
Python is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation.
Zope is a family of free and open-source web application servers written in Python, and their associated online community. Zope stands for "Z Object Publishing Environment", and was the first system using the now common object publishing methodology for the Web. Zope has been called a Python killer app, an application that helped put Python in the spotlight.
Coroutines are computer program components that allow execution to be suspended and resumed, generalizing subroutines for cooperative multitasking. Coroutines are well-suited for implementing familiar program components such as cooperative tasks, exceptions, event loops, iterators, infinite lists and pipes.
IronPython is an implementation of the Python programming language targeting the .NET Framework and Mono. The project is currently maintained by a group of volunteers at GitHub. It is free and open-source software, and can be implemented with Python Tools for Visual Studio, which is a free and open-source extension for Microsoft's Visual Studio IDE.
Stackless Python, or Stackless, is a Python programming language interpreter, so named because it avoids depending on the C call stack for its own stack. In practice, Stackless Python uses the C stack, but the stack is cleared between function calls. The most prominent feature of Stackless is microthreads, which avoid much of the overhead associated with usual operating system threads. In addition to Python features, Stackless also adds support for coroutines, communication channels, and task serialization.
In computing, a solution stack or software stack is a set of software subsystems or components needed to create a complete platform such that no additional software is needed to support applications. Applications are said to "run on" or "run on top of" the resulting platform.
CherryPy is an object-oriented web application framework using the Python programming language. It is designed for rapid development of web applications by wrapping the HTTP protocol but stays at a low level and does not offer much more than what is defined in RFC 7231.

Django is a free and open-source, Python-based web framework that follows the model–template–views (MTV) architectural pattern. It is maintained by the Django Software Foundation (DSF), an independent organization established in the US as a 501(c)(3) non-profit.

Seaside, an acronym that stands for “Squeak Enterprise Aubergines Server with Integrated Development Environment,” is computer software, a web framework to develop web applications in the programming language Smalltalk. It is distributed as free and open-source software under an MIT License.
Nevow is a Python web application framework originally developed by the company Divmod. Template substitution is achieved via a small Tag Attribute Language, which is usually embedded in on-disk XML templates, though there is also a pure-Python domain-specific language called Stan, for expressing this markup programmatically. Nevow integrates well with Twisted, a framework for event-driven programming.

Lift is a free and open-source web framework that is designed for the Scala programming language. It was originally created by David Pollak who was dissatisfied with certain aspects of the Ruby on Rails framework. Lift was launched as an open source project on 26 February 2007 under the Apache License 2.0. A commercially popular web platform often cited as being developed using Lift is Foursquare.
Google App Engine is a cloud computing platform as a service for developing and hosting web applications in Google-managed data centers. Applications are sandboxed and run across multiple servers. App Engine offers automatic scaling for web applications—as the number of requests increases for an application, App Engine automatically allocates more resources for the web application to handle the additional demand.
Phusion Passenger is a free web server and application server with support for Ruby, Python and Node.js. It is designed to integrate into the Apache HTTP Server or the nginx web server, but also has a mode for running standalone without an external web server. Phusion Passenger supports Unix-like operating systems, and is available as a gem package, as a tarball, or as native Linux packages.

Rack is a modular interface between web servers and web applications developed in the Ruby programming language. With Rack, application programming interfaces (APIs) for web frameworks and middleware are wrapped into a single method call handling HTTP requests and responses.

Flask is a micro web framework written in Python. It is classified as a microframework because it does not require particular tools or libraries. It has no database abstraction layer, form validation, or any other components where pre-existing third-party libraries provide common functions. However, Flask supports extensions that can add application features as if they were implemented in Flask itself. Extensions exist for object-relational mappers, form validation, upload handling, various open authentication technologies and several common framework related tools.
Pylons Project is an open-source organization that develops a set of web application technologies written in Python. Initially the project was a single web framework called Pylons, but after the merger with the repoze.bfg framework under the new name Pyramid, the Pylons Project now consists of multiple related web application technologies.
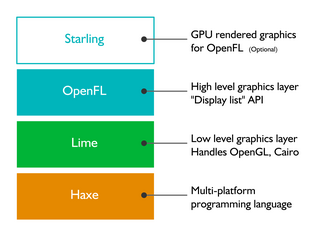
OpenFL is a free and open-source software framework and platform for the creation of multi-platform applications and video games. OpenFL applications can be written in Haxe, JavaScript, or TypeScript, and may be published as standalone applications for several targets including iOS, Android, HTML5, Windows, macOS, Linux, WebAssembly, Flash, AIR, PlayStation 4, PlayStation 3, PlayStation Vita, Xbox One, Wii U, TiVo, Raspberry Pi, and Node.js.






