
Geoffroy's rousette is a species of megabat or Old World fruit bats. It is one of ten species in the genus Rousettus.

The dwarf dog-faced bat is a species of free-tailed bat from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Paraguay and Uruguay, typically at lower elevations. It is one of two species in the genus Molossops, the other being the rufous dog-faced bat. Three subspecies are often recognized, though mammalogist Judith Eger considers it monotypic with no subspecies. It is a small free-tailed bat, with a forearm length of 28.9–32.5 mm (1.14–1.28 in) and a weight of 5–8 g (0.18–0.28 oz); males are larger than females. It is brown, with paler belly fur and darker back fur. Its wings are unusual for a free-tailed bat, with exceptionally broad wingtips. Additionally, it has low wing loading, meaning that it has a large wing surface area relative to its body weight. Therefore, it flies more similarly to a vesper bat than to other species in its own family. As it forages at night for its insect prey, including moths, beetles, and others, it uses two kinds of frequency-modulated echolocation calls: one type is to navigate in open areas and to search for prey, while the other type is used for navigating in cluttered areas or while approaching a prey item.

Murina is a genus of vesper bats. They are found throughout temperate and tropical regions of Asia.

Nyctophilus geoffroyi is a vespertilionid bat. a flying nocturnal mammal found in Australia, The species is relatively common. They have been referred to as the lesser long-eared bat.

The flute-nosed bat is a vespertilionid bat with an unusually shaped nose, the tubular nostrils facing outward from the end of the muzzle. They occur in the north of the Australian state of Queensland, in Indonesia, and on Papua New Guinea.

The Ussuri tube-nosed bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is threatened by habitat loss. It is the only species of bat that hibernates in snowbanks.

The fraternal fruit-eating bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae that is found in drier habitats in Ecuador and Peru. It was formerly considered to be a subspecies of the Jamaican fruit bat, but was raised to species level in 1978. The smallest species in the group of large Artibeus, it has a forearm length of 52–59 mm (2.0–2.3 in), a total length of 64–76 mm (2.5–3.0 in), and a weight of 30–55 g (1.1–1.9 oz).

The intermediate horseshoe bat is a bat species of the family Rhinolophidae that is very widespread throughout much of the Indian subcontinent, southern and central China and Southeast Asia. It is listed by IUCN as Least Concern as it is considered common where it occurs, without any known major threats.
Bourret's horseshoe bat is a species of horseshoe bat native to Southeast Asia. The name "paradoxolophus" is derived from the Greek words paradoxos, meaning "contrary to expectation", and lophos, meaning "crest". This name refers to the bat's difference in nose-leaf morphology compared to other Rhinolophus species. There are no recognised subspecies.

The white-striped free-tailed bat is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. Its echolocation calls are audible to humans, which is a characteristic found in only a few microbat species. The species was formerly classified as Tadarida australis.
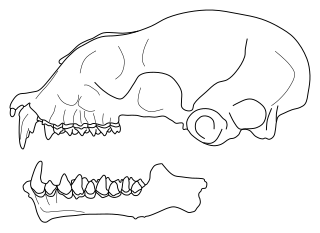
Triaenops menamena is a bat in the genus Triaenops found on Madagascar, mainly in the drier regions. It was known as Triaenops rufus until 2009, when it was discovered that that name had been incorrectly applied to the species. Triaenops rufus is a synonym of Triaenops persicus, a Middle Eastern species closely related to T. menamena— the Malagasy species had previously been placed as a subspecies of T. persicus by some authors. Triaenops menamena is mostly found in forests, but also occurs in other habitats. It often roosts in large colonies and eats insects such as butterflies and moths. Because of its wide range, common occurrence, and tolerance of habitat degradation, it is not considered to be threatened.
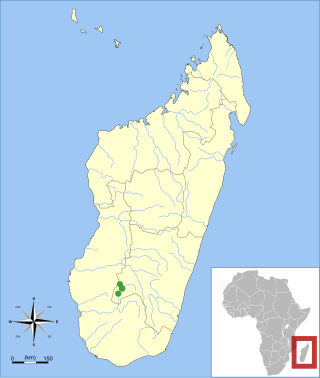
The Isalo serotine is a vesper bat of Madagascar in the genus Laephotis. It is known only from the vicinity of the Isalo National Park in the southwestern part of the island, where it has been caught in riverine habitats. After the first specimen was caught in 1967, it was described as a subspecies of Eptesicus somalicus in 1995. After four more specimens were collected in 2002 and 2003, it was recognized as a separate species. Because of its small distribution and the threat of habitat destruction, it is considered "vulnerable" in the IUCN Red List.

The cinnamon red bat is a species of bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It was first described from a specimen that had been collected in Chile. For more than one hundred years after its initial description, it was largely considered a synonym of the eastern red bat. From the 1980s onward, it was frequently recognized as distinct from the eastern red bat due to its fur coloration and differences in range. It has deep red fur, lacking white "frosting" on the tips of individual hairs seen in other members of Lasiurus. It has a forearm length of 39–42 mm (1.5–1.7 in) and a weight of 9.5–11.0 g (0.34–0.39 oz).
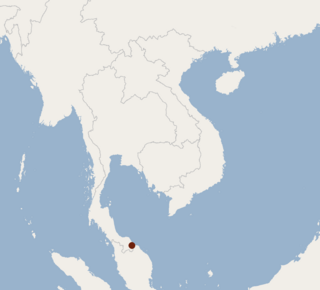
The Bala tube-nosed bat is a critically endangered species of bat found in Thailand.

The Kachin woolly bat is a species of bat found in Southeast Asia.
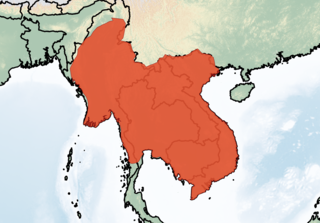
Rhinolophus microglobosus is a species of horseshoe bat found in Southeast Asia.

Hipposideros atrox, commonly known as the lesser bicolored leaf-nosed bat, is a species of bat found in Southeast Asia. Originally described as a subspecies in 1918, it was recognized as a full species in 2010. It uses echolocation to navigate and find prey, and roosts in caves during the day.

Pendlebury's roundleaf bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It was previously considered a subspecies of H. turpis, but has now been raised to full species level. It is endemic to Thailand and is found in limestone karst areas.
The Nicobar leaf-nosed bat is an endangered species of bat endemic to the Nicobar Islands.
Kerivoula depressa, commonly called Miller's flat-headed woolly bat or the flat-skulled woolly bat, is a species of vesper bat found in Southeast Asia.
















