
Vespertilionidae is a family of microbats, of the order Chiroptera, flying, insect-eating mammals variously described as the common, vesper, or simple nosed bats. The vespertilionid family is the most diverse and widely distributed of bat families, specialised in many forms to occupy a range of habitats and ecological circumstances, and it is frequently observed or the subject of research. The facial features of the species are often simple, as they mainly rely on vocally emitted echolocation. The tails of the species are enclosed by the lower flight membranes between the legs. Over 300 species are distributed all over the world, on every continent except Antarctica. It owes its name to the genus Vespertilio, which takes its name from a word for bat, vespertilio, derived from the Latin term vesper meaning 'evening'; they are termed "evening bats" and were once referred to as "evening birds".

The New World leaf-nosed bats (Phyllostomidae) are bats found from southern North America to South America, specifically from the Southwest United States to northern Argentina. They are ecologically the most varied and diverse family within the order Chiroptera. Most species are insectivorous, but the phyllostomid bats include within their number true predatory species and frugivores. For example, the spectral bat, the largest bat in the Americas, eats vertebrate prey, including small, dove-sized birds. Members of this family have evolved to use food groups such as fruit, nectar, pollen, insects, frogs, other bats, and small vertebrates, and in the case of the vampire bats, even blood.

Murina is a genus of vesper bats. They are found throughout temperate and tropical regions of Asia.

Phyllostominae is a subfamily of bats that include big-eared, spear-nosed, sword-nosed bats and relatives.

Harrison's tube-nosed bat is a species of vesper bats (Vespertilionidae). Within the genus Murina, it belongs to the so-called 'cyclotis-group'.

Beelzebub's tube-nosed bat, also Beelzebub bat or demon bat, is a species in the vesper bat family Vespertilionidae, found in the Greater Mekong region of Southeast Asia, specifically the Quảng Trị and Gia Lai provinces of Vietnam. They have tube-shaped nostrils which assist them with their feeding.

Fea's tube-nosed bat, also known as the ashy tube-nosed bat, is a species in the vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae, found in southeastern Asia and southern China. They have tube-shaped nostrils which assist them with their feeding. It is named after Italian naturalist Leonardo Fea.
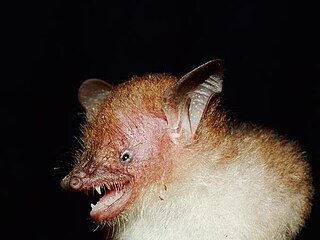
Walston's tube-nosed bat is a species in the vesper bat family Vespertilionidae, found in the Greater Mekong region of Southeast Asia, specifically the Đắk Lắk Province of Vietnam and the Koh Kong and Ratanakiri provinces of Cambodia. This species was discovered in northeastern Cambodia in the Van Sai Protected Forest. They have tube-shaped nostrils which assist them with their feeding.
Harpiola is a genus of vesper bats within the subfamily Murininae. It contains Peters's tube-nosed bat and the Formosan golden tube-nosed bat.
The Formosan golden tube-nosed bat is native to the high-altitude regions of Taiwan.
The Bala tube-nosed bat is a critically endangered species of bat found in Thailand.
Tube-nosed bat may refer to any of the following species:









