
No. 10 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) maritime patrol squadron based at RAAF Base Edinburgh, South Australia, is part of No. 42 Wing RAAF. The squadron was formed in 1939 and saw active service during the Second World War, conducting anti-submarine operations and patrols from bases in the United Kingdom until it disbanded in late 1945. It was re-formed in Australia in 1949 and since then has contributed to Australia's East Timor intervention, and has been deployed to the Middle East as part of the War on Terrorism and the 2003 Gulf War.

No. 16 Air Observation Post Flight was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) unit that saw action in World War II supporting Australian Army operations. It was formed in October 1944 and disbanded in June 1947. The flight was reestablished in September 1958, and was disbanded again in December 1960, when its responsibilities were transferred to a joint Army-RAAF unit.

No. 42 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) mine laying and maritime patrol squadron of World War II. It was formed in June 1944 and conducted patrol and mine-laying operations over the Netherlands East Indies (NEI) from August 1944 until the war ended a year later, as well as operations in the waters off southern China in early 1945. Following the Japanese surrender, the squadron performed transport and reconnaissance flights until it was disbanded in November 1945.

No. 41 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) transport squadron of World War II. It was formed in August 1942 and operated flying boats in the South West Pacific area. The squadron was disbanded in September 1945.

No. 40 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) transport squadron of World War II. It was formed in March 1944 and operated flying boats between Australia and New Guinea. The squadron was disbanded in June 1946.

No. 87 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) air intelligence squadron. It saw action during World War II as a photo reconnaissance squadron, being raised in September 1944 through the re-designation of No. 1 Photo Reconnaissance Unit, which had been formed in June 1942. Throughout the war, No. 87 Squadron flew a variety of aircraft from bases in Australia, gathering photographic intelligence on Japanese forces and installations throughout the Pacific. At the conclusion of hostilities, the squadron was disbanded but was later re-formed in 1948, carrying out aerial survey operations in Australia until 1953. In 2006, it was re-raised again as a non-flying squadron tasked with air intelligence analysis as part of the Information Warfare Directorate within the RAAF's Air Warfare Centre.

No. 14 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force maritime patrol squadron of World War II. It was formed in 1939 and was based in Western Australia throughout the war. While it conducted many patrols over the waters off Western Australia, it did not see combat. The squadron was disbanded in December 1945.

No. 200 Flight was a Royal Australian Air Force special duties flight of World War II. The flight was formed in February 1945 to support the Allied Intelligence Bureau (AIB) and saw action over Borneo and the Netherlands East Indies (NEI) from March that year until the end of the war in August. No. 200 Flight was disbanded in December 1945.

No. 12 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) general purpose, bomber and transport squadron. The squadron was formed in 1939 and saw combat in the South West Pacific theatre of World War II. From 1941 to 1943, it mainly conducted maritime patrols off northern Australia. The squadron was based at Merauke in western New Guinea from November 1943 to July 1944, when it was withdrawn from operations. After being re-equipped, it operated as a heavy bomber unit from February 1945 until the end of the war. The squadron continued in this role until it was redesignated No. 1 Squadron RAAF in February 1948. The squadron was reformed in 1973 to operate transport helicopters but was again disbanded in 1989.

No. 67 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) maritime patrol squadron of World War II. It was formed in January 1943, conducted patrols off the southern Australian coastline until the end of the war, and was disbanded in November 1945.

No. 1 Long Range Flight was a temporary Royal Australian Air Force unit formed to participate in the 1953 London-to-Christchurch air race. The flight was established in February 1953 and was equipped with three Canberra bombers, specially modified between June and August. Following extensive training, two Canberras departed for the UK in mid-September. The race began on 9 October, and one of the flight's aircraft placed second, with a total flying time of 22 hours and 29 minutes. The other aircraft was forced out of the race when one of its tyres burst while landing at Cocos Island to refuel, but completed its flight to Christchurch after being repaired. After a brief period in New Zealand both aircraft returned to Australia to be modified back to a standard configuration, and the flight was disbanded in November.

No. 102 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) heavy bomber squadron of World War II. The squadron was only active for less than nine months before being disbanded. No. 102 Squadron was formed at Cecil Plains, Queensland on 31 May 1945. The Squadron's B-24 Liberator bombers arrived in July. While the Squadron began training on these aircraft, the war ended before it reached operational status. Following the end of the war the squadron operated in the transport role until December 1945. No. 102 Squadron was disbanded on 19 March 1946.

No. 82 Wing is the strike and reconnaissance wing of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). It is headquartered at RAAF Base Amberley, Queensland. Coming under the control of Air Combat Group, the wing operates F/A-18F Super Hornet multirole fighters and Pilatus PC-9 forward air control aircraft. Its units include Nos. 1 and 6 Squadrons, operating the Super Hornet, and No. 4 Squadron, operating the PC-9.
No. 23 Squadron of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) is a non-flying base operations and training squadron headquartered at RAAF Base Amberley near Brisbane, Queensland. The squadron was formed in 1937 and saw action against the Japanese during World War II as a bomber squadron. Operating from Archerfield during the early stages of the war, the squadron undertook maritime patrols off Australia's east coast before converting to a dive-bomber role and taking part in the New Guinea campaign. Later in the war, the squadron converted to Liberator heavy bombers and flew missions against Japanese targets in the Netherlands East Indies. After the war, No. 23 Squadron was used to reform No. 6 Squadron and was then re-raised as a Citizens Air Force unit based in Brisbane. Until 1960, the squadron flew jet fighter aircraft before converting to a ground support role and now forms part of the RAAF's Combat Support Group.

No. 73 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) maritime patrol squadron of World War II. It was formed in July 1942 and conducted patrols off the east coast of Australia until July 1944. The squadron was disbanded in September 1944.
No. 462 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) squadron which forms part of the Information Warfare Directorate in the RAAF's Air Warfare Centre. The squadron was first formed in 1942 as a heavy bomber unit and saw combat in this role in the Mediterranean area until it was disbanded in March 1944. It was reformed in the United Kingdom in August 1944 to participate in the bombing campaign against Germany, and in December that year converted to a specialist electronic warfare unit. No. 462 Squadron continued in this role until the end of the European war in May 1945 and was disbanded in September that year. The squadron was reformed in its current role during April 2005.

No. 17 Air Observation Post Flight was a Royal Australian Air Force artillery-spotting and liaison unit which saw action as part of the Bougainville campaign and New Britain campaign in World War II. The flight was established in October 1944 and disbanded in December the next year.

No. 482 Squadron was a maintenance unit of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). It was formed in May 1942 as No. 4 Repair and Salvage Unit, renamed No. 4 Repair and Servicing Unit in January 1945 and re-formed as No. 482 (Maintenance) Squadron in May 1946. The squadron then became a component of No. 82 (Bomber) Wing at RAAF Station Amberley, Queensland. Over the years it serviced the wing's Consolidated B-24 Liberators, Avro Lincolns, English Electric Canberras, McDonnell Douglas F-4E Phantoms, and General Dynamics F-111Cs. No. 482 Squadron merged with No. 3 Aircraft Depot to form No. 501 Wing in March 1992. No. 501 Wing continued to provide maintenance and logistics support for the F-111Cs at Amberley until disbanding in 2001.

No. 1 Aircraft Depot (No. 1 AD) was a maintenance unit of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). Formed in July 1921 at RAAF Point Cook, Victoria, it relocated to the nearby RAAF Laverton in March 1926. As well as servicing aircraft and other equipment, in its early years the depot supported survey flights in Australia and the Pacific region. It was also responsible for training maintenance staff.
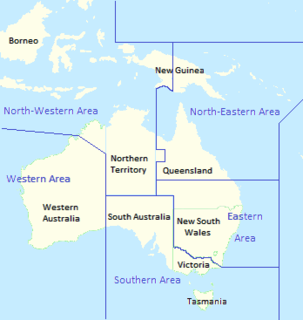
North-Western Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. Its wartime sphere of operations included the Northern Territory, adjacent portions of Queensland and Western Australia, and the Dutch East Indies. The command was formed in January 1942, following the outbreak of the Pacific War, from the western part of Northern Area Command, which had covered all of northern Australia and Papua. Headquartered at Darwin, North-Western Area Command was initially responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries.


















