
Propyl acetate, also known as propyl ethanoate, is an organic compound. Nearly 20,000 tons are produced annually for use as a solvent. This colorless liquid is known by its characteristic odor of pears. Due to this fact, it is commonly used in fragrances and as a flavor additive. It is formed by the esterification of acetic acid and propan-1-ol, often via Fischer–Speier esterification, with sulfuric acid as a catalyst and water produced as a byproduct.
Dioctyl adipate (DOA) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2CO2C8H17)2. It is a colorless oily liquid. As well as related diesters derived from 2-ethylhexanol, decanol, isodecanol, etc., it is used as a plasticizer.
An occupational exposure limit is an upper limit on the acceptable concentration of a hazardous substance in workplace air for a particular material or class of materials. It is typically set by competent national authorities and enforced by legislation to protect occupational safety and health. It is an important tool in risk assessment and in the management of activities involving handling of dangerous substances. There are many dangerous substances for which there are no formal occupational exposure limits. In these cases, hazard banding or control banding strategies can be used to ensure safe handling.
The Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of the German Social Accident Insurance is a German institute located in Sankt Augustin near Bonn and is a main department of the German Social Accident Insurance. Belonging to the Statutory Accident Insurance means that IFA is a non-profit institution.
Arsenic pentafluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine. It is a toxic, colorless gas. The oxidation state of arsenic is +5.
1,2,3-Trimethylbenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H3(CH3)3. Classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon, it is a flammable colorless liquid. It is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
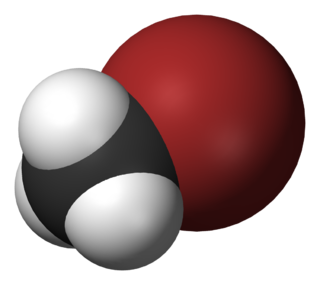
The monohalomethanes are organic compounds in which a hydrogen atom in methane is replaced by a halogen. They belong to the haloalkanes or to the subgroup of halomethanes.
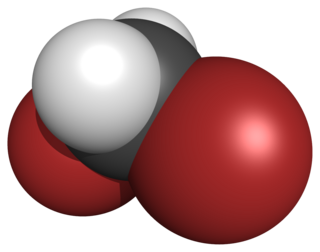
The dihalomethanes are organic compounds in which two hydrogen atoms in methane are replaced by halogen atoms. They belong to the haloalkanes, specifically the subgroup of halomethanes, and contains ten members.
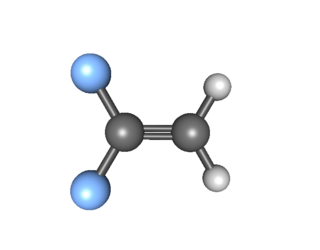
1,1-Difluoroethylene, also known as vinylidene fluoride, is a hydrofluoroolefin. This colorless, flammable gas is a difluorinated derivative of ethylene. Global production in 1999 was approximately 33,000 metric tons. It is primarily used in the production of fluoropolymers such as polyvinylidene fluoride and FKM.
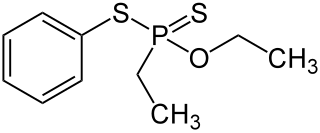
Fonofos is an organothiophosphate insecticide primarily used on corn. It is highly toxic and listed as an extremely hazardous substance.

Tributylamine (TBA) is an organic compound with the molecular formula (C4H9)3N. It is a colorless liquid with an amine-like odor.

Bromopropylate is a chemical compound used as an acaricide against spider mites in apiaries and on fruit crops such as citrus and grapes. It was banned by the European Union in 2011.
Dinitrobenzenes are nitrobenzenes composed of a benzene ring and two nitro group (-NO2) substituents. The three possible arrangements of the nitro groups afford three isomers, 1,2-dinitrobenzene, 1,3-dinitrobenzene, and 1,4-dinitrobenzene. Each isomer has the chemical formula C6H4N2O4 and a molar mass of about 168.11 g/mol. 1,3-Dinitrobenzene is the most common isomer and it is used in the manufacture of explosives.

Dinitroanilines are a class of chemical compounds with the chemical formula C6H5N3O4. They are derived from both aniline and dinitrobenzenes. There are six isomers: 2,3-dinitroaniline, 2,4-dinitroaniline, 2,5-dinitroaniline, 2,6-dinitroaniline, 3,4-dinitroaniline, and 3,5-dinitroaniline.
1-Tridecanol is an alcohol with the formula C13H28OH. It is a colorless fatty alcohol that turns white when solid. 1-Tridecanol usually occurs as a mixture of different isomeric to compounds such as 2-tridecanol, 3-tridecanol, 4-tridecanol, 5-tridecanol, 6-tridecanol, and isotridecanol.
Pentyl nitrite is a chemical compound with the molecular formula, classified as an alkyl nitrite, used as an antihypertensive medicine. It is also used to treat cyanide poisoning.
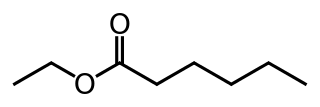
Ethyl hexanoate is the ester resulting from the condensation of hexanoic acid and ethanol. It has fruity aroma similar to apple peel.
GESTIS Substance Database is a freely accessible online information system on chemical compounds. It is maintained by the Institut für Arbeitsschutz der Deutschen Gesetzlichen Unfallversicherung. Information on occupational medicine and first aid is compiled by Henning Heberer and his team.
1-Octanethiol, also called 1-mercaptooctane, is an organic compound.
The diisopropylbenzenes(DIPB) are organic compounds with the formula C6H4(CH(CH3)2)2. Three isomers exist: 1,2- 1,3-, and 1,4-diisopropylbenzene. All are colorless liquids, immiscible in water, with similar boiling points. They are classified are aromatic hydrocarbons bearing a pair of isopropyl (CH(CH3)2) substituents. DIPB has been referred to as "a common diluent" alongside hexane.



 [1] [2] [3]
[1] [2] [3] 







