
Bulmer's fruit bat is a megabat endemic to New Guinea. It is listed as a critically endangered species due to habitat loss and hunting. It is the only member of the genus Aproteles. Due to its imperiled status, it is identified by the Alliance for Zero Extinction as a species in danger of imminent extinction.

The New Guinea big-eared bat or Papuan big-eared bat,, is a vesper bat endemic to Papua New Guinea. It is listed as a critically endangered species due to ongoing habitat loss. It is the only known member of the genus Pharotis, which is closely related to Nyctophilus.

Murina is a genus of vesper bats. They are found throughout temperate and tropical regions of Asia.

The gilded tube-nosed bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae.
The Ryukyu tube-nosed bat(Murina ryukyuana) is a species of vesper bat found only in Japan.
Scully's tube-Nosed bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It can be found in the following countries: India, Laos, Myanmar, Pakistan, Thailand, and Viet Nam.

The Ussuri tube-nosed bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is threatened by habitat loss. It is the only species of bat that hibernates in snowbanks.

The Banks flying fox is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to Vanuatu. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and subtropical or tropical swamps. These small fruit bats are about 15 cm. long with grey and brown on its head and back with a yellow-orange neck and yellow-gray bellies. Its diet consists of coconut flowers and Vaveli trees fruit since its home is tropical.

The Temotu flying fox is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to the Solomon Islands. It is threatened by habitat destruction due to subsistence agricultural practices, as well as natural disasters such as tropical cyclones. Due to its imperiled status, it is identified by the Alliance for Zero Extinction as a species in danger of imminent extinction. In 2013, Bat Conservation International listed this species as one of the 35 species of its worldwide priority list of conservation.

The Rodrigues flying fox or Rodrigues fruit bat is a species of bat in the family Pteropodidae, the flying foxes or fruit bats. It is endemic to Rodrigues, an island in the Indian Ocean belonging to Mauritius. Its natural habitat is tropical lowland forests. The bats are sociable, roost in large groups during the day and feed at night, squeezing the juice and flesh out of fruits. They are hunted by humans for food and their numbers have been dwindling, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated the species as being "endangered". In an effort to preserve them from extinction, some bats have been caught and are being bred in various zoos around the world.

The Fijian monkey-faced bat Also known as Fijian flying fox or Fijian flying monkey, is a megabat endemic to Fiji. It was discovered in old-growth cloud forest on Des Vœux Peak, the second highest mountain peak on the island of Taveuni by William and Ruth Beckon in 1976, and is Fiji's only endemic mammal. It has recently been transferred from Pteralopex to its own monotypic genus Mirimiri.
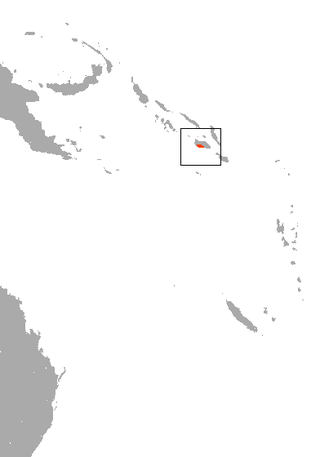
The montane monkey-faced bat or montane flying monkey is a megabat endemic to the Solomon Islands. It is listed as a critically endangered species. Due to its imperilled status, it is identified by the Alliance for Zero Extinction as a species in danger of imminent extinction. In 2013, Bat Conservation International listed this species as one of the 35 species of its worldwide priority list of conservation. Only one individual has ever been found.
Bat Conservation International (BCI) is an international nongovernmental organization working to conserve bats and their habitats through conservation, education, and research efforts.

Harrison's tube-nosed bat is a species of vesper bats (Vespertilionidae). Within the genus Murina, it belongs to the so-called 'cyclotis-group'.

Hilgendorf's tube-nosed bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. In Japan they are called 'tengu komori', after the mythical creature called the Tengu. It was formerly thought to be a subspecies of Murina leucogaster, but is now known to be a distinct species.

Beelzebub's tube-nosed bat, also Beelzebub bat or demon bat, is a species in the vesper bat family Vespertilionidae, found in the Greater Mekong region of Southeast Asia, specifically the Quảng Trị and Gia Lai provinces of Vietnam. They have tube-shaped nostrils which assist them with their feeding.
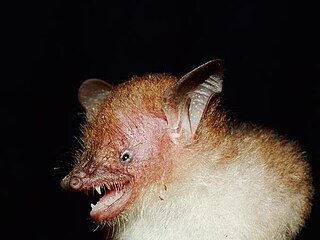
Walston's tube-nosed bat is a species in the vesper bat family Vespertilionidae, found in the Greater Mekong region of Southeast Asia, specifically the Đắk Lắk Province of Vietnam and the Koh Kong and Ratanakiri provinces of Cambodia. This species was discovered in northeastern Cambodia in the Van Sai Protected Forest. They have tube-shaped nostrils which assist them with their feeding.













