
Sassafras is a genus of three extant and one extinct species of deciduous trees in the family Lauraceae, native to eastern North America and eastern Asia. The genus is distinguished by its aromatic properties, which have made the tree useful to humans.

Caryophyllene, more formally (−)-β-caryophyllene,(BCP), is a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene that is a constituent of many essential oils, especially clove oil, the oil from the stems and flowers of Syzygium aromaticum (cloves), the essential oil of Cannabis sativa, rosemary, and hops. It is usually found as a mixture with isocaryophyllene (the cis double bond isomer) and α-humulene (obsolete name: α-caryophyllene), a ring-opened isomer. Caryophyllene is notable for having a cyclobutane ring, as well as a trans-double bond in a 9-membered ring, both rarities in nature.
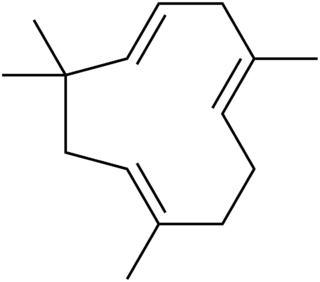
Humulene, also known as α-humulene or α-caryophyllene, is a naturally occurring monocyclic sesquiterpene (C15H24), containing an 11-membered ring and consisting of 3 isoprene units containing three nonconjugated C=C double bonds, two of them being triply substituted and one being doubly substituted. It was first found in the essential oils of Humulus lupulus (hops), from which it derives its name. Humulene is an isomer of β-caryophyllene, and the two are often found together as a mixture in many aromatic plants.

Bisabolol, or more formally α-(−)-bisabolol or also known as levomenol, is a natural monocyclic sesquiterpene alcohol. It is a colorless viscous oil that is the primary constituent of the essential oil from German chamomile and Myoporum crassifolium. High concentrations of bisabolol can also be found in certain medicinal cannabis cultivars. It is poorly soluble in water and glycerine, but soluble in ethanol. The enantiomer, α-(+)-bisabolol, is also found naturally but is rare. Synthetic bisabolol is usually a racemic mixture of the two, α-(±)-bisabolol. It is the terpenoid responsible for distinctive aroma of chamomile flowers, and when isolated, its scent has also has been likened to apples, sugar and honey.

Neolitsea is a genus of about 85 species of evergreen shrubs and small trees in the laurel family Lauraceae. They range from Indo-Malaysia to East Asia to Australia. The leaves are alternate, clustered, or verticillate, rarely subopposite. Species are dioecious, with separate male and female plants.

Cannabis flower essential oil, also known as hemp essential oil, is an essential oil obtained by steam distillation from the flowers, panicles, stem, and upper leaves of the hemp plant. Hemp essential oil is distinct from hemp seed oil and hash oil: the former is a vegetable oil that is cold-pressed from the seeds of low-THC varieties of hemp, the latter is a THC-rich extract of dried female hemp flowers (marijuana) or resin (hashish).

Helenalin, or (-)-4-Hydroxy-4a,8-dimethyl-3,3a,4a,7a,8,9,9a-octahydroazuleno[6,5-b]furan-2,5-dione, is a toxic sesquiterpene lactone which can be found in several plants such as Arnica montana and Arnica chamissonis Helenalin is responsible for the toxicity of the Arnica spp. Although toxic, helenalin possesses some in vitro anti-inflammatory and anti-neoplastic effects. Helenalin can inhibit certain enzymes, such as 5-lipoxygenase and leukotriene C4 synthase. For this reason the compound or its derivatives may have potential medical applications.
Neolitsea daibuensis is a species of plant in the family Lauraceae endemic to Taiwan. It is a small semi-deciduous tree that grows in the broad-leaved forests in southern Taiwan at altitudes of 800–1,000 m (2,600–3,300 ft). It is threatened by habitat loss.
Neolitsea fischeri is a species of plant in the family Lauraceae. It is a small tree endemic to the Anaimalai and Palni Hills in southern India.

Sassafras randaiense is a species of deciduous tree in the family Lauraceae belonging to the genus Sassafras. It is a relict species endemic to Taiwan. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Cymbopogon citratus, commonly known as West Indian lemon grass or simply lemon grass, is a tropical plant native to Maritime Southeast Asia and introduced to many tropical regions.

Polygodial is chemical compound found in dorrigo pepper, mountain pepper, horopito, canelo, paracress, water-pepper, and Dendrodoris limbata.

Cinnamomum osmophloeum, commonly known as pseudocinnamomum or indigenous cinnamon, is a medium-sized evergreen tree in the genus Cinnamomum. It is native to broad-leaved forests of central and northern Taiwan.

Nimbin is a triterpenoid isolated from Neem. Nimbin is thought to be responsible for much of the biological activities of neem oil, and is reported to have anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, fungicidal, antihistamine and antiseptic properties.

α-Cadinol or 10α-hydroxy-4-cadinene is an organic compound, a sesquiterpenoid alcohol.

Neolitsea aciculata is a species of small evergreen tree in the family Lauraceae. It is found in Japan and Taiwan. In Taiwan, it grows often in mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forests in valleys throughout the island.

Neolitsea sericea is a species of tree in the family Lauraceae. It is found in China, Taiwan, south Korea, and Japan. Its natural habitat is on forest margins and slopes, and it is often found in well-progressed secondary forests.
Daphnephila truncicola is a species of gall midges first associated with stem galls on Lauraceae species, particularly Machilus thunbergii in Taiwan. Based on analysis on sequences of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I, it has been suggested that in this genus, the stem-galling habit is a more ancestral state as opposed to the leaf-galling habit. This genus appears to have originated tropically and dispersed to Japan through Taiwan.
Daphnephila ornithocephala is a species of gall midge first associated with leaf galls on Lauraceae species, particularly Machilus thunbergii in Taiwan. Based on analysis on sequences of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I, it has been suggested that in this genus, the stem-galling habit is a more ancestral state as opposed to the leaf-galling habit. This genus appears to have originated tropically and dispersed to Japan through Taiwan.

Viridiflorol is a chemical compound, classified as a sesquiterpenoid, that has been isolated from the essential oils of a variety of plants including Melaleuca quinquenervia, Melaleuca alternifolia, and Allophylus edulis.
















