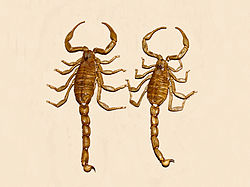
The deathstalker is a species of scorpion, a member of the family Buthidae. It is also known as the Palestine yellow scorpion, Omdurman scorpion, Naqab desert scorpion and by many other colloquial names, which generally originate from the commercial captive trade of the animal. To eliminate confusion, especially important with potentially dangerous species, the scientific name is normally used to refer to them. The name Leiurus quinquestriatus roughly translates into English as "five-striped smooth-tail". In 2014, the subspecies L. q. hebraeus was separated from it and elevated to its own species Leiurus hebraeus. Other species of the genus Leiurus are also often referred to as "deathstalkers".

Marquis Giacomo Doria was an Italian naturalist, botanist, herpetologist, and politician.

Fattail scorpion or fat-tailed scorpion is the common name given to scorpions of the genus Androctonus, one of the most dangerous groups of scorpions species in the world. They are found throughout the semi-arid and arid regions of the Middle East and Africa. They are a moderate sized scorpion, attaining lengths of 10 cm. Their common name is derived from their distinctly fat metasoma, or tail, while the Latin name originates from Greek and means "man killer". Their venom contains powerful neurotoxins and is especially potent. Stings from Androctonus species are known to cause several human deaths each year. Several pharmaceutical companies manufacture an antivenom for treatment of Androctonus envenomations.

The Buthidae are the largest family of scorpions, containing about 80 genera and over 800 species as of mid-2008. Its members are known as, for example, fat-tailed scorpions and bark scorpions. A few very large genera are known, but a high number of species-poor or monotypic ones also exist. New taxa are being described at a rate of several to several dozen new species per year. They occur in the warmer parts of every major landmass on Earth, except on New Zealand. Together with four other families the Buthidae make up the superfamily Buthoidea. The family was established by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1837.

Androctonus maroccanus is a species of scorpion of the family Buthidae. Along with other members of the genus Androctonus it is also known by the collective vernacular name fat-tailed scorpion. A. maroccanus is endemic to the Atlantic coast of central Morocco.
Buthacus is a genus of scorpion of the family Buthidae. It is distributed across northern and western Africa, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Syria, the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan.

Hottentotta is a genus of scorpions of the family Buthidae. It is distributed widely across Africa, except for most of the Sahara desert. Species in the genus also occur in the Middle East, the Arabian Peninsula, southeastern Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Nepal, Cape Verde Islands, and Sri Lanka (introduced).

Leiurus is a genus of scorpion of the family Buthidae. The most common species, L. quinquestriatus, is also known under the common name Deathstalker. It is distributed widely across North Africa and the Middle East, including the western and southern Arabian Peninsula and southeastern Turkey. At least one species occurs in West Africa.

Tityus serrulatus, the Brazilian yellow scorpion, is a species of scorpion of the family Buthidae. It is native to Brazil, and its venom is extremely toxic. It's the most dangerous scorpion in South America and responsible by the most fatal cases.

Mesobuthus eupeus is a polymorphic scorpion species belonging to the well-known family Buthidae. Commonly known as the lesser Asian scorpion or the mottled scorpion. It is thought to be the most widely dispersed species of the genus Mesobuthus, perhaps even of the family Buthidae.

Androctonus bicolor, the black fat-tailed scorpion, is a scorpion species of the family Buthidae. It is black in color and can grow up to 9 cm.

Buthus is a genus of scorpion belonging and being eponymous to the family Buthidae. It is distributed widely across northern Africa, including Morocco, Mauritania, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Senegal, Guinea-Bissau, Nigeria, Sudan, Somalia, Ethiopia, Djibouti, as well as the Middle East, including Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, Iraq, Yemen, and possibly Saudi Arabia and southern Turkey. Its European range includes the Iberian Peninsula, southern France, and Cyprus.

Centruroides gracilis is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae, the bark scorpions. Its common names include Florida bark scorpion, brown bark scorpion, and slender brown scorpion. In Cuba it is known as alacran prieto and alacran azul. Contrary to one of its common names, it is not actually native to Florida in the United States. It is native to northern parts of the middle Americas, including Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, and Honduras. It is present in other parts as an introduced species, including Cuba, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador, Jamaica, and Florida in the United States. It is also introduced in parts of Africa, including Cameroon and Gabon, as well as the Canary Islands.

Odontobuthus is a genus of scorpions of the family Buthidae.

Lauren Esposito is the Assistant Curator and Schlinger Chair of Arachnology at the California Academy of Sciences. She is the co-founder of the network 500 Queer Scientists.

Leiurus hebraeus, the Hebrew deathstalker, is a species of scorpion, a member of the family Buthidae. It is also known as the Israeli yellow scorpion, It was once considered as a subspecies of Leiurus quinquestriatus but recently it was elevated to the rank of a species. It is currently known from Israel, but it may live in other countries in the Middle East. Other species of the genus Leiurus are also often referred to as "deathstalkers".

Leiurus abdullahbayrami is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. Its venom is highly toxic to humans, but can be used in medical development.

Afghanobuthus is a little known monotypic genus of pale yellow psammophilic scorpions. The genus contains a single species, Afghanobuthus naumanni, which is endemic to Afghanistan.

Scorpionism is defined as the accidental envenomation of humans by toxic scorpions. If the injection of venom in a human results in death, this is defined as scorpionism. This is seen all over the world but is predominantly seen in the tropical and subtropical areas. These areas include Mexico, northern South America and southeast Brazil in the Western hemisphere. In the Eastern hemisphere, scorpionism poses a public health threat in regions of South Africa, the Middle East, and the Indian subcontinent.
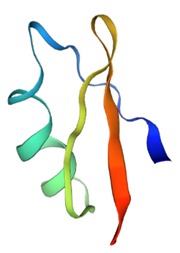
OdK2 is a toxin found in the venom of the Iranian scorpion Odonthobuthus doriae. It belongs to the α-KTx family, and selectively blocks the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 (KCNA3).