
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.
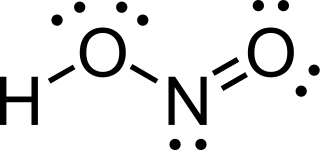
Nitrous acid is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase and in the form of nitrite salts. Nitrous acid is used to make diazonium salts from amines. The resulting diazonium salts are reagents in azo coupling reactions to give azo dyes.

Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl.
In organic chemistry, the diazo group is an organic moiety consisting of two linked nitrogen atoms at the terminal position. Overall charge-neutral organic compounds containing the diazo group bound to a carbon atom are called diazo compounds or diazoalkanes and are described by the general structural formula R2C=N+=N−. The simplest example of a diazo compound is diazomethane, CH2N2. Diazo compounds should not be confused with azo compounds or with diazonium compounds.

Methyl yellow, or C.I. 11020, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5N2C6H4N(CH3)2. It is an azo dye derived from dimethylaniline. It is a yellow solid. According to X-ray crystallography, the C14N3 core of the molecule is planar.

Sudan I is an organic compound, typically classified as an azo dye. It is an intensely orange-red solid that is added to colourise waxes, oils, petrol, solvents, and polishes. Sudan I has also been adopted for colouring various foodstuffs, especially curry powder and chili powder, although the use of Sudan I in foods is now banned in many countries, because Sudan I, Sudan III, and Sudan IV have been classified as category 3 carcinogens by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Sudan I is still used in some orange-coloured smoke formulations and as a colouring for cotton refuse used in chemistry experiments.

Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C-N=N-C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group, but some dyes contain two or three azo groups, called "diazo dyes" and "triazo dyes" respectively. Azo dyes comprise 60-70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents.
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an organic reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile and the activated carbon act as a nucleophile. In most cases, including the examples below, the diazonium compound is also aromatic.

Sudan Red 7B, also known as Solvent Red 19, Ceres Red 7B, Fat Red 7B, Hexatype carmine B, Lacquer red V3B, Oil violet, Organol bordeaux B, Sudanrot 7B, Typogen carmine, and C.I. 26050, is a red diazo dye. Chemically it is N-ethyl-1-[[p-(phenylazo)phenyl]azo]-2-naphthalenamine. It is soluble in oils and insoluble in water.
This is the list of extremely hazardous substances defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act. The list can be found as an appendix to 40 C.F.R. 355. Updates as of 2006 can be seen on the Federal Register, 71 FR 47121.

DSP-4, or N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine, is a neurotoxin selective for noradrenergic neurons, capable of crossing the blood–brain barrier.
Pyrazolone is 5-membered heterocycle containing two adjacent nitrogen atoms. It can be viewed as a derivative of pyrazole possessing an additional carbonyl (C=O) group. Compounds containing this functional group are useful commercially in analgesics and dyes.
The formazans are compounds of the general formula [R-N=N-C(R')=N-NH-R"], formally derivatives of formazan [H2NN=CHN=NH], unknown in free form.

Sulfanilic acid (4-aminobenzenesulfonic acid) is an organic compound with the formula H3NC6H4SO3. It is an off-white solid. It is a zwitterion, which explains its high melting point. It is a common building block in organic chemistry.
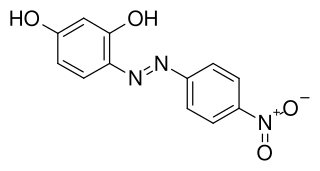
Azo violet (Magneson I; p-nitrobenzeneazoresorcinol) is an azo compound with the chemical formula C12H9N3O4. It is used commercially as a violet dye and experimentally as a pH indicator, appearing yellow below pH 11, and violet above pH 13. It also turns deep blue in the presence of magnesium salt in a slightly alkaline, or basic, environment. Azo violet may also be used to test for the presence of ammonium ions. The color of ammonium chloride or ammonium hydroxide solution will vary depending upon the concentration of azo violet used. Magneson I is used to test Be also; it produces an orange-red lake with Be(II) in alkaline medium.

Acid red 88 is an azo dye. Due to its intense colour, solid samples appear almost black. It is used to dye cotton textiles red. A closely related acid dye is Acid Red 13.
Basic Red 18 is a cationic azo dye used for coloring textiles. The chromophore is the cation, which contains many functional groups, but most prominently the quaternary ammonium center.
2-Chloroethyl ethyl sulfide is the organosulfur compound with the formula C2H5SC2H4Cl. It is a colorless liquid. The compound is part of the family of vesicant compounds known as half mustards, has been heavily investigated because of its structural similarity to the sulfur mustard S(C2H4Cl)2. The LD50s of the half and full mustard are 252 and 2.4 mg/kg (oral, rats).












