
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among other animals.
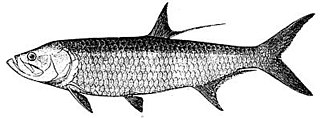
The Elopiformes are the order of ray-finned fish including the tarpons, tenpounders, and ladyfish, as well as a number of extinct types. They have a long fossil record, easily distinguished from other fishes by the presence of an additional set of bones in the throat.
Squalus is a genus of dogfish sharks in the family Squalidae. Commonly known as spurdogs, these sharks are characterized by smooth dorsal fin spines, teeth in upper and lower jaws similar in size, caudal peduncle with lateral keels; upper precaudal pit usually present, and caudal fin without subterminal notch. In spurdogs, the hyomandibula is oriented at a right angle to the neurocranium, while in other sharks, the hyomandibula runs more parallel to the body. This led some to think that the upper jaw of Squalus would not be as protractile as the jaws of other sharks. However, a study that compared different jaw suspension types in sharks showed that this is not the case and that Squalus is quite capable of protruding its upper jaw during feeding.
Murid gammaherpesvirus 4 (MuHV-4) is a species of virus in the genus Rhadinovirus. It is a member of the subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae in the family Herpesviridae. This species infects mice via the nasal passages and causes an acute infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome with elevated levels of leukocytes, and shifts in the relative proportion of lymphocytes along with the appearance of atypical mononuclear cells. Murid gammaherpesvirus 4 currently serves as a model for study of human gammaherpesvirus pathogenesis.

Echinamoebidae is a family of Amoebozoa, containing the genera Echinamoeba and Filamoeba. It was established by Frederick Page in 1975.
Gamasellus is a genus of mites in the family Ologamasidae.
Rhodacarus is a genus of mites in the family Rhodacaridae.
Veigaia is a genus of mites in the family Veigaiidae.

Macrochelidae is a family of mites in the order Mesostigmata, containing the following genera and species:
Parholaspididae is a family of mites in the order Mesostigmata.
Gamasholaspis is a genus of mites in the family Parholaspididae. There are about 15 described species in Gamasholaspis.
Holaspulus is a genus of mites in the family Parholaspididae. There are about 16 described species in Holaspulus.

Ameroseius is a genus of mites in the family Ameroseiidae. There are more than 60 described species in Ameroseius.
Arctoseius is a genus of mites in the family Ascidae.
Protogamasellus is a genus of mites in the family Ascidae.
Zerconidae is a family of mites in the order Mesostigmata.
Neparholaspis monticola is a species of mite in the family Parholaspididae.
Neparholaspis serratichela is a species of mite in the family Parholaspididae.

The Blissidae are a family in the Hemiptera, comprising nearly 50 genera and 400 species. The group has often been treated as a subfamily of the Lygaeidae, but was resurrected as a full family by Thomas Henry (1997).

Hallomenus is a genus of polypore fungus beetles in the family Tetratomidae. There are about nine described species in Hallomenus.






