
Messier 100 is a grand design intermediate spiral galaxy in the southern part of the mildly northern Coma Berenices. It is one of the brightest and largest galaxies in the Virgo Cluster and is approximately 55 million light-years from our galaxy, its diameter being 107,000 light years, and being about 60% as large. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 and 29 days later seen again and entered by Charles Messier in his catalogue "of nebulae and star clusters".. It was one of the first spiral galaxies to be discovered, and was listed as one of fourteen spiral nebulae by Lord William Parsons of Rosse in 1850. NGC 4323 and NGC 4328 are satellite galaxies of M100; the former is connected with it by a bridge of luminous matter.

Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux.
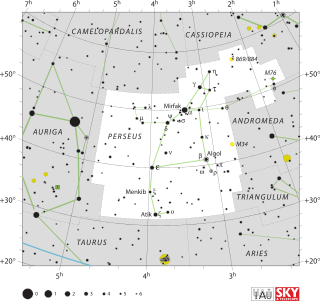
Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose asterism was named together as Perseus et Caput Medusae; however, this never came into popular usage.

NGC 4314 is a barred spiral galaxy approximately 53 million light-years away in the northern constellation of Coma Berenices. It is positioned around 3° to the north and slightly west of the star Gamma Comae Berenices and is visible in a small telescope. The galaxy was discovered by German-born astronomer William Herschel on March 13, 1785. It was labelled as peculiar by Allan Sandage in 1961 because of the unusual structure in the center of the bar. NGC 4314 is a member of the Coma I group of galaxies.

NGC 4261 is an elliptical galaxy located around 100 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered April 13, 1784 by the German-born astronomer William Herschel. The galaxy is a member of its own somewhat meager galaxy group known as the NGC 4261 group, which is part of the Virgo Cluster.

NGC 3621 is a field spiral galaxy about 22 Mly (6.7 Mpc) away in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It is comparatively bright and can be well seen in moderate-sized telescopes. The galaxy is around 93,000 ly (29,000 pc) across and is inclined at an angle of 25° from being viewed edge on. It shines with a luminosity equal to 13 billion times that of the Sun. The morphological classification is SA(s)d, which indicates this is an ordinary spiral with loosely wound arms. There is no evidence for a bulge. Although it appears to be isolated, NGC 3621 belongs to the Leo spur.

NGC 3783 is a barred spiral galaxy located about 135 million light years away in the constellation Centaurus. It is inclined by an angle of 23° to the line of sight from the Earth along a position angle of about 163°. The morphological classification of SBa indicates a bar structure across the center (B) and tightly-wound spiral arms (a). Although not shown by this classification, observers note the galaxy has a luminous inner ring surrounding the bar structure. The bright compact nucleus is active and categorized as a Seyfert 1 type. This nucleus is a strong source of X-ray emission and undergoes variations in emission across the electromagnetic spectrum.

NGC 1288 is an intermediate barred spiral galaxy located about 196 million light years away in the constellation Fornax. In the nineteenth century, English astronomer John Herschel described it as "very faint, large, round, very gradually little brighter middle." The morphological classification of SABc(rs) indicates weak bar structure across the nucleus (SAB), an incomplete inner ring orbiting outside the bar (rs), and the multiple spiral arms are moderately wound (c). The spiral arms branch at intervals of 120° at a radius of 30″ from the nucleus. The galaxy is most likely surrounded by a dark matter halo, giving it a mass-to-light ratio of 14 M☉/L☉.

NGC 1052 is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Cetus. It was discovered on January 10, 1785 by the astronomer William Herschel. It is a member of the eponymous NGC 1052 Group.

NGC 5559 is a barred spiral galaxy, located 240 million light-years away in the constellation of Boötes. It was discovered on April 10, 1785, by the astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 3972 is a spiral galaxy located in the northern constellation of Ursa Major. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 14, 1789. This galaxy is located 66 million light years away and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 846 km/s. It is a member of the NGC 3992 Group of galaxies.

NGC 2998 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is 195 million light-years away from the Earth. It is an intermediate spiral galaxy. Its stellar mass is about that of the Milky Way.

NGC 3319 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by William Herschel on Feb 3, 1788. It is rich in gas and lacks a galactic bulge.

NGC 3005 is an edge-on spiral galaxy in the constellation of Ursa Major, discovered by Bindon Stoney on January 25, 1851. It is a member of the NGC 2998 group, which also includes NGC 2998, NGC 3002, NGC 3006, NGC 3008, and a few others.

NGC 3006 is an edge-on spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It has an apparent magnitude of 15. It was discovered by the astronomer Bindon Stoney on January 25, 1851.

NGC 1325 is a flocculent spiral galaxy situated in the constellation of Eridanus. Located about 75 million light years away, it is a member of the Eridanus cluster of galaxies, a cluster of about 200 galaxies. It was discovered by William Herschel on 19 December 1799.

NGC 3156 is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Sextans. It is located at a distance of about 75 million light-years from Earth and is forming a pair with NGC 3169. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on December 13, 1784.

NGC 3902 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Leo. It was discovered on April 6, 1785, by William Herschel and observed on February 19, 1827, by John Herschel. It is estimated to be 180 to 185 million light-years away, and its redshift-independent distance estimates to about 185 to 240 million light-years. It is around 75,000 light-years in diameter.

NGC 7513 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Sculptor. It is located at a distance of circa 62.5 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 7513 is about 75,000 light years across. It was discovered by Albert Marth on September 24, 1864.

NGC 4343 is an unbarred spiral galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by the astronomer William Herschel on April 13, 1784. At a distance of 80 million light-years, it is located in the Virgo Cluster. It contains an active galactic nucleus.




















