
Fra Angelico, O.P. was a Dominican friar and Italian Renaissance painter of the Early Renaissance, described by Giorgio Vasari in his Lives of the Artists as having "a rare and perfect talent". He earned his reputation primarily for the series of frescoes he made for his own friary, San Marco, in Florence, then worked in Rome and other cities. All his known work is of religious subjects.

Filippino Lippi was an Italian Renaissance painter mostly working in Florence, Italy during the later years of the Early Renaissance and first few years of the High Renaissance. He also worked in Rome for a period from 1488, and later in the Milan area and Bologna.

Luca Signorelli was an Italian Renaissance painter from Cortona, in Tuscany, who was noted in particular for his ability as a draftsman and his use of foreshortening. His massive frescos of the Last Judgment (1499–1503) in Orvieto Cathedral are considered his masterpiece.

Pinturicchio, or Pintoricchio, also known as Benetto di Biagio or Sordicchio, was an Italian Renaissance painter. He acquired his nickname because of his small stature and he used it to sign some of his artworks that were created during the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries.

Benedetto Bonfigli was an Italian Renaissance painter born in Perugia, and part of the Umbria school of painters including Raphael and Perugino. He is also known as Buonfiglio. Influenced by the style of Domenico Veneziano, Benozzo Gozzoli, and Fra Angelico, Bonfigli primarily painted frescos for the church and was at one point employed in the Vatican. His best-preserved work is the Annunciation, but his masterpiece is the decoration of the chapel of the Palazzo dei Priori. Bonfigli specialized in gonfaloni, a Perugian style using banners painted on canvas or linen. Little is known of his personal life, but he was an esteemed painter in Perugia before Perugino, who is said to be his pupil.

Pietro Perugino, an Italian Renaissance painter of the Umbrian school, developed some of the qualities that found classic expression in the High Renaissance. Raphael became his most famous pupil.

The Deposition, also known as the Pala Baglioni, Borghese Entombment or The Entombment, is an oil painting by the Italian High Renaissance painter Raphael. Signed and dated "Raphael. Urbinas. MDVII", the painting is in the Galleria Borghese in Rome. It is the central panel of a larger altarpiece commissioned by Atalanta Baglioni of Perugia in honor of her slain son, Grifonetto Baglioni. Like many works, it shares elements of the common subjects of the Deposition of Christ, the Lamentation of Christ, and the Entombment of Christ. The painting is on wood panel and measures 184 x 176 cm.

The Mond Crucifixion or Gavari Altarpiece is an oil on poplar panel dated to 1502–1503, making it one of the earliest works by Italian Renaissance artist Raphael, perhaps the second after the c.1499-1500 Baronci Altarpiece. It originally comprised four elements, of which three survive, now all separated: a main panel of the Crucified Christ with the Virgin Mary, Saints and Angels which was bequeathed to the National Gallery, London, by Ludwig Mond, and a three-panel predella from which one panel is lost; the two surviving panels are Eusebius of Cremona raising Three Men from the Dead with Saint Jerome's Cloak in the Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga, in Lisbon, and Saint Jerome saving Silvanus and punishing the Heretic Sabinianus in the North Carolina Museum of Art.

The Coronation of the Virgin or Coronation of Mary is a subject in Christian art, especially popular in Italy in the 13th to 15th centuries, but continuing in popularity until the 18th century and beyond. Christ, sometimes accompanied by God the Father and the Holy Spirit in the form of a dove, places a crown on the head of Mary as Queen of Heaven. In early versions the setting is a Heaven imagined as an earthly court, staffed by saints and angels; in later versions Heaven is more often seen as in the sky, with the figures seated on clouds. The subject is also notable as one where the whole Christian Trinity is often shown together, sometimes in unusual ways. Crowned Virgins are also seen in Eastern Orthodox Christian icons, specifically in the Russian Orthodox church after the 18th century. Mary is sometimes shown, in both Eastern and Western Christian art, being crowned by one or two angels, but this is considered a different subject.

The Annunziata Polyptych is a painting cycle started by Filippino Lippi and finished by Pietro Perugino, whose central panel is now divided between the Galleria dell'Accademia and the Basilica dell'Annunziata, both in Florence, Italy. The polyptych had other six panels, which are housed in the Lindenau-Museum of Altenburg, the Metropolitan Museum of New York City, the Galleria Nazionale d'Arte Antica in Rome and in a private collection in South Africa.

The Ascension of Jesus to Heaven as stated in the New Testament has been a frequent subject in Christian art, as well as a theme in theological writings.

The Vallombrosa Altarpiece is a painting by the Italian Renaissance painter Pietro Perugino, dating to 1500–01. It is housed in the Accademia Gallery of Florence, Italy.

The San Pietro Polyptych is a polyptych by Italian Renaissance master Perugino, painted around 1496–1500. The panels are now in different locations: the lunette and the central panel, depicting the Ascension of Christ, are in the Museum of Fine Arts of Lyon, France.

The Sant'Agostino Altarpiece is a painting by Perugino, produced in two stages between around 1502 and 1512 and then around 1513 to 1523. The altarpiece's 28, 29 or 30 panels were split up during the Napoleonic suppression of religious houses - most of its panels are now in the Galleria Nazionale dell'Umbria in Perugia. It is notable as the painter's last masterwork before he moved into his late phase producing more provincial commissions.

Madonna della Consolazione is an oil on panel painting by Perugino, datable c. 1496–1498. The work, completed in April 1498, was carried out in the Sala delle Udienze of the Collegio del Cambio. Since c. 1820 it is preserved in the National Gallery of Umbria in Perugia.

The Crucifixion with Mary Magdalene is a fresco of c. 1495 of the Crucifixion of Christ by Perugino in the chapter house of the Cistercian monastery of Santa Maria Maddalena dei Pazzi in Florence. It is his most notable work in Florence. It was a commission from the Pucci family - Antonio Billi's account book reports Dionigi and Giovanna Pucci commissioning a work from "Master Piero della Pieve a Chastello, a Perugian" on 20 November 1493 and paying 55 gold ducats on its completion on 20 April 1496.

The Corciano Altarpiece is a 1513 painting by Perugino now in the parish church of Santa Maria in Corciano. It was produced following a past commission for Perugino to decorate the high altar of the parish church in Corciano.
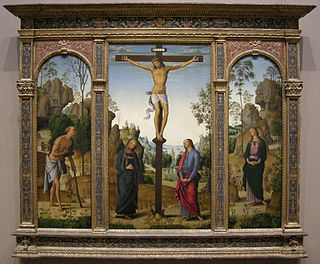
The Galitzin Triptych is a c.1485 painting by Perugino, now in the National Gallery of Art in Washington.

The Madonna of Loreto is a c.1507 oil on panel painting by Perugino, now in the National Gallery, London, which bought it in 1879. It shows the Madonna and Child flanked by Jerome (left) and Francis of Assisi (right). Two angels hover over Mary's head holding a crown. It reuses the low parapet from Madonna and Child with St Rose and St Catherine (1492) and probably also involved the master's studio assistants.
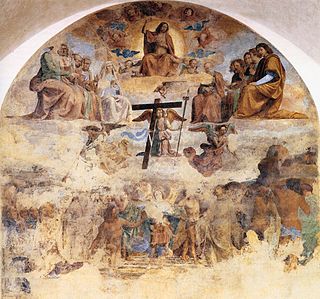
Last Judgement is a fresco, begun by the Italian Renaissance painter Fra Bartolomeo in 1499 and completed by his colleague Mariotto Albertinelli in 1501. Originally commissioned for a cemetery chapel of Ospedale di Santa Maria Nuova, it is now in the Museo Nazionale di San Marco in Florence. Parts of the composition are illegible as a result of centuries of surface losses. The painting was a key influence on contemporary artists such as Raphael.






















