
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of (homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each of two parents; each set contains the same number of chromosomes, and the chromosomes are joined in pairs of homologous chromosomes. However, some organisms are polyploid. Polyploidy is especially common in plants. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Males of bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis; the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.

Silene dioica, known as red campion and red catchfly, is a herbaceous flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae, native to Europe and introduced to the Americas.

Lydia Ernestine Becker was a leader in the early British suffrage movement, as well as an amateur scientist with interests in biology and astronomy. She established Manchester as a centre for the suffrage movement and with Richard Pankhurst she arranged for the first woman to vote in a British election and a court case was unsuccessfully brought to exploit the precedent. Becker is also remembered for founding and publishing the Women's Suffrage Journal between 1870 and 1890.

Microbotryum violaceum, also known as the anther smut fungus, was formerly known as Ustilago violacea. It is a basidiomycete obligate parasite of many Caryophyllaceae. But it has now separated into many species due to its host specificity.
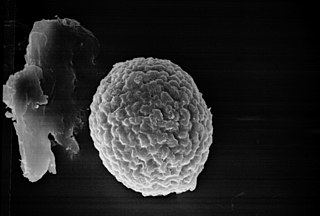
Tilletia is a genus of smut fungi in the Tilletiaceae family. Species in this genus are plant pathogens that affect various grasses. Tilletia indica, which causes Karnal bunt of wheat, and Tilletia horrida, responsible for rice kernel smut, are examples of species that affect economically important crops.

Succisa pratensis, also known as devil's-bit or devil's-bit scabious, is a flowering plant in the honeysuckle family Caprifoliaceae. It differs from other similar species in that it has four-lobed flowers, whereas Scabiosa columbaria and Knautia arvensis have five lobes and hence it has been placed in a separate genus in the same family. It also grows on damper ground.
Nodulosphaeria is a genus of fungi in the family Phaeosphaeriaceae.

Stellaria borealis is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae known by the common name boreal starwort. It has a circumboreal distribution, occurring throughout northern areas of the Northern Hemisphere. It occurs in many types of moist and wet habitat, including marshes, riverbanks, lakesides, floodplains, talus, ditches, and moist spots in forests and woodlands. It is quite variable in appearance, especially across subspecies. In general, it is a rhizomatous perennial herb forming mats of branching, four-angled stems lined with lance-shaped leaves a few centimeters in length. The inflorescence bears many flowers each with five deeply lobed white petals. Some flowers lack petals and have only the five pointed green sepals.

Heliosperma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Caryophyllaceae. As such, it is closely related to the large genus Silene, but its members can be told apart from Silene by the crest of long papillae on the seeds. The majority of the species are narrow endemics from the Balkan Peninsula, but H. alpestre is endemic to the Eastern Alps, and H. pusillum is found from the Cordillera Cantábrica in northern Spain to the Carpathians. Like members of the genus Silene and other related genera, Heliosperma is attacked by species of the anther smut fungus Microbotryum. Cases of parallel divergence events between alpine and mountain populations have been reported in this genus.
Liroa is a monotypic genus of fungi found in the family Microbotryaceae. It contains the single species Liroa emodensis, common name Microbotryum emodensis.

Microbotryum is a genus of smut fungi found in the family Microbotryaceae. It contains about 89 species, which are parasites of plants.

Secalonic acids are a group of xanthone derivatives closely related to ergoflavin and ergochrysin A that are collectively called ergochromes and belong to a class of mycotoxins initially isolated as major ergot pigments from the fungi Claviceps purpurea that grows parasitically on rye grasses. From early times and particularly in medieval Europe the consumption of grains containing ergot has repeatedly lead to mass poisonings known as ergotism which was caused by toxic ergot alkaloids and mycotoxins such as the ergochromes, due to contamination of flour by C. purpurea. A cluster of genes responsible for the synthesis of secalonic acids in C. purpurea has been identified. Secalonic acid D the enantiomer of secalonic acid A is a major environmental toxin, isolated from the fungus Penicillium oxalicum, and is a major microbial contaminant of freshly-harvested corn which causes toxicity through contamination of foodstuffs.
Microbotryum silenes-dioicae is a species of fungus first isolated from Brittany, France. Its name refers to its host species, Silene dioica. The fungus is the cause of anther-smut disease, which results in fungal spores replacing the pollen in the anthers. The species that most resembles ‘’M. silenes-dioicae’’ morphologically is M. lychnidis-dioicae.

Acacia microbotrya, commonly known as manna wattle or gum wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to Western Australia.

Microbotryum violaceum is a host-specific anther smut (fungus) disease that infects Silene latifolia and sterilizes the host plant. When infected with this disease, the flowers generate pathogenic spores, which can then be transferred to other plants by pollinating insects. Therefore, this disease is sometimes classified as a sexually transmitted infection.

Silene nivalis is a flowering plant in the pink family (Caryophyllaceae) native to Romania. A smut fungus, Microbotryum violaceum affects the anthers.
Farysia is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Anthracoideaceae.
Chromatomyia is a genus of flies belonging to the family Agromyzidae.
Epitrimerus is a genus of small mites. The name was raised by the Austrian zoologist Alfred Nalepa in 1898.

Microbotryum scabiosae is a smut fungus that infects plants in the genus Knautia. It produces pale ochraceous spores in the host plant's anthers.













