Fossil water, fossil groundwater, or paleowater is an ancient body of water that has been contained in some undisturbed space, typically groundwater in an aquifer, for millennia. Other types of fossil water can include subglacial lakes, such as Antarctica's Lake Vostok. UNESCO defines fossil groundwater as "water that infiltrated usually millennia ago and often under climatic conditions different from the present, and that has been stored underground since that time."

The Arabian-Nubian Shield (ANS) is an exposure of Precambrian crystalline rocks on the flanks of the Red Sea. The crystalline rocks are mostly Neoproterozoic in age. Geographically – and from north to south – the ANS includes parts of Israel, Jordan, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Yemen, and Somalia. The ANS in the north is exposed as part of the Sahara Desert and Arabian Desert, and in the south in the Ethiopian Highlands, Asir province of Arabia and Yemen Highlands.

The Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System (NSAS) is the world's largest known fossil water aquifer system. It is located underground in the Eastern end of the Sahara desert and spans the political boundaries of four countries in north-eastern Africa. NSAS covers a land area spanning just over two million km2, including north-western Sudan, north-eastern Chad, south-eastern Libya, and most of Egypt. Containing an estimated 150,000 km3 of groundwater, the significance of the NSAS as a potential water resource for future development programs in these countries is large. The Great Man-Made River (GMMR) project in Libya makes use of the system, extracting substantial amounts of water from this aquifer, removing an estimated 2.4 km3 of fresh water for consumption and agriculture per year.
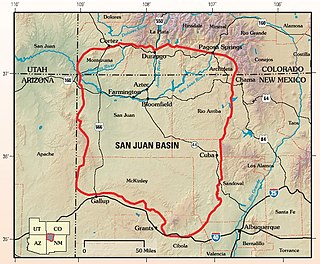
The San Juan Basin is a geologic structural basin located near the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. The basin covers 7,500 square miles and resides in northwestern New Mexico, southwestern Colorado, and parts of Utah and Arizona. Specifically, the basin occupies space in the San Juan, Rio Arriba, Sandoval, and McKinley counties in New Mexico, and La Plata and Archuleta counties in Colorado. The basin extends roughly 100 miles (160 km) N-S and 90 miles (140 km) E-W.

The Gulf of Suez Rift is a continental rift zone that was active between the Late Oligocene and the end of the Miocene. It represented a continuation of the Red Sea Rift until break-up occurred in the middle Miocene, with most of the displacement on the newly developed Red Sea spreading centre being accommodated by the Dead Sea Transform. During its brief post-rift history, the deepest part of the remnant rift topography has been filled by the sea, creating the Gulf of Suez.

The main points that are discussed in the geology of Iran include the study of the geological and structural units or zones; stratigraphy; magmatism and igneous rocks; ophiolite series and ultramafic rocks; and orogenic events in Iran.
The Moghra Oasis is an uninhabited oasis in the northeastern part of the Qattara Depression in the Western Desert of Egypt. It has a 4 km2 (1.5 sq mi) lake containing brackish water, salt marshes and a swamp with reeds.
One of the major depositional strata in the Himalaya is the Lesser Himalayan Strata from the Paleozoic to Mesozoic eras. It had a quite different marine succession during the Paleozoic, as most parts of it are sparsely fossiliferous or even devoid of any well-defined fossils. Moreover, it consists of many varied lithofacies, making correlation work more difficult. This article describes the major formations of the Paleozoic – Mesozoic Lesser Himalayan Strata, including the Tal Formation, Gondwana Strata, Singtali Formation and Subathu Formation.
The geology of Western Sahara includes rock units dating back to the Archean more than two billion years old, although deposits of phosphorus formed in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic have helped to prompt the current Moroccan occupation of most of the country.
The geology of Somalia is built on more than 700 million year old igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rock, which outcrops at some places in northern Somalia. These ancient units are covered in thick layers of sedimentary rock formed in the last 200 million years and influenced by the rifting apart of the Somali Plate and the Arabian Plate. The geology of Somaliland, the de facto independent country recognized as part of Somalia, is to some degree better studied than that of Somalia as a whole. Instability related to the Somali Civil War and previous political upheaval has limited geologic research in places while heightening the importance of groundwater resources for vulnerable populations.

The geology of Tanzania began to form in the Precambrian, in the Archean and Proterozoic eons, in some cases more than 2.5 billion years ago. Igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rock forms the Archean Tanzania Craton, which is surrounded by the Proterozoic Ubendian belt, Mozambique Belt and Karagwe-Ankole Belt. The region experienced downwarping of the crust during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic, as the massive Karoo Supergroup deposited. Within the past 100 million years, Tanzania has experienced marine sedimentary rock deposition along the coast and rift formation inland, which has produced large rift lakes. Tanzania has extensive, but poorly explored and exploited natural resources, including coal, gold, diamonds, graphite and clays.

The geological history of Zambia begins in the Proterozoic eon of the Precambrian. The igneous and metamorphic basement rocks tend to be highly metamorphosed and may have formed earlier in the Archean, but heat and pressure has destroyed evidence of earlier conditions. Major sedimentary and metamorphic groups formed in the mid-Proterozoic, followed by a series of glaciations in the Neoproterozoic and much of the Paleozoic which deposited glacial conglomerate as well as other sediments to form the Katanga Supergroup and rift-related Karoo Supergroup. Basalt eruptions blanketed the Karoo Supergroup in the Mesozoic and Zambia shifted to coal and sandstone formation. Geologically recent windblown sands from the Kalahari Desert and alluvial deposits near rivers play an important role in the modern surficial geology of Zambia. The country has extensive natural resources, particularly copper, but also cobalt, emeralds, other gemstones, uranium and coal.

The geology of Morocco formed beginning up to two billion years ago, in the Paleoproterozoic and potentially even earlier. It was affected by the Pan-African orogeny, although the later Hercynian orogeny produced fewer changes and left the Maseta Domain, a large area of remnant Paleozoic massifs. During the Paleozoic, extensive sedimentary deposits preserved marine fossils. Throughout the Mesozoic, the rifting apart of Pangaea to form the Atlantic Ocean created basins and fault blocks, which were blanketed in terrestrial and marine sediments—particularly as a major marine transgression flooded much of the region. In the Cenozoic, a microcontinent covered in sedimentary rocks from the Triassic and Cretaceous collided with northern Morocco, forming the Rif region. Morocco has extensive phosphate and salt reserves, as well as resources such as lead, zinc, copper and silver.
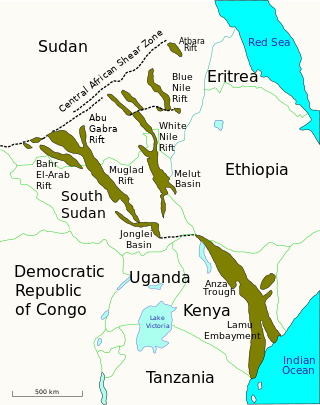
The geology of Sudan formed primarily in the Precambrian, as igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rock. Ancient terranes and inliers were intruded with granites, granitoids, and volcanic rocks. Units of all types were deformed, reactivated, intruded, and metamorphosed during the Proterozoic Pan-African orogeny. Dramatic sheet flow erosion prevented almost any sedimentary rocks from forming during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic. From the Mesozoic into the Cenozoic, the formation of the Red Sea depression and complex faulting led to massive sediment deposition in some locations and regional volcanism. Sudan has petroleum, chromite, salt, gold, limestone, and other natural resources.

The geology of South Dakota began to form more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Archean eon of the Precambrian. Igneous crystalline basement rock continued to emplace through the Proterozoic, interspersed with sediments and volcanic materials. Large limestone and shale deposits formed during the Paleozoic, during prevalent shallow marine conditions, followed by red beds during terrestrial conditions in the Triassic. The Western Interior Seaway flooded the region, creating vast shale, chalk and coal beds in the Cretaceous as the Laramide orogeny began to form the Rocky Mountains. The Black Hills were uplifted in the early Cenozoic, followed by long-running periods of erosion, sediment deposition and volcanic ash fall, forming the Badlands and storing marine and mammal fossils. Much of the state's landscape was reworked during several phases of glaciation in the Pleistocene. South Dakota has extensive mineral resources in the Black Hills and some oil and gas extraction in the Williston Basin. The Homestake Mine, active until 2002, was a major gold mine that reached up to 8000 feet underground and is now used for dark matter and neutrino research.

The geology of Arizona began to form in the Precambrian. Igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rock may have been much older, but was overwritten during the Yavapai and Mazatzal orogenies in the Proterozoic. The Grenville orogeny to the east caused Arizona to fill with sediments, shedding into a shallow sea. Limestone formed in the sea was metamorphosed by mafic intrusions. The Great Unconformity is a famous gap in the stratigraphic record, as Arizona experienced 900 million years of terrestrial conditions, except in isolated basins. The region oscillated between terrestrial and shallow ocean conditions during the Paleozoic as multi-cellular life became common and three major orogenies to the east shed sediments before North America became part of the supercontinent Pangaea. The breakup of Pangaea was accompanied by the subduction of the Farallon Plate, which drove volcanism during the Nevadan orogeny and the Sevier orogeny in the Mesozoic, which covered much of Arizona in volcanic debris and sediments. The Mid-Tertiary ignimbrite flare-up created smaller mountain ranges with extensive ash and lava in the Cenozoic, followed by the sinking of the Farallon slab in the mantle throughout the past 14 million years, which has created the Basin and Range Province. Arizona has extensive mineralization in veins, due to hydrothermal fluids and is notable for copper-gold porphyry, lead, zinc, rare minerals formed from copper enrichment and evaporites among other resources.

The geology of North Dakota includes thick sequences oil and coal bearing sedimentary rocks formed in shallow seas in the Paleozoic and Mesozoic, as well as terrestrial deposits from the Cenozoic on top of ancient Precambrian crystalline basement rocks. The state has extensive oil and gas, sand and gravel, coal, groundwater and other natural resources.

The geology of Uzbekistan consists of two microcontinents and the remnants of oceanic crust, which fused together into a tectonically complex but resource rich land mass during the Paleozoic, before becoming draped in thick, primarily marine sedimentary units.
The geology of Turkmenistan includes two different geological provinces: the Karakum, or South Turan Platform, and the Alpine Orogen.
The geology of Saudi Arabia includes Precambrian igneous and metamorphic basement rocks, exposed across much of the country. Thick sedimentary sequences from the Phanerozoic dominate much of the country's surface and host oil.














