
Musca is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It was one of 12 constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman, and it first appeared on a celestial globe 35 cm (14 in) in diameter published in 1597 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction of this constellation in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer's Uranometria of 1603. It was also known as Apis for 200 years. Musca remains below the horizon for most Northern Hemisphere observers.

Musca Borealis was a constellation, now discarded, located between the constellations of Aries and Perseus. It was originally called Apes by Petrus Plancius when he created it in 1612. It was made up of a small group of stars, now called 33 Arietis, 35 Arietis, 39 Arietis, and 41 Arietis, in the north of the constellation of Aries.

Muscidae are a family of flies found in the superfamily Muscoidea.

The carrot fly is a pest of gardens and farms, and mainly affects the crop of carrots, but can also attack parsnips, parsley and celery. It is a member of the family Psilidae.

Musca is a genus of flies. It includes Musca domestica, as well as Musca autumnalis. It is part of the family Muscidae.

Lucilia is a genus of blow flies in the family Calliphoridae. Various species in this genus are commonly known as green bottle flies.

Eristalis horticola is a Palearctic species of hoverfly.

The housefly is a fly of the suborder Cyclorrhapha. It is believed to have evolved in the Cenozoic Era, possibly in the Middle East, and has spread all over the world as a commensal of humans. It is the most common fly species found in houses. Adults are gray to black, with four dark, longitudinal lines on the thorax, slightly hairy bodies, and a single pair of membranous wings. They have red eyes, set farther apart in the slightly larger female.
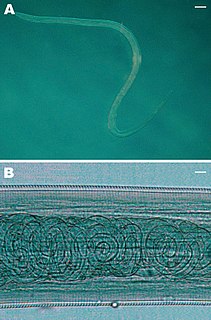
Thelazia is a genus of nematode worms which parasitize the eyes and associated tissues of various bird and mammal hosts, including humans. They are often called "eyeworms", and infestation with Thelazia species is referred to as "thelaziasis". Adults are usually found in the eyelids, tear glands, tear ducts, or the so-called "third eyelid". Occasionally, they are found in the eyeball itself, either under the conjunctiva or in the vitreous cavity of the eyeball. All species of Thelazia for which the life cycle has been studied are transmitted by species of Diptera (flies) which do not bite, but which feed on tears.

Hydrotaea is a genus of insects in the housefly family, Muscidae. They occur in most regions of the world but are more populous in warmer climates. They are often found on feces in summer months, and are therefore generally found in close proximity to livestock. Among the 130 known species in this genus, one of the most commonly recognized is the dump fly.

Musca vetustissima, commonly known as the Australian bush fly, is a species of fly found in Australia. It is the specific fly that has given rise to the expression "Aussie salute".

The Roșia Poieni copper mine is a large open pit copper mine in the centre of Romania, 90 km northwest of Alba Iulia and 484 km north of the capital, Bucharest. Geographically the mine is located in the Apuseni Mountains, 7 km (4.3 mi) south of the Arieş River in Lupșa commune. The access to the site is made through a south-west industrial haul road from Cornii Valley that crosses the National Road no. 74 Alba-Iulia – Zlatna – Abrud when entering Abrud and through a north industrial haul road from Mușca Valley that crosses the National Road no. 75 Câmpeni – Turda in Mușca village, Lupșa commune.
Musca vitripennis is a species of fly in the genus Musca. According to Willi Hennig, M. vitripennis is one of only two species of Musca native to the Palearctic realm, the other being Musca osiris. The two species are frequently confused with each other.
Musca albina is a widespread Old World species of fly, known from the dry areas of the Afrotropical realm, North Africa and the Middle East, Central Asia, India and Sri Lanka. It is a sun-loving species, and adults have been found clustering around domestic animals to feed on sweat and other secretions and on their feces. The Namibian population at least is clearly kleptoparasitic and very specific in its oviposition behaviour, laying eggs only in dung balls being interred by one out of several co-occurring dung-rolling scarab beetle species.
In the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, Carl Linnaeus classified the arthropods, including insects, arachnids and crustaceans, among his class "Insecta". Insects with simply two wings were brought together under the name Diptera.

Entomologia Carniolica exhibens insecta Carnioliae indigena et distributa in ordines, genera, species, varietates is a taxonomic work by Giovanni Antonio Scopoli, published in Vienna in 1763. As well as describing hundreds of new species, Entomologia Carniolica contained observations on the species' biology, including the first published account of queen bees mating outside the hive.
Hytrosaviridae is a family of double stranded DNA viruses that infect insects.
The name is derived from Hytrosa, sigla from the Greek Hypertrophia for 'hypertrophy' and 'sialoadenitis' for 'salivary gland inflammation.'
Muscavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Hytrosaviridae. The fly Musca domestica is the natural host. There is currently only one species in this genus: the type species Musca hytrosavirus. Diseases associated with this genus include: salivary gland hypertrophy, and complete sterility of infected female flies by inhibiting eggs development.

V357 Muscae was a bright nova in the constellation Musca. It was discovered on January 14, 2018 by Rob Kaufman of Bright, Victoria, Australia with a magnitude of 7.0.











