
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.

Minkowski 2-9, abbreviated M2-9 is a planetary nebula that was discovered by Rudolph Minkowski in 1947. It is located about 2,100 light-years away from Earth in the direction of the constellation Ophiuchus. This bipolar nebula takes the peculiar form of twin lobes of material that emanate from a central star. Astronomers have dubbed this object as the Twin Jet Nebula because of the jets believed to cause the shape of the lobes. Its form also resembles the wings of a butterfly. The nebula was imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope in the 1990s.

NGC 2438 is a planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Puppis. Parallax measurements by Gaia put the central star at a distance of roughly 1,370 light years. It was discovered by William Herschel on March 19, 1786. NGC 2438 appears to lie within the cluster M46, but it is most likely unrelated since it does not share the cluster's radial velocity.

R Monocerotis, abbreviated R Mon, is a very young binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Monoceros. The apparent magnitude of R Mon varies between 10 and 12 and the spectral type is B8IIIe.

A protoplanetary nebula or preplanetary nebula is an astronomical object which is at the short-lived episode during a star's rapid evolution between the late asymptotic giant branch (LAGB)[a] phase and the subsequent planetary nebula (PN) phase. A PPN emits strongly in infrared radiation, and is a kind of reflection nebula. It is the second-from-the-last high-luminosity evolution phase in the life cycle of intermediate-mass stars.

NGC 1514, also known as the Crystal Ball Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the zodiac constellation of Taurus, positioned to the north of the star Psi Tauri along the constellation border with Perseus. Distance to the nebula is 466 pc, according to GAIA DR2 data.

A bipolar outflow comprises two continuous flows of gas from the poles of a star. Bipolar outflows may be associated with protostars, or with evolved post-AGB stars.

NGC 5882 is a small planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Lupus, positioned about 1.5° to the southwest of the star Epsilon Lupi. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on July 2, 1834 from the Cape of Good Hope observatory. John L. E. Dreyer described it as "very small, round, quite sharp". It is located at a distance of approximately 7.7 kilolight-years from the Sun.
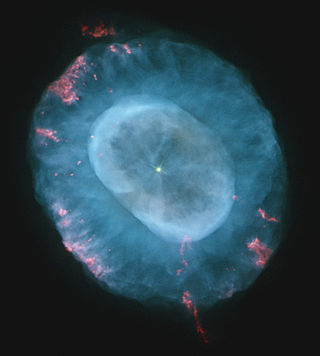
NGC 7662 is a planetary nebula located in the northern constellation Andromeda. It is known as the Blue Snowball Nebula, Snowball Nebula, and Caldwell 22. This nebula was discovered October 6, 1784 by the German-born English astronomer William Herschel. In the New General Catalogue it is described as a "magnificent planetary or annular nebula, very bright, pretty small in angular size, round, blue, variable nucleus". The object has an apparent visual magnitude of 8.3 and spans an angular size of 32″ × 28″. Parallax measurements give a distance estimate of 5,730 ± 340 ly (1,757 ± 103 pc).
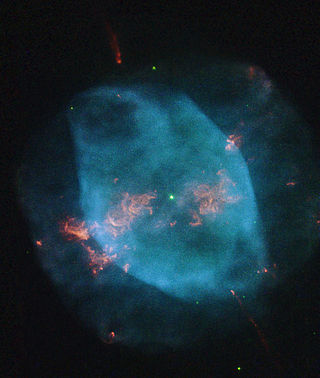
NGC 7354 is a planetary nebula located in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cepheus, at a distance of approximately 5.5 kly from the Sun. It was discovered by German-born astronomer William Herschel on November 3, 1787. John L. E. Dreyer described it as, "a planetary nebula, bright, small, round, pretty gradually a very little brighter middle".

NGC 3195 is a planetary nebula located in the southern constellation of Chamaeleon. Discovered by Sir John Herschel in 1835, this 11.6 apparent magnitude planetary nebula is slightly oval in shape, with dimensions of 40×35 arc seconds, and can be seen visually in telescopic apertures of 10.5 centimetres (4.1 in) at low magnifications.

NGC 6884 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Cygnus, less than a degree to the southwest of the star Ο1 Cygni. It lies at a distance of approximately 12.5 kly from the Sun. The nebula was discovered on May 8, 1883, by American astronomer Edward C. Pickering.

NGC 6072 is a planetary nebulae in the southern constellation of Scorpius. It has a dynamical age of 104 years. Its circumstellar envelope is likely to be rich in carbon as it has very strong CN (cyanide) spectral lines. CN spectral lines are generally not detected in oxygen rich AGB (asymptotic giant branch) circumstellar envelopes. NGC 6072 also shows H2 (hydrogen) emission and intense CO (carbon monoxide) emission which has been mapped displaying bipolarity and some gas at high velocity. The evolution of this planetary nebulae is likely to be dominated by photodissociation and ion/radical molecular reactions. Shock chemistry is also likely to be important.

Little Ghost Nebula, also known as NGC 6369, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Ophiuchus. It was discovered by William Herschel.

NGC 1501 is a complex planetary nebula located in the constellation of Camelopardalis, it was discovered on 27 August 1787 by William Herschel.

NGC 6905, also known as the Blue Flash Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Delphinus. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1784. The central star is 14.0 mag. The distance of the nebula, as with most planetary nebulae, is not well determined and estimates range between 1.7 and 2.6 kpc.

NGC 6445, also known as the Little Gem Nebula or Box Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by William Herschel on May 28, 1786. The distance of NGC 6445 is estimated to be slightly more than 1,000 parsecs based on the parallax measured by Gaia, which was measured at 0.9740±0.3151 mas.

NGC 6778 is a planetary nebula (PN) located about 10,300 light years away from the Sun in the equatorial constellation of Aquila. It is positioned 5° to the SSW of the prominent star Delta Aquilae. This nebula was discovered by German astronomer Albert Marth during the period 1863–1865. English astronomer John Herschel may have mistakenly catalogued it as NGC 6785, as nothing can be found now at the coordinates he gave for it. In the New General Catalogue it was described as a "small, elongated, ill-defined disc".
LoTr 5 is a large, faint planetary nebula in the constellation of Coma Berenices. In 2018, its parallax was measured by Gaia, giving a distance of about 1,650 light-years.
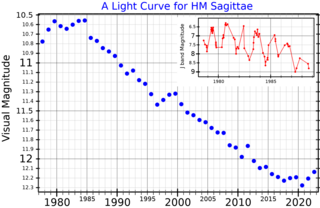
HM Sagittae is a dusty-type symbiotic nova in the northern constellation of Sagitta. It was discovered by O. D. Dokuchaeva and colleagues in 1975 when it increased in brightness by six magnitudes. The object displays an emission line spectrum similar to a planetary nebula and was detected in the radio band in 1977. Unlike a classical nova, the optical brightness of this system did not rapidly decrease with time, although it showed some variation. It displays activity in every band of the electromagnetic spectrum from X-ray to radio.




















