
The Alps are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately 750 mi (1,210 km) across eight Alpine countries : France, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia.

The Lepontine Alps are a mountain range in the north-western part of the Alps. They are located in Switzerland and Italy.
This article lists the principal mountain passes and tunnels in the Alps, and gives a history of transport across the Alps.

Ticino, sometimes Tessin, officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts and its capital city is Bellinzona. It is also traditionally divided into the Sopraceneri and the Sottoceneri, respectively north and south of Monte Ceneri. Red and blue are the colours of its flag.

The Apennines or Apennine Mountains are a mountain range consisting of parallel smaller chains extending c. 1,200 km (750 mi) along the length of peninsular Italy. In the northwest they join with the Ligurian Alps at Altare. In the southwest they end at Reggio di Calabria, the coastal city at the tip of the peninsula. Since 2000 the Environment Ministry of Italy, following the recommendations of the Apennines Park of Europe Project, has been defining the Apennines System to include the mountains of north Sicily, for a total distance of 1,500 kilometres (930 mi). The system forms an arc enclosing the east side of the Ligurian and Tyrrhenian Seas.
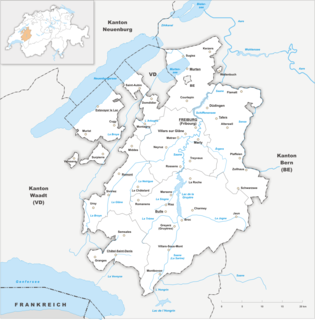
The canton of Fribourg, also canton of Freiburg is located in western Switzerland. The canton is bilingual, with French spoken by more than two thirds of the citizens and German by a little more than a quarter. Both are official languages in the canton. The canton takes its name from its capital city of Fribourg.

The Gotthard Base Tunnel is a railway tunnel through the Alps in Switzerland. It opened on 1 June 2016 and full service began on 11 December 2016. With a route length of 57.09 km, it is the world's longest railway and deepest traffic tunnel and the first flat, low-level route through the Alps. It lies at the heart of the Gotthard axis and constitutes the third tunnel connecting the cantons of Uri and Ticino, after the Gotthard Tunnel and the Gotthard Road Tunnel.

Bellinzona is a municipality, a historic Swiss town, and the capital of the canton of Ticino in Switzerland. The town is famous for its three castles that have been UNESCO World Heritage Sites since 2000.

The Gotthard Road Tunnel in Switzerland runs from Göschenen in the canton of Uri at its northern portal, to Airolo in Ticino to the south, and is 16.9 kilometres (10.5 mi) in length below the St Gotthard Pass, a major pass of the Alps. At time of construction, in 1980, it was the longest road tunnel in the world; it is currently the fifth-longest. Although it is a motorway tunnel, part of the A2 from Basel to Chiasso, it consists of only one bidirectional tube with two lanes. With a maximum elevation of 1,175 metres (3,855 ft) at the tunnel's highest point, the A2 motorway has the lowest maximum elevation of any direct north-south road through the Alps.

The Gotthard Pass or St. Gotthard Pass at 2,106 m (6,909 ft) is a mountain pass in the Alps traversing the Saint-Gotthard Massif and connecting northern with southern Switzerland. The pass lies between Airolo in the Italian-speaking canton of Ticino, and Andermatt in the German-speaking canton of Uri, and connects further Bellinzona to Lucerne, Basel, and Zurich. The Gotthard Pass lies at the heart of the Gotthard, a major transport axis of Europe, and it is crossed by three traffic tunnels, each being the world's longest at the time of their construction: the Gotthard Rail Tunnel (1882), the Gotthard Road Tunnel (1980) and the Gotthard Base Tunnel (2016). With the Lötschberg to the west, the Gotthard is one of the two main north-south routes through the Swiss Alps.

Monte Rosa is a mountain massif in the eastern part of the Pennine Alps. It is between Italy's and Switzerland's (Valais). Monte Rosa is the second highest mountain in the Alps and western Europe, after Mont Blanc.
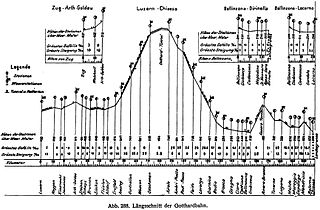
The Gotthard railway is the Swiss trans-alpine railway line from northern Switzerland to the canton of Ticino. The line forms a major part of an important international railway link between northern and southern Europe, especially on the Rotterdam-Basel-Genoa corridor. The Gotthard Railway Company was the former private railway company which financed the construction of, and originally operated, that line.
The construction and operation of Swiss railways during the 19th century was carried out by private railways. The first internal line was a 16 km line opened from Zürich to Baden in 1847. By 1860 railways connected western and northeastern Switzerland. The first Alpine railway to be opened was under the Gotthard Pass in 1882. A second alpine line was opened under the Simplon Pass in 1906.
The Gotthard nappe is, in the geology of the Alps a nappe in the Helvetic zone of Switzerland. It consists of crystalline rocks that were, before the formation of the Alps, part of the upper crust of the southern margin of the European continent. As it names suggests, the Gotthard nappe lies in close proximity to the Gotthard Massif.

The Gotthard Massif, also Saint-Gotthard Massif is a mountain range in the Alps in Switzerland, located at the border of four cantons: Valais, Ticino, Uri and Graubünden. It is delimited by the Nufenen Pass on the west, by the Furka Pass and the Oberalp Pass on the north and by the Lukmanier Pass on the east. The homonymous Gotthard Pass, lying at the heart of the massif, is the main route from north to south.
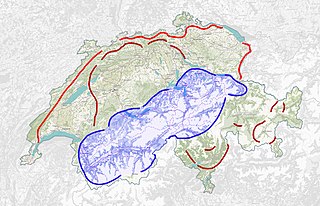
The Swiss National Redoubt is a defensive plan developed by the Swiss government beginning in the 1880s to respond to foreign invasion. In the opening years of the Second World War the plan was expanded and refined to deal with a potential German invasion. The term "National Redoubt" primarily refers to the fortifications begun in the 1880s that secured the mountainous central part of Switzerland, providing a defended refuge for a retreating Swiss Army.

The Tremola San Gottardo, located in the Canton of Ticino, is the longest road monument in Switzerland and is listed in the inventory of the historic Swiss roads (IVS). It connects the municipality of Airolo to the Gotthard Pass.

The Rotondo Granite is a late Variscan granitic intrusion located in the Saint-Gotthard Massif in the Swiss Alps. Its name comes from the Pizzo Rotondo.


















