
The Main is the longest tributary of the Rhine. It rises as the White Main in the Fichtel Mountains of northeastern Bavaria and flows west through central Germany for 525 kilometres (326 mi) to meet the Rhine below Rüsselsheim, Hesse. The cities of Mainz and Wiesbaden are close to the confluence.

Dacia was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to present-day Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, and Ukraine.

The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. It was once called "the most Hungarian river" because it used to flow entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders.

The Dacians were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area includes mainly the present-day countries of Romania and Moldova, as well as parts of Ukraine, Eastern Serbia, Northern Bulgaria, Slovakia, Hungary and Southern Poland. The Dacians and the related Getae spoke the Dacian language, which has a debated relationship with the neighbouring Thracian language and may be a subgroup of it. Dacians were somewhat culturally influenced by the neighbouring Scythians and by the Celtic invaders of the 4th century BC.

The Iazyges were an ancient Sarmatian tribe that traveled westward in c. 200 BC from Central Asia to the steppes of modern Ukraine. In c. 44 BC, they moved into modern-day Hungary and Serbia near the Dacian steppe between the Danube and Tisza rivers, where they adopted a semi-sedentary lifestyle.

The Iller is a river of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg in Germany. It is a right tributary of the Danube, 146 kilometres (91 mi) long.

The Isar is a river in Austria and in Bavaria, Germany. Its source is in the Karwendel mountain range of the Alps. The Isar river enters Germany near Mittenwald and flows through Bad Tölz, Munich, and Landshut before reaching the Danube near Deggendorf. With 295 km length, it is among the longest rivers in Bavaria. It is Germany's second most important tributary of the Danube.

Banat is a geographical and historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central and Eastern Europe. It is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania ; the western part of Banat is in northeastern Serbia ; and a small northern part lies within southeastern Hungary.
Several theories, in great extent mutually exclusive, address the issue of the origin of the Romanians. The Romanian language descends from the Vulgar Latin dialects spoken in the Roman provinces north of the "Jireček Line" in Late Antiquity. The theory of Daco-Roman continuity argues that the Romanians are mainly descended from the Daco-Romans, a people developing through the cohabitation of the native Dacians and the Roman colonists in the province of Dacia Traiana north of the river Danube. The competing immigrationist theory states that the Romanians' ethnogenesis commenced in the provinces south of the river with Romanized local populations spreading through mountain refuges, both south to Greece and north through the Carpathian Mountains. Other theories state that the Romanized local populations were present over a wide area on both sides of the Danube and the river itself did not constitute an obstacle to permanent exchanges in both directions; according to the "admigration" theory, migrations from the Balkan Peninsula to the lands north of the Danube contributed to the survival of the Romance-speaking population in these territories.

The Sava is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally through Serbia, feeding into the Danube in its capital, Belgrade. The Sava forms the main northern limit of the Balkan Peninsula, and the southern edge of the Pannonian Plain.
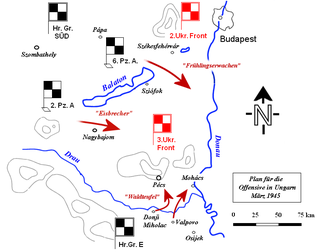
Operation Spring Awakening was the last major German offensive of World War II. The operation was referred to in Germany as the Plattensee Offensive and in the Soviet Union as the Balaton Defensive Operation. It took place in Western Hungary on the Eastern Front and lasted from 6 March until 15 March, 1945. The objective was to secure the last significant oil reserves still available to the European Axis powers and prevent the Red Army from advancing towards Vienna. The Germans failed in their objectives.

The Argeș is a river in Southern Romania, a left tributary of the Danube. It is 350 km (220 mi) long, and its basin area is 12,550 km2 (4,850 sq mi). Its source is in the Făgăraș Mountains, in the Southern Carpathians and it flows into the Danube at Oltenița. Its average discharge at the mouth is 71 m3/s (2,500 cu ft/s).

The Danube Swabians is a collective term for the ethnic German-speaking population who lived in Kingdom of Hungary of east-central Europe, especially in the Danube River valley, first in the 12th century, and in greater numbers in the 17th and 18th centuries. Most were descended from earlier 18th-century Swabian settlers from Upper Swabia, the Swabian Jura, northern Lake Constance, the upper Danube, the Swabian-Franconian Forest, the Southern Black Forest and the Principality of Fürstenberg, followed by Hessians, Bavarians, Franconians and Lorrainers recruited by Austria to repopulate the area and restore agriculture after the expulsion of the Ottoman Empire. They were able to keep their language and religion and initially developed strongly German communities in the region with German folklore.

The Timok, sometimes also known as Great Timok, is a river in eastern Serbia, a right tributary of the Danube. For the last 15 km of its run it forms a border between eastern Serbia and western Bulgaria.

Mehadia is a small market town and commune in Caraș-Severin County, Banat, Romania. It lies on the European route E70, in the Cerna River valley. The town is located on the site of the ancient Roman colony Ad Mediam and was noted for its Hercules baths. It had a population of 2,492 in 1900, and of 4,118 in 2011. The commune is prone to major recurring flooding. The 1838 floods destroyed some 2,000 houses in the valley and the 1841 floods in Mehadia were also devastating. It experienced major flooding more recently in May 2005.

The Shoes on the Danube Bank is a memorial erected on 16 April 2005, in Budapest, Hungary. Conceived by film director Can Togay, he created it on the east bank of the Danube River with sculptor Gyula Pauer to honour the Jews who were massacred by fascist Hungarian militia belonging to the Arrow Cross Party in Budapest during the Second World War. They were ordered to take off their shoes, and were shot at the edge of the water so that their bodies fell into the river and were carried away. The memorial represents their shoes left behind on the bank.

The flora of Romania comprises around 3,450 species of vascular plants, which represents around 30% of the vascular flora of Europe.

The Danube is the second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest south into the Black Sea. A large and historically important river, it was once a frontier of the Roman Empire. In the 21st century, it connects ten European countries, running through their territories or marking a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for 2,850 km (1,770 mi), passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine. Among the many cities on the river are four national capitals: Vienna, Bratislava, Budapest, and Belgrade. Its drainage basin amounts to 817,000 km² and extends into nine more countries.

SMS Körös was the name ship of the Körös-class river monitors built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy. Completed in 1892, the ship was part of the Danube Flotilla, and fought various Allied forces from Belgrade down the Danube to the Black Sea during World War I. After brief service with the Hungarian People's Republic at the end of the war, she was transferred to the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, and renamed Morava. She remained in service throughout the interwar period, although budget restrictions meant she was not always in full commission.


















