
The Antarctic toothfish is a species of notothen native to the Southern Ocean. It is often mistakenly referred to as an Antarctic cod, consistent with the misnaming of other notothenioid Antarctic fish as rock cods. However, notothenioid fishes are not closely related to cods, which are in another taxonomic order, the Gadiformes. The generic name Dissostichus is from the Greek dissos (twofold) and stichus (line) and refers to the presence of two long lateral lines, which are very important to the species’ ecology. The common name "toothfish" refers to the presence of biserial dentition in the upper jaw, thought to give it a shark-like appearance. The habitat of the Antarctic toothfish is in subzero degree water below latitude 60°S.

The Patagonian toothfish is a species of notothen found in cold waters between depths of 45 and 3,850 m in the southern Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans and Southern Ocean on seamounts and continental shelves around most Subantarctic islands.

Notothenia angustata, the Maori chief or black cod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Southern Ocean

Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes, is a family of ray-finned fishes, part of the suborder Notothenioidei which is traditionally placed within the order Perciformes. They are largely found in the Southern Ocean.

The Antarctic silverfish, or Antarctic herring, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Southern Ocean and the only truly pelagic fish in the waters near Antarctica. It is a keystone species in the ecosystem of the Southern Ocean.

The marbled rockcod is a species of notothen native to the Southern Ocean, where it can be found at depths from 5 to 350 m. This is a commercially important species.

Notothenia is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes with the species in this genus often having the common name of rockcod. They are native to the Southern Ocean and other waters around Antarctica.

Dissostichus, the toothfishes, is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. These fishes are found in the Southern Hemisphere. Toothfish are marketed in the United States as Chilean sea bass or less frequently as white cod. "Chilean sea bass" is a marketing name coined in 1977 by Lee Lantz, a fish wholesaler who wanted a more attractive name for selling the Patagonian toothfish to Americans. In 1994, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accepted "Chilean sea bass" as an "alternative market name" for Patagonian toothfish. The toothfish was remarkably successful in the United States, Europe and Asia, and earned the nickname “white gold” within the market. Toothfishes are vital to the ecological structure of Southern Ocean ecosystems. For this reason, on 4 September a national day is dedicated to the toothfish in South Georgia.

Gobionotothen is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. They are native to the Southern Ocean.

Gvozdarus is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Southern Ocean.
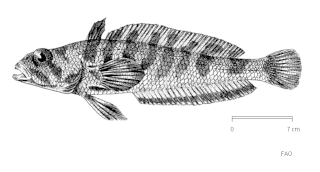
The grey rockcod, also known as the grey notothen, stripe-eyes notothen or stripe-eyed rockcod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Southern Ocean,The grey rockcod feed mainly on macrozooplankton and is of minor importance to commercial fisheries. It is the only species in the genus Lepidonotothen

Lindbergichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes.
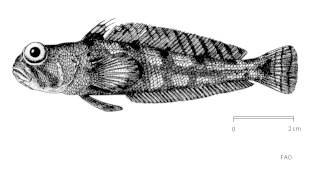
The toad notie, or toad notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Indian sector of the Southern Ocean.

Notothenia coriiceps, also known as the black rockcod, Antarctic yellowbelly rockcod, or Antarctic bullhead notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is widely spread around the Antarctic continent. Like other Antarctic notothenioid fishes, N. coriiceps evolved in the stable, ice-cold environment of the Southern Ocean. It is not currently targeted by commercial fisheries.
Notothenia neglecta, the yellowbelly rockcod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is found in the Southern Ocean in Antarctica. They are omnivorous, and are found in both benthic and pelagic regions of the ocean. Their diet includes krill, bivalves, and gastropods. They have evolved unique behaviors and morphological features in order to thrive in the cold and harsh Antarctic climate. N. neglecta is also commercially fished, although not in high numbers.
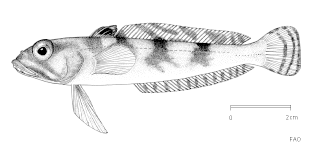
Lindbergichthys nudifrons, the yellowfin rockcod, also known as the yellow notie or the gaudy notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean.

Gvozdarus svetovidovi, the naked-head toothfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is found in the Ross and Cooperation Seas, probably south of the Antarctic Polar Front from pelagic waters down to depths of 550 m, though it is normally found in a pelagic environment.

Gobionotothen gibberifrons, the humped rockcod or the humphead notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the islands of the Scotia Arc, the northern part of the Antarctic Peninsula, and Heard Island in the Southern Ocean. This species inhabits depths of 6-429 m, but is most abundant at depths of 100-400 m, at least around Elephant Island.

Gobionotothen marionensis, the lobe-lip notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in the Atlantic Ocean, and the Crozet and Prince Edward Islands in the Indian Ocean.>
Gobionotothen acuta, the triangular rockcod or the triangular notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the French Southern and Antarctic Lands, the Heard Islands and the Kerguelen Plateau in the Southern Ocean.














