An emission nebula is a nebula formed of ionized gases that emit light of various wavelengths. The most common source of ionization is high-energy ultraviolet photons emitted from a nearby hot star. Among the several different types of emission nebulae are H II regions, in which star formation is taking place and young, massive stars are the source of the ionizing photons; and planetary nebulae, in which a dying star has thrown off its outer layers, with the exposed hot core then ionizing them.

The Eagle Nebula is a young open cluster of stars in the constellation Serpens, discovered by Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux in 1745–46. Both the "Eagle" and the "Star Queen" refer to visual impressions of the dark silhouette near the center of the nebula, an area made famous as the "Pillars of Creation" imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope. The nebula contains several active star-forming gas and dust regions, including the aforementioned Pillars of Creation. The Eagle Nebula lies in the Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way.

The Eskimo Nebula, also known as the Clown-faced Nebula, Lion Nebula, or Caldwell 39, is a bipolar double-shell planetary nebula (PN). It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1787. The formation resembles a person's head surrounded by a parka hood. It is surrounded by gas that composed the outer layers of a Sun-like star. The visible inner filaments are ejected by a strong wind of particles from the central star. The outer disk contains unusual, light-year-long filaments.

The Carina Nebula or Eta Carinae Nebula is a large, complex area of bright and dark nebulosity in the constellation Carina, located in the Carina–Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way galaxy. The nebula is approximately 8,500 light-years (2,600 pc) from Earth.

NGC 5189 is a planetary nebula in the constellation Musca. It was discovered by James Dunlop on 1 July 1826, who catalogued it as Δ252. For many years, well into the 1960s, it was thought to be a bright emission nebula. It was Karl Gordon Henize in 1967 who first described NGC 5189 as quasi-planetary based on its spectral emissions.

NGC 2362, also known as Caldwell 64, is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Canis Major. It was discovered by the Italian court astronomer Giovanni Batista Hodierna, who published his finding in 1654. William Herschel called it a "beautiful cluster", while William Henry Smyth said it "has a beautiful appearance, the bright white star being surrounded by a rich gathering of minute companions, in a slightly elongated form, and nearly vertical position". In the past it has also been listed as a nebula, but in 1930 Robert J. Trumpler found no evidence of nebulosity. The brightest member star system is Tau Canis Majoris, and therefore it is sometimes called the Tau Canis Majoris Cluster.

NGC 1999, also known as The Cosmic Keyhole, is a dust-filled bright nebula with a vast hole of empty space represented by a black patch of sky, as can be seen in the photograph. It is a reflection nebula, and shines from the light of the variable star V380 Orionis.

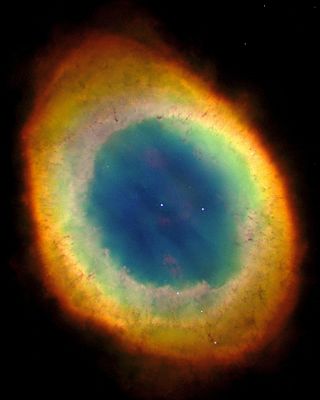
NGC 3132 is a bright and extensively studied planetary nebula in the constellation Vela. Its distance from Earth is estimated at about 613 pc. or 2,000 light-years.

NGC 7129 is a reflection nebula located 3,300 light years away in the constellation Cepheus. A young open cluster is responsible for illuminating the surrounding nebula. A recent survey indicates the cluster contains more than 130 stars less than 1 million years old. NGC 7129 is located just half a degree from nearby cluster NGC 7142.

NGC 246 is a planetary nebula in the constellation Cetus. It is the first known planetary nebula to have a hierarchical triple star system at its center. The nebula and the stars associated with it are listed in several catalogs, as summarized by the SIMBAD database. NGC 246 was discovered by William Herschel in 1785.

The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus.

NGC 1788 is a reflection nebula in the constellation of Orion. It is rather sharply defined on its southwest perimeter where it is flanked by the dark nebula known as Lynds 1616. Lynds 1616 is apparently part of NGC 1788. The brightest involved star is 10th magnitude and lies in the northwest sector.

NGC 7635, also known as the Bubble Nebula, Sharpless 162, or Caldwell 11, is an H II region emission nebula in the constellation Cassiopeia. It lies close to the open cluster Messier 52. The "bubble" is created by the stellar wind from a massive hot, 8.7 magnitude young central star, SAO 20575 (BD+60°2522). The nebula is near a giant molecular cloud which contains the expansion of the bubble nebula while itself being excited by the hot central star, causing it to glow. It was discovered in November 1787 by William Herschel. The star BD+60°2522 is thought to have a mass of about 44 M☉.
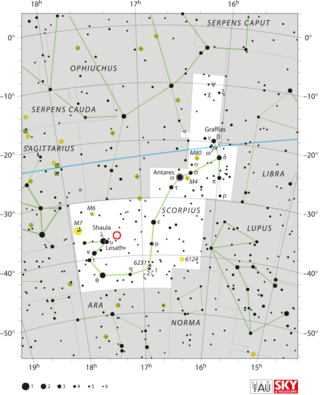
NGC 6334, colloquially known as the Cat's Paw Nebula, Bear Claw Nebula, or Gum 64, is an emission nebula and star-forming region located in the constellation Scorpius. NGC 6334 was discovered by astronomer John Herschel in 1837, who observed it from the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa. The nebula is located in the Carina–Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way, at a distance of approximately 5.5 kilolight-years from the Sun.

NGC 2818 is a planetary nebula located in the southern constellation Pyxis. It consists largely of glowing gases from the star's outer layers ejected during the final stages of its life when it had run out of the fuel necessary to sustain its core fusion processes. The remnants of its core will remain as a white dwarf.

NGC 7008, also known as the Fetus Nebula is a planetary nebula with a diameter of approximately 1 light-year located at a distance of 2800 light years in northern Cygnus. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1787, in Slough, England. NGC 7008 is included in the Astronomical League's Herschel 400 observing program.

RCW 49, also known as NGC 3247, is a H II region nebula located 13,700 light years away. Other designations for the RCW 49 region include NGC 3247 and G29 and it is commonly known as the Whirling Dervish Nebula. It is a dusty stellar nursery that contains more than 2,200 stars and is about 300-400 light years across. RCW 49 is recognized as among the brightest and most massive HII regions.

IC 2177 is a region of nebulosity that lies along the border between the constellations Monoceros and Canis Major. It is a roughly circular H II region centered on the Be star HD 53367. This nebula was discovered by Welsh amateur astronomer Isaac Roberts and was described by him as "pretty bright, extremely large, irregularly round, very diffuse."

NGC 2020 is an HII Region surrounding the Wolf-Rayet star BAT99-59. It is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud.



















