
Lanternfishes are small mesopelagic fish of the large family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, the Myctophidae are represented by 246 species in 33 genera, and are found in oceans worldwide. Lanternfishes are aptly named after their conspicuous use of bioluminescence. Their sister family, the Neoscopelidae, are much fewer in number but superficially very similar; at least one neoscopelid shares the common name 'lanternfish': the large-scaled lantern fish, Neoscopelus macrolepidotus.

Ridgeheads, also known as bigscales, are a family of small, deep-sea stephanoberyciform fish. The family contains approximately 37 species in five genera; their distribution is worldwide, but ridgeheads are absent from the Arctic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Although the family is one of the most widespread and plentiful of deep-sea families, none of its members are of interest to commercial fishery.
The scaly dragonfish or boa dragonfish, is a medium-sized abyssal barbeled dragonfish of the family Stomiidae. It is found at great depths worldwide in tropical to temperate oceans but is absent from the northern Pacific and northwest Atlantic Oceans.

Warming's lantern fish, Ceratoscopelus warmingii, is a lanternfish of the family Myctophidae, found circumglobally in both hemispheres, at depths of between 700 and 1,500 m during the day and between 20 and 200 m at night. Its length is about 8 cm (3.15 in).

Mycteroperca is a genus of marine ray-finned fish, groupers from the subfamily Epinephelinae, part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. They are predatory fish, largely associated with reefs and are found in tropical and subtropical seas in the Atlantic Ocean and the eastern Pacific Ocean. They are important target species for fisheries.

The black scorpionfish is a venomous scorpionfish, common in marine subtropical waters. It is widespread in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean from the British Isles to the Azores and Canary Islands, near the coasts of Morocco, in the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.

The red gurnard, also known as the East Atlantic red gurnard, is a fish species of Triglidae family. Widespread in the Eastern Atlantic from British Isles to Mauritania. Also known throughout the Mediterranean and possibly in the Black Sea.
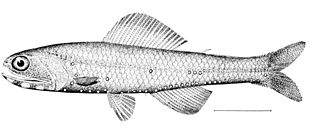
Notoscopelus is a genus of lanternfishes.

Chaetodon hoefleri, the four-banded butterflyfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a butterflyfish from the family Chaetodontidae. It is native to the tropical eastern Atlantic and has been recorded in the Mediterranean.

Astronesthes niger, commonly known as snaggletooth, is a species of small, deep sea fish in the family Stomiidae. It occurs in the tropical and subtropical Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, as well as the Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean, at depths to 1,000 m (3,300 ft).

Notoscopelus elongatus is a species of lanternfish in the family Myctophidae. It is endemic to the Mediterranean Sea where it is found in deep water habitats, rising to near the surface to feed at night and descending to great depths by day. It is a common species with no particular threats, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has listed its conservation status as being of least concern.
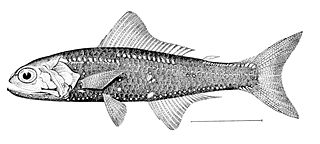
Notoscopelus resplendens, commonly known as the patchwork lampfish or patchwork lanternfish, is a species of lanternfish in the family Myctophidae. It is found in the eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean and parts of the Pacific Ocean. It spends the daylight hours in deep water, rising at night to near the surface. This fish was first described by the Scottish naturalist and arctic explorer John Richardson in 1845.
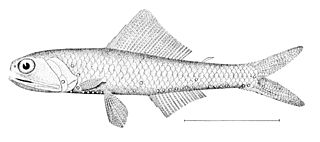
Notoscopelus caudispinosus is a species of lanternfish in the family Myctophidae. It is found in the eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean and parts of the Pacific Ocean. It spends the day below 1,000 m (3,300 ft), rising towards the surface to feed at night.
Notoscopelus bolini is a species of lanternfish in the family Myctophidae. It is found in the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It was first described in 1975 by the American ichthyologist Basil Nafpaktitis and named in honour of the American marine biologist Rolf Ling Bolin who had reviewed the genus in 1959.

Cottunculus microps, the polar sculpin, is a species of fathead sculpin, a deepwater fish found in the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans. It was first described in 1875 by the Norwegian zoologist Robert Collett, curator of the Natural History Museum at the University of Oslo.

The short beard codling is a species of marine bony fish in the family Moridae. Native to the western Atlantic Ocean, it is found on the continental slope at depths between 50 and 1,620 m.

Exocoetus obtusirostris, commonly known as the oceanic two-wing flyingfish or the blunt-snouted flyingfish, is a species of ray-finned fish native to the tropical and subtropical western Atlantic Ocean. It has the ability to glide above the surface of the water to escape from predators.
Barbantus curvifrons, commonly known as the palebelly searsid, is a species of ray-finned fish known from the Indian Ocean, the Pacific Ocean and the eastern Atlantic Ocean where it has been found at depths below 500 metres (1,600 ft). The generic name Barbantus is derived from the Latin, "barba", a beard.

The Spanish flag is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean. It is the only species in the genus Gonioplectrus.

The headlight fish is a species of lanternfish in the family Myctophidae. It is also sometimes referred to as the headlight lanternfish, or even the lanternfish, though it is not the only species to be called this.

















