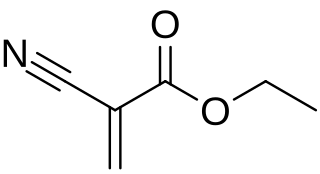
Cyanoacrylates are a family of strong fast-acting adhesives with industrial, medical, and household uses. They are derived from ethyl cyanoacrylate and related esters. The cyanoacrylate group in the monomer rapidly polymerizes in the presence of water to form long, strong chains. They have some minor toxicity.

Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants. The word "surfactant" is a blend of surface-active agent, coined c. 1950.
Ethoxylation is a chemical reaction in which ethylene oxide adds to a substrate. It is the most widely practiced alkoxylation, which involves the addition of epoxides to substrates.
Fatty alcohols (or long-chain alcohols) are usually high-molecular-weight, straight-chain primary alcohols, but can also range from as few as 4–6 carbons to as many as 22–26, derived from natural fats and oils. The precise chain length varies with the source. Some commercially important fatty alcohols are lauryl, stearyl, and oleyl alcohols. They are colourless oily liquids (for smaller carbon numbers) or waxy solids, although impure samples may appear yellow. Fatty alcohols usually have an even number of carbon atoms and a single alcohol group (–OH) attached to the terminal carbon. Some are unsaturated and some are branched. They are widely used in industry. As with fatty acids, they are often referred to generically by the number of carbon atoms in the molecule, such as "a C12 alcohol", that is an alcohol having 12 carbons, for example dodecanol.
Dodecanol, or lauryl alcohol, is an organic compound produced industrially from palm kernel oil or coconut oil. It is a fatty alcohol. Sulfate esters of lauryl alcohol, especially sodium lauryl sulfate, are very widely used as surfactants. Sodium lauryl sulfate, ammonium lauryl sulfate, and sodium laureth sulfate are all used in shampoos. Lauryl alcohol is tasteless and colorless with a floral odor.

Octyl methoxycinnamate or ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate (INCI) or octinoxate (USAN), trade names Eusolex 2292 and Uvinul MC80, is an organic compound that is an ingredient in some sunscreens and lip balms. It is an ester formed from methoxycinnamic acid and 2-ethylhexanol. It is a liquid that is insoluble in water.
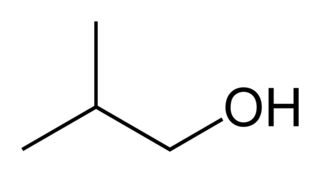
Isobutanol (IUPAC nomenclature: 2-methylpropan-1-ol) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCH2OH (sometimes represented as i-BuOH). This colorless, flammable liquid with a characteristic smell is mainly used as a solvent either directly or as its esters. Its isomers are 1-butanol, 2-butanol, and tert-butanol, all of which are important industrially.
1-Tetradecanol, or commonly myristyl alcohol (from Myristica fragrans – the nutmeg plant), is a straight-chain saturated fatty alcohol, with the molecular formula CH3(CH2)12CH2OH. It is a white waxy solid that is practically insoluble in water, soluble in diethyl ether, and slightly soluble in ethanol.

Bisabolol, or more formally α-(−)-bisabolol or also known as levomenol, is a natural monocyclic sesquiterpene alcohol. It is a colorless viscous oil that is the primary constituent of the essential oil from German chamomile and Myoporum crassifolium. High concentrations of bisabolol can also be found in certain medicinal cannabis cultivars. It is poorly soluble in water and glycerine, but soluble in ethanol. The enantiomer, α-(+)-bisabolol, is also found naturally but is rare. Synthetic bisabolol is usually a racemic mixture of the two, α-(±)-bisabolol. It is the terpenoid responsible for distinctive aroma of chamomile flowers, and when isolated, its scent has also has been likened to apples, sugar and honey.

Octyl acetate, or octyl ethanoate, is an organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)7O2CCH3. It is classified as an ester that is formed from 1-octanol (octyl alcohol) and acetic acid. It is found in oranges, grapefruits, and other citrus products.

Octyl salicylate, or 2-ethylhexyl salicylate, is an organic compound used as an ingredient in sunscreens and cosmetics to absorb UVB (ultraviolet) rays from the sun. It is an ester formed by the condensation of salicylic acid with 2-ethylhexanol. It is a colorless oily liquid with a slight floral odor.

2-Ethylhexanol (abbreviated 2-EH) is an organic compound with formula C8H18O. It is a branched, eight-carbon chiral alcohol. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents. It is produced on a large scale (>2,000,000,000 kg/y) for use in numerous applications such as solvents, flavors, and fragrances and especially as a precursor for production of other chemicals such as emollients and plasticizers. It is encountered in plants, fruits, and wines. The odor has been reported as "heavy, earthy, and slightly floral" for the R enantiomer and "a light, sweet floral fragrance" for the S enantiomer.
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings (monocyclic and bicyclic). Modified terpenes, such as those containing oxygen functionality or missing a methyl group, are called monoterpenoids. Monoterpenes and monoterpenoids are diverse. They have relevance to the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, agricultural, and food industries.
The Guerbet reaction, named after Marcel Guerbet (1861–1938), is an organic reaction that converts a primary alcohol into its β-alkylated dimer alcohol with loss of one equivalent of water. The process is of interest because it converts simple inexpensive feedstocks into more valuable products. Its main disadvantage is that the reaction produces mixtures.

Isothiazolinone (sometimes isothiazolone) is an organic compound with the formula (CH)2SN(H)CO. A white solid, it is structurally related to isothiazole. Isothiazolone itself is of limited interest, but several of its derivatives are widely used preservatives and antimicrobials.
Heptanal or heptanaldehyde is an alkyl aldehyde. It is a colourless liquid with a strong fruity odor, which is used as precursor to components in perfumes and lubricants.

Hydrogen auto-transfer, also known as borrowing hydrogen, is the activation of a chemical reaction by temporary transfer of two hydrogen atoms from the reactant to a catalyst and return of those hydrogen atoms back to a reaction intermediate to form the final product. Two major classes of borrowing hydrogen reactions exist: (a) those that result in hydroxyl substitution, and (b) those that result in carbonyl addition. In the former case, alcohol dehydrogenation generates a transient carbonyl compound that is subject to condensation followed by the return of hydrogen. In the latter case, alcohol dehydrogenation is followed by reductive generation of a nucleophile, which triggers carbonyl addition. As borrowing hydrogen processes avoid manipulations otherwise required for discrete alcohol oxidation and the use of stoichiometric organometallic reagents, they typically display high levels of atom-economy and, hence, are viewed as examples of Green chemistry.

1-Octanol, also known as octan-1-ol, is the organic compound with the molecular formula CH3(CH2)7OH. It is a fatty alcohol. Many other isomers are also known generically as octanols. 1-Octanol is manufactured for the synthesis of esters for use in perfumes and flavorings. It has a pungent odor. Esters of octanol, such as octyl acetate, occur as components of essential oils. It is used to evaluate the lipophilicity of pharmaceutical products.
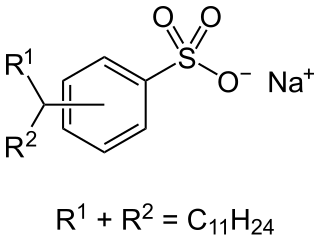
Alkylbenzene sulfonates are a class of anionic surfactants, consisting of a hydrophilic sulfonate head-group and a hydrophobic alkylbenzene tail-group. Along with sodium laureth sulfate, they are one of the oldest and most widely used synthetic detergents and may be found in numerous personal-care products and household-care products . They were first introduced in the 1930s in the form of branched alkylbenzene sulfonates (BAS). However following environmental concerns these were replaced with linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) during the 1960s. Since then production has increased significantly from about one million tons in 1980, to around 3.5 million tons in 2016, making them most produced anionic surfactant after soaps.

1-Pentadecanol is an organic chemical compound classified as an alcohol. At room temperature, it is a white, flaky solid. It is a saturated long-chain fatty alcohol consisting of a pentadecane chain with a hydroxy group as substituent on one end. It is an achiral molecule.












