
Monogeneans, members of the class Monogenea, are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.

Balantidium is a genus of ciliates. It contains the parasitic species Balantidium coli, the only known cause of balantidiasis.

Tapeworms of the order Cyclophyllidea are the most important cestode parasites of humans and domesticated animals. All have multiple proglottid "segments", and all have four suckers on their scolices (heads), though some may have other structures, as well. Proglottids of this order have genital openings on one side, and a compact yolk gland or vitellarium posterior to the ovary.

Myxobolus is a genus of myxozoa that includes important parasites of fish like Myxobolus cerebralis. The genus is polyphyletic, with members scattered throughout the myxozoa. Some stages of Myxobolus species were previously thought to be different organisms entirely, but are now united in this group. Some fish species, such as the thicklip grey mullet, can harbour a dozen of Myxobolus species.
Kudoa thyrsites is a myxosporean parasite of marine fishes. It has a worldwide distribution, and infects a wide range of host species. This parasite is responsible for causing economic losses to the fisheries sector, by causing post-mortem "myoliquefaction", a softening of the flesh to such an extent that the fish becomes unmarketable. It is not infective to humans.
Elmer Ray Noble, was a professor of zoology at the University of California, Santa Barbara, and an internationally recognized protozoologist and parasitologist.

Blastocladiomycota is one of the currently recognized phyla within the kingdom Fungi. Blastocladiomycota was originally the order Blastocladiales within the phylum Chytridiomycota until molecular and zoospore ultrastructural characters were used to demonstrate it was not monophyletic with Chytridiomycota. The order was first erected by Petersen for a single genus, Blastocladia, which was originally considered a member of the oomycetes. Accordingly, members of Blastocladiomycota are often referred to colloquially as "chytrids." However, some feel "chytrid" should refer only to members of Chytridiomycota. Thus, members of Blastocladiomycota are commonly called "blastoclads" by mycologists. Alternatively, members of Blastocladiomycota, Chytridiomycota, and Neocallimastigomycota lumped together as the zoosporic true fungi. Blastocladiomycota contains 5 families and approximately 12 genera. This early diverging branch of kingdom Fungi is the first to exhibit alternation of generations. As well, two (once) popular model organisms—Allomyces macrogynus and Blastocladiella emersonii—belong to this phylum.

The Haemosporida are an order of intraerythrocytic parasitic alveolates.

Chlaenius is a large and diverse genus of ground beetle. It is native to the Palearctic realm, Afrotropical realm, and Nearctic realm. Worldwide, roughly 1,000 species are currently recognized with the majority of known species occurring in the Oriental and Afrotropical regions. The genus is divided into many subgenera.

The Alabama map turtle is a species of emydid turtle endemic to the southern United States. Differentiation from other turtle species includes a black stripe running down the center of its back with knobs extruding from it, but these projections wear down with age. T.H. Bean and L. Kumlen first collected the Alabama map turtle in July 1876 from a lake near Montgomery, Alabama. Type locality for this species is Montgomery County, Alabama. Baur described and named the Alabama map turtle in 1893. The genus Graptemys includes nine species of mostly aquatic turtles.
Garnia is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexia.

The Haemoproteidae are a family of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa.
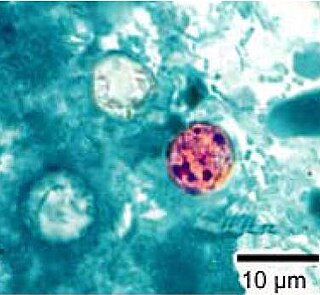
Cyclospora is a genus of apicomplexan parasites. It includes the species Cyclospora cayetanensis, the causative agent of cyclosporiasis. Members of Cyclospora are characterized as having oocysts with two sporocysts, each containing two sporozoites.
Frenkelia is a genus of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. The species in this genus infect the gastrointestinal tracts of birds of prey and the tissues of small rodents.
Defretinella is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.
Cardiosporidium is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. It infects the ascidian Ciona intestinalis.
Hyaloklossia is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Only two species in this genus are currently recognised.

Louis Euzet was a French parasitologist.
Quadrigyrus is a genus in Acanthocephala.
Ellipsomyxa is a genus of cnidarian that is part of the family Ceratomyxidae.









