natori in Japan. Microbacterium natoriense produces D-aminoacylase.
Microbacterium paludicola is a Gram-positive, xylanolytic, short-rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from swamp forest soil from Ulsan, Korea.
Microbacterium petrolearium is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped and aerobic bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from oil-contaminated water from the Dagang Oilfield in China.
Microbacterium profundi is a Gram-positive, neutrophilic, aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from deep-sea sediments from the Pacific Ocean.
Microbacterium pseudoresistens is a Gram-positive and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from the fungus Agaricus blazei in Taiwan.
Microbacterium sediminis is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, aerobic, psychrotolerant, thermotolerant, halotolerant, alkalitolerant bacterium from the genus Microbacterium which has been isolated from deep-sea sediments from the Indian Ocean.

