
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland, and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by US Congressman Claude Pepper.
PubMed Central (PMC) is a free digital repository that archives open access full-text scholarly articles that have been published in biomedical and life sciences journals. As one of the major research databases developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), PubMed Central is more than a document repository. Submissions to PMC are indexed and formatted for enhanced metadata, medical ontology, and unique identifiers which enrich the XML structured data for each article. Content within PMC can be linked to other NCBI databases and accessed via Entrez search and retrieval systems, further enhancing the public's ability to discover, read and build upon its biomedical knowledge.
Enteropathy refers to any pathology of the intestine. Although enteritis specifically refers to an inflammation of the intestine, and is thus a more specific term than "enteropathy", the two phrases are sometimes used interchangeably.

Karyolysidae is a family of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.

Demeton, sold as an amber oily liquid with a sulphur like odour under the name Systox™, is an organophosphate derivative causing irritability and shortness of breath to individuals repeatedly exposed. It was used as a phosphorothioate insecticide and acaricide and has the chemical formula C8H19O3PS2. Although it was previously used as an insecticide, it is now largely obsolete due to its relatively high toxicity to humans. Demeton consists of two components, demeton-S and demeton-O in a ratio of approximately 2:1 respectively. The chemical structure of demeton is closely related to military nerve agents such as VX and a derivative with one of the ethoxy groups replaced by methyl was investigated by both the US and Soviet chemical-weapons programs under the names V.sub.X and GD-7.
In chemistry, methanetetracarboxylate is a tetravalent anion with formula C
5O4−
8 or C(COO−)4. It has four carboxylate groups attached to a central carbon atom; so it has the same carbon backbone as neopentane. It is an oxocarbon anion, that is, consists only of carbon and oxygen.
Wolfgang Axel Tomé is a Physicist working in Medicine as a researcher; inventor; and educator. He is noted for his contributions to the use of photogrammetry in high precision radiation therapy; his work on risk adaptive radiation therapy which is based on the risk level for recurrence in tumor sub-volumes using biological objective functions; and the development of hippocampal avoidant cranial radiation therapy techniques to alleviate hippocampal-dependent neurocognitive impairment following cranial irradiation.
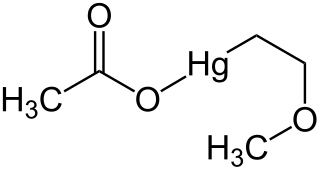
Methoxyethylmercuric acetate is a chemical compound formerly used as a pesticide for seeds of cotton and small grains. It is highly toxic, and can pose a threat to the brain and central nervous system.
In genetics, the gene density of an organism's genome is the ratio of the number of genes per number of base pairs, usually written in terms of a million base pairs, or megabase (Mb). The human genome has a gene density of 11-15 genes/Mb, while the genome of the C. elegans roundworm is estimated to have 200.

Leucine rich repeat containing 24 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the LRRC24 gene. The protein is represented by the official symbol LRRC24, and is alternatively known as LRRC14OS. The function of LRRC24 is currently unknown. It is a member of the leucine-rich repeat (LRR) superfamily of proteins.
American Journal of Public Health and the Nation's Health was a publication of the American Public Health Association that existed from 1928 to 1970. It was created by the merger of American Journal of Public Health and The Nation's Health. In 1971, the publication split back into its two original distinct publications.

Transmembrane Protein 176B, or TMEM176B is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM176B gene. It is thought to play a role in the process of maturation of dendritic cells.

Retrotransposon Gag Like 6 is a protein encoded by the RTL6 gene in humans. RTL6 is a member of the Mart family of genes, which are related to Sushi-like retrotransposons and were derived from fish and amphibians. The RTL6 protein is localized to the nucleus and has a predicted leucine zipper motif that is known to bind nucleic acids in similar proteins, such as LDOC1.
Sodium bromite is a sodium salt of bromous acid. Its trihydrous form has been isolated in crystal form. It is used by the textile refining industry as a desizing agent for oxidative starch removal.
Yuyuevirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect invertebrates. Member viruses have bisegmented genomes. It is the only genus in the family Yueviridae, which in turn is the only family in the order Goujianvirales and class Yunchangviricetes. Two species are recognized: Beihai yuyuevirus and Shahe yuyuevirus.

A dibromoanthracene is a derivative of anthracene with two bromine atoms. All compounds have the formula C14H8Br2.
Embryo loss is the death of an embryo at any stage of its development which in humans, is between the fifth and tenth week of gestation. Failed development of an embryo often results in the disintegration and assimilation of its tissue in the uterus. Loss during the early stages of prenatal development of the fetus results in the similar process of fetal resorption. Embryo loss often happens without an awareness of pregnancy, and an estimated 40 to 60% of all embryos do not survive.

The FAM214B, also known as protein family with sequence similarity 214, B (FAM214B) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the FAM214B gene located on the human chromosome 9. The protein has 538 amino acids. The gene contain 9 exon. There has been studies that there are low expression of this gene in patients with major depression disorder. In most organisms such as mammals, amphibians, reptiles, and birds, there are high levels of gene expression in the bone marrow and blood. For humans in fetal development, FAM214B is mostly expressed in the brains and bone marrow.
Proline-rich protein 29, encoded by the PRR29 gene in humans, is a protein which is located in the human genome at 17q23. Its function is not fully understood. Its name is derived from the chain of 5 proline amino acids located toward the end of the protein. The primary domain within the sequence of this protein is known as DUF4587. It is reported to have high levels of expression in tissues pertaining to the circulatory system and the immune system. It is hypothesized that PRR29 is a nuclear protein that facilitates communication between the nucleus and the mitochondria.








