
Thermus is a genus of thermophilic bacteria. It is one of several bacteria belonging to the Deinococcota phylum. Thermus species can be distinguished from other genera in the family Thermaceae as well as all other bacteria by the presence of eight conserved signature indels (CSIs) found in proteins such as adenylate kinase and replicative DNA helicase as well as 14 conserved signature proteins (CSPs) that are exclusively shared by members of this genus.

Pseudomonas putida is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, saprophytic soil bacterium. It has a versatile metabolism and is amenable to genetic manipulation, making it a common organism used in research, bioremediation, and synthesis of chemicals and other compounds.
Sulfur-reducing bacteria are microorganisms able to reduce elemental sulfur (S0) to hydrogen sulfide (H2S). These microbes use inorganic sulfur compounds as electron acceptors to sustain several activities such as respiration, conserving energy and growth, in absence of oxygen. The final product of these processes, sulfide, has a considerable influence on the chemistry of the environment and, in addition, is used as electron donor for a large variety of microbial metabolisms. Several types of bacteria and many non-methanogenic archaea can reduce sulfur. Microbial sulfur reduction was already shown in early studies, which highlighted the first proof of S0 reduction in a vibrioid bacterium from mud, with sulfur as electron acceptor and H
2 as electron donor. The first pure cultured species of sulfur-reducing bacteria, Desulfuromonas acetoxidans, was discovered in 1976 and described by Pfennig Norbert and Biebel Hanno as an anaerobic sulfur-reducing and acetate-oxidizing bacterium, not able to reduce sulfate. Only few taxa are true sulfur-reducing bacteria, using sulfur reduction as the only or main catabolic reaction. Normally, they couple this reaction with the oxidation of acetate, succinate or other organic compounds. In general, sulfate-reducing bacteria are able to use both sulfate and elemental sulfur as electron acceptors. Thanks to its abundancy and thermodynamic stability, sulfate is the most studied electron acceptor for anaerobic respiration that involves sulfur compounds. Elemental sulfur, however, is very abundant and important, especially in deep-sea hydrothermal vents, hot springs and other extreme environments, making its isolation more difficult. Some bacteria – such as Proteus, Campylobacter, Pseudomonas and Salmonella – have the ability to reduce sulfur, but can also use oxygen and other terminal electron acceptors.
Mycobacteroides immunogenum is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacteroides.

Ensifer is a genus of nitrogen-fixing bacteria (rhizobia), three of which have been sequenced.
Nitrospirota is a phylum of bacteria. It includes multiple genera, such as Nitrospira, the largest. The first member of this phylum, Nitrospira marina, was discovered in 1985. The second member, Nitrospira moscoviensis, was discovered in 1995.
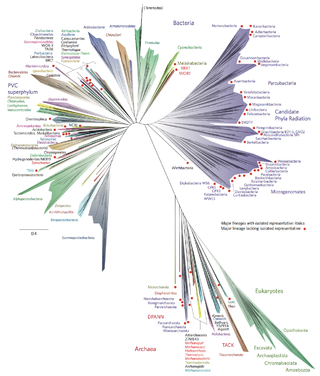
Bacterial phyla constitute the major lineages of the domain Bacteria. While the exact definition of a bacterial phylum is debated, a popular definition is that a bacterial phylum is a monophyletic lineage of bacteria whose 16S rRNA genes share a pairwise sequence identity of ~75% or less with those of the members of other bacterial phyla.
Algoriphagus is a genus in the phylum Bacteroidota (Bacteria).
Desulfosporosinus is a genus of strictly anaerobic, sulfate-reducing bacteria, often found in soil.
Desulfitobacterium hafniense is a species of gram positive bacteria, its type strain is DCB-2T..
Mannheimia varigena is a bacterial species, predominantly encountered in ruminants and historically classified within the former bacterial Pasteurella haemolytica complex, a group of bacteria involved in bovine respiratory disease (BRD). It is pathogenic.
Nocardiopsis kunsanensis is a species of moderately halophilic actinomycete bacteria. Its type strain is HA-9T.
Thermotoga naphthophila is a hyperthermophilic, anaerobic, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped fermentative heterotroph, with type strain RKU-10T.
Thiomicrospira aerophila is an obligately alkaliphilic and obligately chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing bacterium that was previously the type species of Thioalkalimicrobium prior to reclassification in 2017. It was first isolated from soda lakes in northern Russia.
Nocardiopsis umidischolae is a species of bacteria. It produces methanol-soluble toxins that paralyse the motility of boar spermatozoa. Its type strain is 66/93T.
Meiothermus timidus is a species of yellow-pigmented Deinococcota bacteria. It was first isolated from the hot spring at São Pedro do Sul, in central Portugal, and at the island of Sao Miguel in the Azores. Its type strain is SPS-243T. The species was differentiated with the 16S rRNA gene sequence and biochemical characteristics.
Nocardiopsis sinuspersici is a species of bacteria that is an aerobic, Gram positive, alkalohalophilic, actinomycete. While species from the genus Nocardiopsis have been found in a variety of environments, primarily soils, strain N. sinuspersici sp. nov was isolated from sandy rhizospheric soils from Sarbandar and Khoramshahr in Iran.
The Coriobacteriia are a class of Gram-positive bacteria within the Actinomycetota phylum. Species within this group are nonsporulating, strict or facultative anaerobes that are capable of thriving in a diverse set of ecological niches. Gordonibacter species are the only members capable of motility by means of flagella within the class. Several species within the Coriobacteriia class have been implicated with human diseases that range in severity. Atopobium, Olsenella, and Cryptobacterium species have responsible for human oral infections including periodontitis, halitosis, and other endodontic infections. Eggerthella species have been associated with severe blood bacteraemia and ulcerative colitis.
Dokdonia is a genus of bacteria in the family Flavobacteriaceae and phylum Bacteroidota.
Acanthopleuribacter pedis is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found in marine environments.



