
Psychodidae, also called drain flies, sink flies, filter flies, sewer flies, or sewer gnats, is a family of true flies. Some genera have short, hairy bodies and wings, giving them a "furry" moth-like appearance, hence one of their common names, moth flies. Members of the sub-family Phlebotominae, which are hematophagous, may be called sand flies in some countries, although this term is also used for other unrelated flies.

The Phlebotominae are a subfamily of the family Psychodidae. In several countries, their common name is sandfly, but that name is also applied to other flies. The Phlebotominae include many genera of blood-feeding (hematophagous) flies, including the primary vectors of leishmaniasis, bartonellosis and pappataci fever. In the New World, leishmaniasis is spread by sand flies in the genus Lutzomyia, which commonly live in caves, where their main hosts are bats. In the Old World, sand flies in the genus Phlebotomus spread leishmaniasis.

Chrysopilus is common, worldwide genus of predatory snipe flies. There are approximately 300 species in the genus, including fossil members that are sometimes found in amber.

The Lauxaniidae are a family of acalyptrate flies. They generally are small flies with large compound eyes that often are brightly coloured in life, sometimes with characteristic horizontal stripes, such as in Cestrotus species. Many species have variegated patterns on their wings, but in contrast they generally do not have variegated bodies, except for genera such as Cestrotus, whose camouflage mimics lichens or the texture of granitic rocks.

Superfamily Tabanoidea are insects in the order Diptera.

Athericidae is a small family of flies known as water snipe flies or ibis flies. They used to be placed in the family Rhagionidae, but were removed by Stuckenberg in 1973. They are now known to be more closely related to Tabanidae. Species of Athericidae are found worldwide.

The Psychodinae are the nominate subfamily of moth flies (Psychodidae), also known as drain flies. Like most of their relatives, they are usually found in damp habitats; some occur in caves. The small larvae are aquatic or semi-terrestrial; the adults are winged and capable of flight. Psychodinae are found worldwide, including some subantarctic islands.

Tabaninae is a subfamily in the family Tabanidae commonly known as horse flies. There are more than 3000 described species in Tabaninae.
Boreofairchildia nearctica, the sugarfoot moth-fly, is a species of nematoceran flies in the family Psychodidae. It is endemic to the United States.
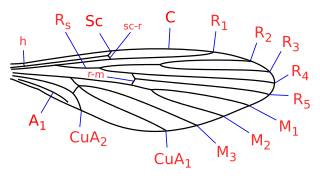
Nemopalpus is a genus of moth fly in the family Psychodidae, in the subfamily Bruchomyiinae. Nemopalpus is sometimes spelled "Nemapalpus" and recently (2018) a number of similar species have been transferred to the genera: Alexanderia, Boreofairchildia, Laurenceomyia and Notofairchildia.
Sycorax is a genus of moth flies and sand flies in the family Psychodidae. There are at least 40 described species in Sycorax.
Feuerborniella is a genus of flies belonging to the family Psychodidae.

Philosepedon is a genus of flies belonging to the family Psychodidae.
Boreofairchildia is a genus of moth flies in the subfamily Bruchomyiinae. Species have been recorded from the Americas, principally Central and South America, with many, including the type, transferred from the genus Nemopalpus.

The subfamily Bruchomyiinae contains genera of moth flies in the order Diptera, was originally described by the American entomologist Charles Paul Alexander.
Laurenceomyia is a genus of moth flies in the subfamily Bruchomyiinae. Species have been recorded principally from south America, with many, including the type, transferred from the genus Nemopalpus.
Alexanderia is a genus of moth flies in the subfamily Bruchomyiinae. This genus circumscribes species from south-east Asia, with three including the type, transferred from the genus Nemopalpus.
Bruchomyia is a genus of moth flies in the subfamily Bruchomyiinae. Species have been recorded principally from South America.
Didicrum is a genus of the family Psychodidae and has a handful of species studied so far. The discovery of this genus in Colombia represents a significant range extension for Didicrum as all previously described species of this genus are distributed in the Australasian region and the southernmost portion of South America.

Elaphropeza is a genus of flies in the family Hybotidae, first described by Pierre-Justin-Marie Macquart in 1827.












