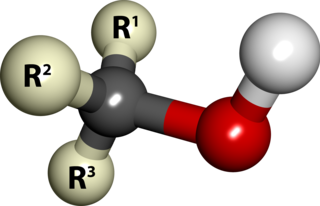
In chemistry, alcohol is an organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl functional group (−OH) bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members, includes all compounds for which the general formula is CnH2n+1OH. Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (RCH2OH), secondary (R2CHOH) and tertiary (R3COH) alcohols.

A carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R–COOH, with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

An ester is a chemical compound derived from an acid in which at least one –OH hydroxyl group is replaced by an –O– alkyl (alkoxy) group, as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils.
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic chemical compound. It is a simple alcohol with the chemical formula C2H6O. Its formula can be also written as CH
3−CH
2−OH or C
2H
5OH (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group), and is often abbreviated as EtOH. Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a slight characteristic odor. It is a psychoactive substance, recreational drug, and the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks.
Chemically, an aldehyde is a compound containing a functional group with the structure −CHO, consisting of a carbonyl center with the carbon atom also bonded to hydrogen and to any generic alkyl or side chain R group,. The functional group itself is known as an aldehyde or formyl group.

The peanut, also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), and taxonomically classified as Arachis hypogaea, is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, being important to both small and large commercial producers. It is classified as both a grain legume and, due to its high oil content, an oil crop. World annual production of shelled peanuts was 44 million tonnes in 2016, led by China with 38% of the world total. Atypically among legume crop plants, peanut pods develop underground (geocarpy) rather than above ground. With this characteristic in mind, the botanist Carl Linnaeus gave peanuts the specific epithet hypogaea, which means "under the earth".
In organic chemistry, transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic group R″ of an ester with the organic group R′ of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of other enzymes, particularly lipases.

Peanut butter is a food paste or spread made from ground, dry-roasted peanuts. It commonly contains additional ingredients that modify the taste or texture, such as salt, sweeteners, or emulsifiers. Peanut butter is consumed in many countries. The United States is a leading exporter of peanut butter and one of the largest consumers of peanut butter annually per capita.

A tincture is typically an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol. Solvent concentrations of 25–60% are common, but may run as high as 90%. In chemistry, a tincture is a solution that has ethanol as its solvent. In herbal medicine, alcoholic tinctures are made with various ethanol concentrations, which should be at least 20% alcohol for preservation purposes.

Fischer esterification or Fischer–Speier esterification is a special type of esterification by refluxing a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. The reaction was first described by Emil Fischer and Arthur Speier in 1895. Most carboxylic acids are suitable for the reaction, but the alcohol should generally be primary or secondary. Tertiary alcohols are prone to elimination. Contrary to common misconception found in organic chemistry textbooks, phenols can also be esterified to give good to near quantitative yield of products. Commonly used catalysts for a Fischer esterification include sulfuric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, and Lewis acids such as scandium(III) triflate. For more valuable or sensitive substrates other, milder procedures such as Steglich esterification are used. The reaction is often carried out without a solvent or in a non-polar solvent to facilitate the Dean-Stark method. Typical reaction times vary from 1–10 hours at temperatures of 60-110 °C.

Arachidic acid, also known as icosanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 20-carbon chain. It is a minor constituent of cupuaçu butter (7%), perilla oil (0–1%), peanut oil (1.1–1.7%), corn oil (3%), and cocoa butter (1%). It also constitutes 7.08% of the fats from the fruit of the durian species Durio graveolens. The salts and esters of arachidic acid are known as arachidates.

Oleic acid is a fatty acid that occurs naturally in various animal and vegetable fats and oils. It is an odorless, colorless oil, although commercial samples may be yellowish. In chemical terms, oleic acid is classified as a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid, abbreviated with a lipid number of 18:1 cis-9. It has the formula CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH. The name derives from the Latin word oleum, which means oil. It is the most common fatty acid in nature. The salts and esters of oleic acid are called oleates.
Linoleic acid is an organic compound with the formula COOH(CH2)7CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)4CH3. Both alkene groups are cis. It is a fatty acid sometimes denoted 18:2 (n-6) or 18:2 cis-9,12. A linoleate is a salt or ester of this acid.

Peanut oil, also known as groundnut oil or arachis oil, is a vegetable oil derived from peanuts. The oil usually has a mild or neutral flavor but, if made with roasted peanuts, has a stronger peanut flavor and aroma. It is often used in American, Chinese, Indian, African and Southeast Asian cuisine, both for general cooking, and in the case of roasted oil, for added flavor.

Behenic acid (also docosanoic acid) is a carboxylic acid, the saturated fatty acid with formula C21H43COOH. In appearance, it consists of white to cream color crystals or powder with a melting point of 80 °C and boiling point of 306 °C.
Lignoceric acid, or tetracosanoic acid, is the saturated fatty acid with formula C23H47COOH. It is found in wood tar, various cerebrosides, and in small amounts in most natural fats. The fatty acids of peanut oil contain small amounts of lignoceric acid (1.1% – 2.2%). This fatty acid is also a byproduct of lignin production.

Vinaigrette is made by mixing an oil with something acidic such as vinegar or lemon juice. The mixture can be enhanced with salt, herbs and/or spices. It is used most commonly as a salad dressing, but can also be used as a marinade. Traditionally, a vinaigrette consists of 2 parts oil and 1 part vinegar mixed into a stable emulsion, but the term is also applied to mixtures with different proportions and to unstable emulsions which last only a short time before separating into layered oil and vinegar phases.

Octyl gallate is the ester of 1-octanol and gallic acid. As a food additive, it is used under the E number E311 as an antioxidant and preservative.
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable chemical compound (chemical formula CH3CHOHCH3) with a strong odor. As an isopropyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, it is the simplest example of a secondary alcohol, where the alcohol carbon atom is attached to two other carbon atoms. It is a structural isomer of 1-propanol and ethyl methyl ether.














