
The Cat's Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Draco, discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786. It was the first planetary nebula whose spectrum was investigated by the English amateur astronomer William Huggins, demonstrating that planetary nebulae were gaseous and not stellar in nature. Structurally, the object has had high-resolution images by the Hubble Space Telescope revealing knots, jets, bubbles and complex arcs, being illuminated by the central hot planetary nebula nucleus (PNN). It is a well-studied object that has been observed from radio to X-ray wavelengths.

NGC 2346 is a planetary nebula near the celestial equator in the constellation of Monoceros, less than a degree to the ESE of Delta Monocerotis. It is informally known as the Butterfly Nebula. The nebula is bright and conspicuous with a visual magnitude of 9.6, and has been extensively studied. Among its most remarkable characteristics is its unusually cool central star, which is a spectroscopic binary, and its unusual shape.

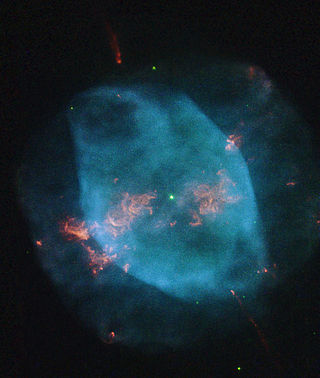
The Eskimo Nebula, also known as the Clown-faced Nebula, Lion Nebula, or Caldwell 39, is a bipolar double-shell planetary nebula (PN). It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1787. The formation resembles a person's head surrounded by a parka hood. It is surrounded by gas that composed the outer layers of a Sun-like star. The visible inner filaments are ejected by a strong wind of particles from the central star. The outer disk contains unusual, light-year-long filaments.

The Saturn Nebula is a planetary nebula in the constellation Aquarius. It appears as a greenish-yellowish hue in a small amateur telescope. It was discovered by William Herschel on September 7, 1782, using a telescope of his own design in the garden at his home in Datchet, England, and was one of his earliest discoveries in his sky survey. The nebula was originally a low-mass star that ejected its layers into space, forming the nebula. The central star is now a bright white dwarf star of apparent magnitude 11.5. The Saturn Nebula gets its name from its superficial resemblance to the planet Saturn with its rings nearly edge-on to the observer. It was so named by Lord Rosse in the 1840s, when telescopes had improved to the point that its Saturn-like shape could be discerned. William Henry Smyth said that the Saturn Nebula was one of Struve's nine "Rare Celestial Objects".

The Owl Nebula is a starburst ("planetary") nebula approximately 2,030 light years away in the northern constellation Ursa Major. The estimated age of the Owl Nebula is about 8,000 years. It is approximately circular in cross-section with faint internal structure. It was formed from the outflow of material from the stellar wind of the central star as it evolved along the asymptotic giant branch. The nebula is arranged in three concentric shells/envelopes, with the outermost shell being about 20–30% larger than the inner shell. A mildly owl-like appearance of the nebula is the result of an inner shell that is not circularly symmetric, but instead forms a barrel-like structure aligned at an angle of 45° to the line of sight.

NGC 2438 is a planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Puppis. Parallax measurements by Gaia put the central star at a distance of roughly 1,370 light years. It was discovered by William Herschel on March 19, 1786. NGC 2438 appears to lie within the cluster M46, but it is most likely unrelated since it does not share the cluster's radial velocity. The case is yet another example of a superposed pair, joining the famed case of NGC 2818.

NGC 7027, also known as the Jewel Bug Nebula, is a very young and dense planetary nebula located around 3,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cygnus. Discovered in 1878 by Édouard Stephan using the 800 mm (31 in) reflector at Marseille Observatory, it is one of the smallest planetary nebulae and by far the most extensively studied.

NGC 1514 is a planetary nebula in the zodiac constellation of Taurus, positioned to the north of the star Psi Tauri along the constellation border with Perseus. Distance to the nebula is 466 pc, according to GAIA DR2 data.

NGC 5882 is a small planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Lupus, positioned about 1.5° to the southwest of the star Epsilon Lupi. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on July 2, 1834 from the Cape of Good Hope observatory. John L. E. Dreyer described it as "very small, round, quite sharp". It is located at a distance of approximately 7.7 kilolight-years from the Sun.

NGC 5307 is a planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Centaurus, positioned less than 3° to the northeast of the star Epsilon Centauri. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on April 15, 1836. The nebula is located at a distance of approximately 10.6 kilolight-years from the Sun. The central star, designated PNG 312.3+10.5, is a weak emission-line star, superficially similar to the WC subtype of Wolf–Rayet stars. It has a spectral class of O(H)3.5 V.
NGC 7354 is a planetary nebula located in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cepheus, at a distance of approximately 5.5 kly from the Sun. It was discovered by German-born astronomer William Herschel on November 3, 1787. John L. E. Dreyer described it as, "a planetary nebula, bright, small, round, pretty gradually a very little brighter middle".

NGC 2867 is an elliptical Type II planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Carina, just over a degree to the NNW of the star Iota Carinae. It was discovered by John Herschel on April 1, 1834. Herschel initially thought he might have found a new planet, but on the following night he checked again and discovered it had not moved. The nebula is located at a distance of 7,270 light-years from the Sun.

NGC 3195 is a planetary nebula located in the southern constellation of Chamaeleon. It is the most southern of all the bright sizable planetary nebula in the sky, and remains concealed from all northern observers. Discovered by Sir John Herschel in 1835, this 11.6 apparent magnitude planetary nebula is slightly oval in shape, with dimensions of 40×35 arc seconds, and can be seen visually in telescopic apertures of 10.5 centimetres (4.1 in) at low magnifications.

NGC 6884 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Cygnus, less than a degree to the southwest of the star Ο1 Cygni. It lies at a distance of approximately 12.5 kly from the Sun. The nebula was discovered on May 8, 1883 by American astronomer Edward C. Pickering.

NGC 6072 is a planetary nebulae in the southern constellation of Scorpius. It has a dynamical age of 104 years. Its circumstellar envelope is likely to be rich in carbon as it has very strong CN (cyanide) spectral lines. CN spectral lines are generally not detected in oxygen rich AGB (asymptotic giant branch) circumstellar envelopes. NGC 6072 also shows H2 (hydrogen) emission and intense CO (carbon monoxide) emission which has been mapped displaying bipolarity and some gas at high velocity. The evolution of this planetary nebulae is likely to be dominated by photodissociation and ion/radical molecular reactions. Shock chemistry is also likely to be important.

NGC 1501 is a complex planetary nebula located in the constellation of Camelopardalis, discovered in 27 Aug 1787 by William Herschel. It is also known as the Oyster Nebula.

WR 31a, commonly referred to as Hen 3-519, is a Wolf–Rayet (WR) star in the southern constellation of Carina that is surrounded by an expanding Wolf–Rayet nebula. It is not a classical old stripped-envelope WR star, but a young massive star which still has some hydrogen left in its atmosphere.

NGC 6445, also known as the Little Gem Nebula or Box Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by William Herschel on May 28, 1786. The distance of NGC 6445 is estimated to be slightly more than 1,000 parsecs based on the parallax measured by Gaia, which was measured at 0.9740±0.3151 mas.

NGC 6778 is a planetary nebula (PNe) located about 10,300 light years away from the Sun in the equatorial constellation of Aquila. It is positioned 5° to the SSW of the prominent star Delta Aquilae. This nebula was discovered by German astronomer Albert Marth during the period 1863–1865. English astronomer John Herschel may have mistakenly catalogued it as NGC 6785, as nothing can be found now at those coordinates. In the New General Catalogue it was described as a "small, elongated, ill-defined disk".
LoTr 5 is a large, faint planetary nebula in the constellation of Coma Berenices. In 2018, its parallax was measured by Gaia, giving a distance of about 1,650 light-years.





















