Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 3(Notch 3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NOTCH3 gene. [5] [6]
Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 3(Notch 3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NOTCH3 gene. [5] [6]
This gene encodes the third discovered human homologue of the Drosophila melanogaster type I membrane protein notch. In Drosophila, notch interaction with its cell-bound ligands (delta, serrate) establishes an intercellular signalling pathway that plays a key role in neural development. Homologues of the notch-ligands have also been identified in human, but precise interactions between these ligands and the human notch homologues remains to be determined.

Mutations in NOTCH3 have been identified as the underlying cause of cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL). [6] Mutations in NOTCH3 have also been identified in families with Alzheimer's disease. [7] Adult Notch3 knock-out mice show incomplete neuronal maturation in the spinal cord dorsal horn, resulting in permanently increased nociceptive sensitivity. [8] Mutations in NOTCH3 are associated to lateral meningocele syndrome. [9]
Notch3 is being investigated as a target for anti-cancer drugs, as it is overexpressed in several types of cancers. [10] Early clinical trials of Pfizer's PF-06650808, an anti-Notch3 antibody linked to a cytotoxic drug, showed efficacy against solid tumors. [11]

Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. The most common presentation of cerebrovascular disease is an ischemic stroke or mini-stroke and sometimes a hemorrhagic stroke. Hypertension is the most important contributing risk factor for stroke and cerebrovascular diseases as it can change the structure of blood vessels and result in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis narrows blood vessels in the brain, resulting in decreased cerebral perfusion. Other risk factors that contribute to stroke include smoking and diabetes. Narrowed cerebral arteries can lead to ischemic stroke, but continually elevated blood pressure can also cause tearing of vessels, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke.
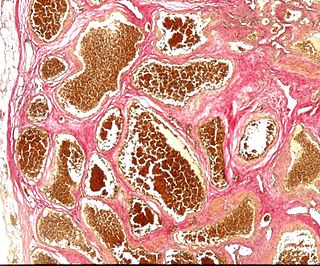
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) is a cavernous hemangioma that arises in the central nervous system (CNS). It can be considered to be a variant of hemangioma, and is characterized by grossly large dilated blood vessels and large vascular channels, less well circumscribed, and more involved with deep structures, with a single layer of endothelium and an absence of neuronal tissue within the lesions. These thinly walled vessels resemble sinusoidal cavities filled with stagnant blood. Blood vessels in patients with cerebral cavernous malformations (CCM) can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Most lesions occur in the brain, but any organ may be involved.

CADASIL or CADASIL syndrome, involving cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, is the most common form of hereditary stroke disorder, and is thought to be caused by mutations of the Notch 3 gene on chromosome 19. The disease belongs to a family of disorders called the leukodystrophies. The most common clinical manifestations are migraine headaches and transient ischemic attacks or strokes, which usually occur between 40 and 50 years of age, although MRI is able to detect signs of the disease years prior to clinical manifestation of disease.

A perivascular space, also known as a Virchow–Robin space, is a fluid-filled space surrounding certain blood vessels in several organs, including the brain, potentially having an immunological function, but more broadly a dispersive role for neural and blood-derived messengers. The brain pia mater is reflected from the surface of the brain onto the surface of blood vessels in the subarachnoid space. In the brain, perivascular cuffs are regions of leukocyte aggregation in the perivascular spaces, usually found in patients with viral encephalitis.
Familial hemiplegic migraine (FHM) is an autosomal dominant type of hemiplegic migraine that typically includes weakness of half the body which can last for hours, days, or weeks. It can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as ataxia, coma, and paralysis. Migraine attacks may be provoked by minor head trauma. Some cases of minor head trauma in patients with hemiplegic migraine can develop into delayed cerebral edema, a life-threatening medical emergency. Clinical overlap occurs in some FHM patients with episodic ataxia type 2 and spinocerebellar ataxia type 6, benign familial infantile epilepsy, and alternating hemiplegia of childhood.

Sporadic hemiplegic migraine (SHM) is a form of hemiplegic migraine headache isolated cases of which are observed. It is a rare disease. It is considered to be a separate type of migraine.
Episodic ataxia (EA) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by sporadic bouts of ataxia with or without myokymia. There are seven types recognized but the majority are due to two recognized entities. Ataxia can be provoked by psychological stress or startle, or heavy exertion, including exercise. Symptoms can first appear in infancy. There are at least six loci for EA, of which 4 are known genes. Some patients with EA also have migraine or progressive cerebellar degenerative disorders, symptomatic of either familial hemiplegic migraine or spinocerebellar ataxia. Some patients respond to acetazolamide though others do not.

The acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the branched-chain amino acids.

Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter is an autosomal recessive neurological disease. The cause of the disease are mutations in any of the 5 genes encoding subunits of the translation initiation factor eIF2B: EIF2B1, EIF2B2, EIF2B3, EIF2B4, or EIF2B5. The disease belongs to a family of conditions called the Leukodystrophies.

The liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) also known as NR5A2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR5A2 gene. LRH-1 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors.

Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1(Notch 1) is a protein encoded in humans by the NOTCH1 gene. Notch 1 is a single-pass transmembrane receptor.

The thrombopoietin receptor also known as the myeloproliferative leukemia protein or CD110 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MPL oncogene.

Membrane protein MLC1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MLC1 gene.

Achaete-scute homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASCL1 gene. Because it was discovered subsequent to studies on its homolog in Drosophila, the Achaete-scute complex, it was originally named MASH-1 for mammalian achaete scute homolog-1.

Delta-like 3 (Drosophila), also known as DLL3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the DLL3 gene. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene.
Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts is a form of hereditary CNS demyelinating disease. It belongs to a group of disorders called leukodystrophies. It is characterized by early-onset enlargement of the head (macrocephaly) as well as delayed-onset neurological deterioration to include spasticity, epilepsy, and lack of muscular coordination. MLC does not appear to be a disease that is fatal at birth or early in life despite its symptoms, although the number of patients throughout history known to have the disease is fairly limited.

Cerebral autosomal recessive arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CARASIL) is disease of the arteries in the brain, which causes tissue loss in the subcortical region of the brain and the destruction of myelin in the CNS. CARASIL is characterized by symptoms such as gait disturbances, hair loss, low back pain, dementia, and stroke. CARASIL is a rare disease, having only been diagnosed in about 50 patients, of which ten have been genetically confirmed. Most cases have been reported in Japan, but Chinese and caucasian individuals have also been diagnosed with the disease. CARASIL is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. There is currently no cure for CARASIL. Other names for CARASIL include familial young-adult-onset arteriosclerotic leukoencephalopathy with alopecia and lumbago without arterial hypertension, Nemoto disease and Maeda syndrome.
Marie-Germaine Bousser is a French neuroscientist. She won the Brain Prize in 2019 for her work on CADASIL.
Élisabeth Tournier-Lasserve is a French neurologist, medical geneticist, university professor and hospital practitioner in genetics. Together with three colleagues, she was the co-recipient of the Brain Prize in 2019, the world's largest brain research prize.
Anne Joutel is a French neurologist and neuroscientist who is Research Director at the Institute of Psychiatry and Neurosciences of Paris. In 2019, together with three colleagues, she was awarded the Brain Prize, the largest prize awarded for brain research.