
The United States, Venezuela, Cuba, and the People's Republic of China have embassies in Grenada. Grenada has been recognized by most members of the United Nations and maintains diplomatic missions in the United Kingdom, the United States, Venezuela, and Canada.

Physically bridging Europe and Asia and being above Africa, Turkey is a secular country that has historically pursued a Western-oriented foreign policy. To this end, Turkey uses its global diplomatic network—the third most extensive—of 252 diplomatic and consular missions.
The foreign relations of Albania are its relations with other governments and peoples. Foreign relations are conducted through the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Tirana. The current minister is Igli Hasani. The current Ambassador to the United Nations is Ferit Hoxha.

Bhutan has diplomatic relations with 54 of 193 member states of the United Nations and the European Union. Bhutan's limited number of such relations, including the absence of formal relations with any of the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council, is part of a deliberate isolationist policy of limiting foreign influence in the state. This stance has been safeguarded by close relations with India, of which Bhutan has previously been considered a protected state.
The Cook Islands maintains diplomatic relations with various countries and is a member of multilateral organisations. While the country is in free association with New Zealand, which can act on the Cook Islands' "delegated authority [...] to assist the Cooks Islands" in foreign affairs, the Cook Islands nevertheless enters into treaty obligations and otherwise "interacts with the international community as a sovereign and independent state."

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is the governmental body responsible for conducting foreign relations of the Republic of Turkey. The Ministry is responsible for Turkey's diplomatic missions abroad as well as for providing support for Turkish citizens who are abroad and for the promotion of Turkish culture, as well as for implementing the country's foreign policy in accordance with its national interests. Established on 2 May 1920, its primary duties are administering diplomatic missions, negotiating international treaties and agreements, and representing the Republic of Turkey at the United Nations. The ministry is headquartered in the Turkish capital of Ankara and counts on more than 200 missions as embassies, permanent representation offices and consulates general, abroad. As of 2021, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs maintains 235 diplomatic posts worldwide. The current Minister of Foreign Affairs is Hakan Fidan, who has held the position since 3 June 2023.

Monaco–Russia relations is the bilateral relationship between the Principality of Monaco and the Russian Federation.

Antigua and Barbuda maintains diplomatic relations with the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and the People's Republic of China, as well as with many Latin American countries and neighbouring Eastern Caribbean states. It is a member of the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Nations, the Organization of American States, the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States, the Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas, Petrocaribe and the Eastern Caribbean's Regional Security System (RSS).

Croatia and Turkey established diplomatic relations in 1992. Turkey recognized independent Croatia in 1991. Croatia has an embassy in Ankara and an consulate-general in Istanbul and an 2 honorary consulates in Antalya and İzmir. Turkey has an embassy in Zagreb. Both countries are full members of Council of Europe and of NATO. Croatia is an EU member and Turkey is an EU candidate. Croatia supports Turkey's accession negotiations to the EU, although negotiations have now been suspended.

Turkey was the first country to recognize the independence of Belarus. Diplomatic relations were established on 25 March 1992. Turkey has an embassy in Minsk. Belarus has an embassy in Ankara, a Consulate General in Istanbul.

The political status of the Cook Islands and Niue is formally defined as being states in free association within the Realm of New Zealand, which is made up of the Cook Islands, Niue, and New Zealand and its territories, Tokelau and the Ross Dependency. The Cook Islands and Niue do not have full constitutional independence from New Zealand but act as independent countries. Some countries have recognised them as sovereign entities and established diplomatic relations. However, New Zealand may carry out defence and foreign affairs on behalf of the two associated states when requested.

Montenegro–Turkey relations are the bilateral relations between Montenegro and Turkey. Turkey officially recognized Montenegro on June 12, 2006. Diplomatic relations between the two countries were established on July 3, 2006. Both countries are full members of the Union for the Mediterranean, Council of Europe and NATO. And Montenegro is with Slovenia is Sectoral dialogue partner countries of Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation.

Kenya–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Kenya has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Nairobi and an honorary consulate in Mombasa.

Estonia–Turkey relations are foreign relations between Estonia and Turkey. Estonia has an embassy in Ankara and Turkey has an embassy in Tallinn. Both countries are full members of Council of Europe and of NATO. Estonia is also an EU member and Turkey is an EU candidate.

Oman–Turkey relations are the foreign relations between Oman and Turkey. Turkey's historic relationship with Oman has wavered between friendly indifference and courtship, but mutual differences were set aside in 2002 when the new Turkish government embraced a policy of engagement with Oman.

Thailand–Turkey relations are the modern foreign relations between Thailand and Turkey. The cordial relations between the two countries date back to 1958, when the two countries established diplomatic relations. Shortly after, Turkey set up its embassy in Bangkok. Thailand reciprocated by opening its embassy in 1972. However, even during the era of the Ottoman Empire, there had been historical contacts between the Empire and Siam at the time -- most notably the visit of Prince Damrong, younger brother of King Chulalongkorn the Great of Siam, to Istanbul as the royal guest of Sultan Abdul Hamid II in 1891.

Slovakia–Turkey relations are the foreign relations between Slovakia and Turkey. In 1993, Turkey was one of the first states to formally recognize both the Slovakia and Czech Republic as separate, and sovereign states after the dissolution. Diplomatic relations and the Turkish Embassy in Bratislava were established on January 4, 1993. Slovakia has an embassy in Ankara and a consulate-general in Istanbul. Before the 1990s split, Turkey held close but also tense relations with Czechoslovakia, specifically during the Cold War due to NATO and the rest of Europe pushing and supporting anti-communist sentiment and approach for its members, such as Turkey, towards Eastern Bloc countries of which Czechoslovakia was a part of.
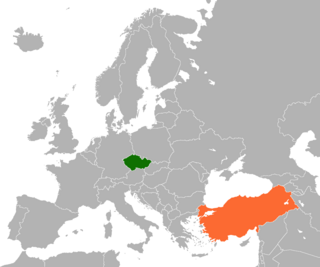
Czech Republic–Turkey relations are foreign relations between Czech Republic and Turkey.
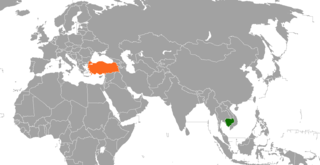
Cambodia–Turkey relations are the foreign relations between Cambodia and Turkey. Diplomatic relations at the legation level were established in 1947 and then to the rank of ambassador in 1959. It was not until 2013, however, that Turkey established a resident embassy in Cambodia's capital, Phnom Penh.
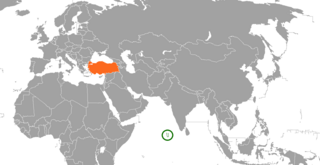
Maldives–Turkey relations are the foreign relations between the Maldives and the Turkey. The diplomatic relations were established in 1979. The Turkish Embassy in New Delhi, India is accredited to the Maldives and the Permanent Mission of the Republic of Maldives to the United Nations Office in Geneva is accredited to Turkey. The two countries have good relations between them mostly in the areas of tourism and defence, while being in close cooperation with one another on international platforms including the United Nations and Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)



















