This is a list of all the groups the Royal Australian Air Force has organised since it was established.

No. 1 Operational Training Unit (No. 1 OTU) was an operational conversion unit of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. Formed in December 1941 at Nhill, Victoria, it relocated to Bairnsdale in mid-1942, and then to East Sale the following year. No. 1 OTU's primary role was to train aircrew for multi-engined aircraft operations. At its peak of activity in August 1944, it was operating over 130 aircraft, the most numerous being Bristol Beauforts. Its aircraft and personnel also conducted transport missions in New Guinea and maritime patrols in southern Australian waters. Following the end of hostilities, the unit was disbanded in December 1945.

No. 75 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) fighter unit based at RAAF Base Tindal in the Northern Territory. The squadron was formed in 1942 and saw extensive action in the South West Pacific theatre of World War II, operating P-40 Kittyhawks. It was disbanded in 1948, but reformed the following year and operated jet aircraft throughout the Cold War. The squadron was based at Malta from 1952 to 1954, flying de Havilland Vampires, and Malaysia from 1968 to 1983, with Dassault Mirage IIIs, before returning to Australia.
The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) traces its history back to the Imperial Conference held in London in 1911, where it was decided aviation should be developed within the Armed Forces of the British Empire. Australia implemented this decision, the only country to do so, by approving the establishment of the Central Flying School (CFS) in 1912. The location for the proposed school was initially to be at Duntroon, Australian Capital Territory, but in July 1913 Point Cook, Victoria, was announced as the preferred location. The first flights by CFS aircraft took place there in March 1914.

No. 31 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) airbase support squadron. It was formed in August 1942 and disbanded in July 1946 after seeing action against the Japanese in the South West Pacific theatre of World War II. During the war, it operated the Bristol Beaufighter, which it operated in long-range fighter and ground-attack missions. The squadron was re-raised for its current role in July 2010.

Air Marshal Sir John Patrick Joseph McCauley, KBE, CB was a senior commander in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). He served as Chief of the Air Staff from 1954 to 1957. A Duntroon graduate, McCauley spent four years in the Australian Military Forces before transferring to the RAAF in 1924. He was Director of Training from 1936 to 1938, and commanded engineering and flying training schools for the first eighteen months of World War II. Having been promoted to group captain in 1940, he was posted to Singapore in June 1941 to take charge of all RAAF units defending the area. He earned praise for his efforts in attacking invading Japanese forces before the fall of Singapore, and for his dedication in evacuating his men. After serving as Deputy Chief of the Air Staff in 1942–44, he was appointed to a senior operational role with the Royal Air Force's 2nd Tactical Air Force in Europe, where he saw out the rest of the war.

Air Vice-Marshal Francis Masson Bladin, was a senior commander in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). Born in rural Victoria, he graduated from the Royal Military College, Duntroon, in 1920. Bladin transferred from the Army to the Air Force in 1923, and learned to fly at RAAF Point Cook, Victoria. He held training appointments before taking command of No. 1 Squadron in 1934. Quiet but authoritative, he was nicknamed "Dad" in tribute to the concern he displayed for the welfare of his personnel.

No. 5 Service Flying Training School was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) flight training unit that operated during World War II. It was one of eight Service Flying Training Schools established by the RAAF to provide intermediate and advanced flying instruction to new pilots as part of Australia's contribution to the Empire Air Training Scheme. No. 5 SFTS was formed at RAAF Station Uranquinty, New South Wales, in October 1941, and disbanded in February 1946. Its staff and equipment were employed to re-establish No. 1 Flying Training School, which transferred to RAAF Station Point Cook, Victoria, the following year. Care and Maintenance Unit Uranquinty was also formed from No. 5 SFTS's facilities, to look after surplus aircraft at the base prior to their disposal, and disbanded in December 1948.

No. 73 Wing was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing of World War II. It was formed in February 1943 at Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea, as part of No. 9 Operational Group. The wing initially comprised three attack squadrons flying CAC Wirraways, Douglas Bostons, and Bristol Beaufighters, with which it took part in the New Guinea campaign until mid-year. It was then reorganised with three fighter squadrons operating P-40 Kittyhawks and Supermarine Spitfires; in this form it saw action in the New Britain and Admiralty Islands campaigns through 1943–44. The wing was disbanded at Los Negros in August 1944, and by the beginning of 1945 its squadrons had been absorbed into other RAAF wings under No. 10 Operational Group.

RAAF Command was the main operational arm of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. The command was formed in September 1942 and by April 1943 comprised 27 squadrons, including units from the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, as well as Australia. Coming under the operational authority of Allied Air Forces Headquarters in the South West Pacific Area, RAAF Command exercised control of its units through geographically based area commands in Australia and, later, New Guinea, as well as large mobile formations including the Australian First Tactical Air Force. The command reached a strength of 41 squadrons in October 1944. From the time of its establishment, until its disbandment in September 1945, it was led by Air Vice Marshal Bill Bostock.

Eastern Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in May 1942, and controlled units located in New South Wales and southern Queensland. Headquartered in Sydney, Eastern Area Command's responsibilities included air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries. Its flying units operated fighters, reconnaissance bombers, and dive bombers, and concentrated on convoy escort, maritime patrol and anti-submarine warfare. The size of the area was such that the RAAF twice considered splitting it, but nothing came of this.

No. 2 Service Flying Training School was a flying training school of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) that operated during World War II. It was formed in July 1940, under the command of Wing Commander Frederick Scherger. Responsible for intermediate and advanced instruction of pilots under the Empire Air Training Scheme (EATS), the school was based at RAAF Station Forest Hill near Wagga Wagga, New South Wales, and operated CAC Wirraway and Avro Anson aircraft. The Ansons were phased out in July 1941, and the school became an all-Wirraway unit. In 1942 the RAAF divided the personnel and equipment of No. 2 SFTS between Nos. 5 and 7 Service Flying Training Schools at Uranquinty and Deniliquin, respectively. No. 2 SFTS was disbanded that April, and the base facilities taken over by No. 5 Aircraft Depot.

No. 1 Aircraft Depot (No. 1 AD) was a maintenance unit of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). Formed in July 1921 at RAAF Point Cook, Victoria, it relocated to the nearby RAAF Laverton in March 1926. As well as servicing aircraft and other equipment, in its early years the depot supported survey flights in Australia and the Pacific region. It was also responsible for training maintenance staff.

Western Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in January 1941, and controlled RAAF units located in Western Australia. Headquartered in Perth, Western Area Command was responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries. Its aircraft conducted anti-submarine operations throughout the war, and attacked targets in the Dutch East Indies during the Borneo campaign in 1945.
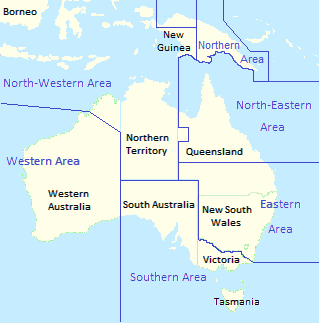
Area commands were the major operational and administrative formations of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) between 1940 and 1954. Established in response to the outbreak of World War II, they underpinned the Air Force's geographically based command-and-control system for the duration of the conflict and into the early years of the Cold War, until being superseded by a functional control system made up of Home, Training, and Maintenance Commands.

Southern Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in March 1940, and initially controlled units located in Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia and southern New South Wales. Headquartered in Melbourne, Southern Area Command was responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries. From 1942 its operational responsibilities excluded New South Wales.

North-Western Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. Its wartime sphere of operations included the Northern Territory, adjacent portions of Queensland and Western Australia, and the Dutch East Indies. The command was formed in January 1942, following the outbreak of the Pacific War, from the western part of Northern Area Command, which had covered all of northern Australia and Papua. Headquartered at Darwin, North-Western Area Command was initially responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries.
No. 5 (Maintenance) Group RAAF was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) group of World War II. It was formed in June 1942 as part of a reorganisation of the air force that saw maintenance functions transferred from area commands to dedicated functional groups. No. 5 (Maintenance) Group was disbanded following the war in January 1946.

No. 4 (Maintenance) Group RAAF was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) group. It was formed in Melbourne in September 1942 as part of a reorganisation of the air force that saw maintenance functions transferred from area commands to dedicated functional groups. In July 1947, No. 4 (Maintenance) Group was renamed Maintenance Group. The area command structure was superseded by a functional command system in October 1953, and Maintenance Group was re-formed as Maintenance Command.
No. 2 (Training) Group RAAF was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) group. It was formed in Sydney in August 1941 as part of a reorganisation of the air force, and was disbanded after the war in March 1946.