 | |
| Formation | November 4, 2009 |
|---|---|
| Type | International organisation |
Membership | |
| Website | http://www.nordefco.org |
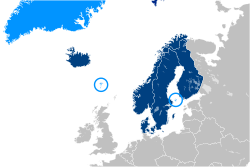
NORDEFCO (Nordic Defence Cooperation) is a collaboration among the Nordic countries in the area of defense. Its five members are Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden.

The Nordic countries or the Nordics are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic, where they are most commonly known as Norden. The term includes Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, as well as Greenland and the Faroe Islands—which are both part of the Kingdom of Denmark—and the Åland Islands and Svalbard and Jan Mayen archipelagos that belong to Finland and Norway respectively, whereas the Norwegian Antarctic territories are often not considered a part of the Nordic countries, due to their geographical location. Several regions in Europe, such as the Northern Isles of Scotland, share cultural or ethnic ties with Nordic nations, but are not considered to be Nordic countries. Scandinavians, who comprise over three quarters of the region's population, are the largest group, followed by Finns, who comprise the majority in Finland; other ethnic groups are the Greenlandic Inuit, the Sami people, and recent immigrants and their descendants. The native languages Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, Icelandic, and Faroese are all North Germanic languages rooted in Old Norse. Native non-Germanic languages are Finnish, Greenlandic and several Sami languages. The main religion is Lutheran Christianity. The Nordic countries have much in common in their way of life, history, religion, their use of Scandinavian languages and social structure. The Nordic countries have a long history of political unions and other close relations, but do not form a separate entity today. The Scandinavist movement sought to unite Denmark, Norway and Sweden into one country in the 19th century, with the indepedence of Finland in the early 20th century, and Iceland in the mid 20th century, this movement expanded into the modern organised Nordic cooperation which includes the Nordic Council and the Nordic Council of Ministers. Especially in English, Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for the Nordic countries, but that term more properly refers to the three monarchies of Denmark, Norway and Sweden. Geologically, the Scandinavian Peninsula comprises the mainland of Norway and Sweden as well as the northernmost part of Finland.

Denmark, officially the Kingdom of Denmark, is a sovereign state in Northern Europe. Denmark proper consists of a peninsula, Jutland, and an archipelago of 443 named islands, with the largest being Zealand, Funen and the North Jutlandic Island. The islands are characterised by flat, arable land and sandy coasts, low elevation and a temperate climate. The southernmost of the Scandinavian nations, Denmark lies southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and is bordered to the south by Germany. The Kingdom of Denmark also comprises two autonomous constituent countries in the North Atlantic Ocean: the Faroe Islands and Greenland. Denmark has a total area of 42,924 km2 (16,573 sq mi), land area of 42,394 km2 (16,368 sq mi), and the total area including Greenland and the Faroe Islands is 2,210,579 km2 (853,509 sq mi), and a population of 5.8 million.

Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, and Gulf of Finland, between Norway to the north, Sweden to the northwest, and Russia to the east. The capital and largest city is Helsinki. Other major cities are Espoo, Vantaa, Tampere, Oulu and Turku.
Contents
The aim of the organization is to strengthen the member countries' defense capabilities by identifying areas for cooperation and to promote effective solutions. The memorandum of understanding was signed in Helsinki on November 4, 2009, succeeding NORDSUP, NORDAC, and NORDCAPS, previous parallel cooperative arrangements. [1]
A memorandum of understanding (MoU) is a type of agreement between two (bilateral) or more (multilateral) parties. It expresses a convergence of will between the parties, indicating an intended common line of action. It is often used either in cases where parties do not imply a legal commitment or in situations where the parties cannot create a legally enforceable agreement. It is a more formal alternative to a gentlemen's agreement.

Helsinki is the capital and most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of Uusimaa in southern Finland, and has a population of 650,058. The city's urban area has a population of 1,268,296, making it by far the most populous urban area in Finland as well as the country's most important center for politics, education, finance, culture, and research. Helsinki is located 80 kilometres (50 mi) north of Tallinn, Estonia, 400 km (250 mi) east of Stockholm, Sweden, and 300 km (190 mi) west of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It has close historical ties with these three cities.
Participation in the NORDEFCO is voluntary and states can choose which areas they want to collaborate within and to what extent. This means that cooperation can occur bilaterally as well as among all five members. It is also considered within the organizational scope to work with non-Nordic countries in fields where there is an added value to doing so. According to the official webpage, the cooperation is based on the conviction that there is much to be gained through cost sharing, joint solutions, and joint actions. However, it also underlines the fact that NORDEFCO is not a military alliance:
The NORDEFCO does not aim for new military or political alliances between the nations. Mutually reinforcing cooperation in capability development can be achieved without negative influence on participating countries' different foreign and security policy orientation and membership obligations in NATO, the EU and the UN. On the contrary, closer practical cooperation in capability development would constitute a supplemental approach in providing the capabilities and forces required by these organisations. [2]
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 29 North American and European countries. The organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty that was signed on 4 April 1949. NATO constitutes a system of collective defence whereby its independent member states agree to mutual defence in response to an attack by any external party. NATO's Headquarters are located in Haren, Brussels, Belgium, while the headquarters of Allied Command Operations is near Mons, Belgium.
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 28 member states that are located primarily in Europe. It has an area of 4,475,757 km2 (1,728,099 sq mi) and an estimated population of about 513 million. The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where members have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market, enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development. For travel within the Schengen Area, passport controls have been abolished. A monetary union was established in 1999 and came into full force in 2002 and is composed of 19 EU member states which use the euro currency.