
Paraná is one of the 26 states of Brazil, in the south of the country. It is bordered in the north by São Paulo state, in the east by the Atlantic Ocean, in the south by Santa Catarina state and the province of Misiones, Argentina, and in the west by Mato Grosso do Sul and Paraguay, with the Paraná River as its western boundary. It is subdivided into 399 municipalities, and its capital is the city of Curitiba. Other major cities are Londrina, Maringá, Ponta Grossa, Cascavel, São José dos Pinhais and Foz do Iguaçu. The state is home to 5.4% of the Brazilian population and generates 6.2% of the Brazilian GDP.
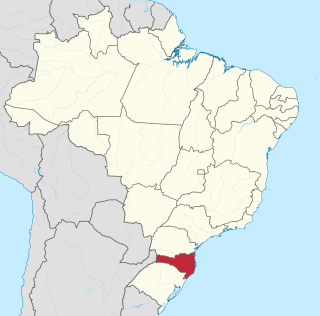
Santa Catarina is a state in the South Region of Brazil. Of Brazil's 26 states, it is the seventh-smallest state in total area and the 11th most populous. Additionally, it is the ninth-largest settlement, with 295 municipalities. The state, with 3.4% of the Brazilian population, generates 3.8% of the national GDP.

Chapecó is a municipality in the state of Santa Catarina, in the Southern Region of Brazil. Being a major industrial, financial and educational center, it is a major producer of industrialized food products. Considered a medium city, with a population estimated at 224,013 inhabitants, it is among the four most important cities in the state. It belongs to the Meso-region of Western Santa Catarina and to the Microregion of Chapecó.

Brazil is geopolitically divided into five regions, by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, which are formed by the federative units of Brazil. Although officially recognized, the division is merely academic, considering geographic, social and economic factors, among others, and has no political effects other than orientating Federal-level government programs. Under the state level, they are further divided into intermediate regions and even further into immediate regions.

The South Region of Brazil is one of the five regions of Brazil. It includes the states of Paraná, Rio Grande do Sul, and Santa Catarina, and covers 576,409.6 square kilometres (222,553.0 sq mi), being the smallest region of the country, occupying only about 6.76% of the territory of Brazil. Its whole area is smaller than that of the state of Minas Gerais, in Southeast Brazil, for example or the whole metropolitan France.
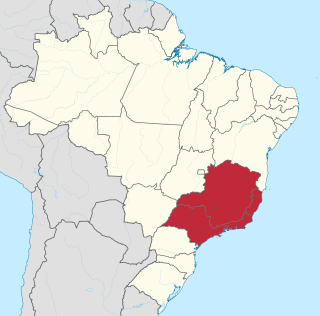
The Southeast Region of Brazil is composed of the states of Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. It is the richest region of the country, responsible for approximately 60% of the Brazilian GDP, as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Minas Gerais are the three richest states of Brazil, the top three Brazilian states in terms of GDP. The Southeast of Brazil also has the highest GDP per capita among all Brazilian regions.

The Brazilian Highway System is a network of trunk roads administered by the Ministry of Transport of Brazil. It is constructed, managed and maintained by the National Department of Transport Infrastructure (DNIT), federal agency linked to the Ministry of Infrastructure, and the public works departments of state governments.

The Trans-Amazonian Highway, was introduced on September 27, 1972. It is 4,000 km long, making it the third longest highway in Brazil. It runs through the Amazon forest and the Brazilian states of Paraíba, Ceará, Piauí, Maranhão, Tocantins, Pará and Amazonas, from the proximities of Saboeiro up until the town of Lábrea.

Itajaí is a municipality in the state of Santa Catarina, Brazil. It is located on the northern central coast of Santa Catarina and is part of the Vale do Itajaí Mesoregion, on the right bank of the Itajaí-Açu river mouth. It lies at the mouth of the Itajaí River, at 20 feet above sea level. The city has the 2nd largest gross domestic product and the highest per capita income in the State of Santa Catarina.
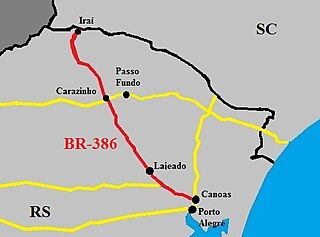
The BR-386 is a Brazilian federal highway running between the southern states of Rio Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina. It has a total length of 525 km (326 mi).

Brazilian industry has its earliest origin in workshops dating from the beginning of the 19th century. Most of the country's industrial establishments appeared in the Brazilian southeast, and, according to the Commerce, Agriculture, Factories and Navigation Joint, 77 establishments registered between 1808 and 1840 were classified as "factories" or "manufacturers". However, most, about 56 establishments, would be considered workshops by today's standards, directed toward the production of soap and tallow candles, snuff, spinning and weaving, foods, melting of iron and metals, wool and silk, amongst others. They used both slaves and free laborers.

Cascalho Rico is a Brazilian municipality located in the west of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 3,092 living in a total area of 368 km2. The city belongs to the statistical mesoregion of Triângulo Mineiro and Alto Paranaíba and to the statistical microregion of Uberlândia. It became a municipality in 1948.

Medeiros is a Brazilian municipality located in the west of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 3,832 people living in a total area of 939 km². The city belongs to the meso-region of Oeste de Minas and to the micro-region of Piumhi. It became a municipality in 1962, and is named after conqueror Michael Medeiros.

Pedra do Indaiá is a Brazilian municipality located in the center of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 3,974 people living in a total area of 349 km². The city belongs to the meso-region of Oeste de Minas and to the micro-region of Formiga. It became a municipality in 1962.

Paraopeba is a Brazilian municipality located in the northeast of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 24,700 people living in a total area of 625 square kilometres (241 sq mi). The city belongs to the meso-region of Metropolitana de Belo Horizonte and to the micro-region of Sete Lagoas. It became a municipality in 1911.

Vargeão is a municipality located in the state of Santa Catarina in the south region of Brazil. It is located in the Immediate Geographic Region of Xanxerê and the Intermediate Geographic Region of Chapecó and at 298 miles away from the capital of Santa Catarina, Florianópolis.

Saudade do Iguaçu is a municipality in the Brazilian state of Paraná. It has an area of 152.085 square kilometres (58.720 sq mi). It has a humid subtropical climate. As of 2020 the estimated population was 5,539. The municipality contains the Salto Santiago Hydroelectric Power Plant on the Iguazu River.
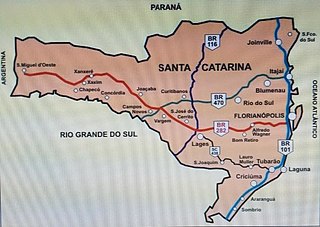
BR-282 is a federal highway in the southern Brazilian state of Santa Catarina. The highway goes the entire length of the state from the state capital, Florianópolis on the Atlantic Ocean in the east, 680.6 km westward to the town of Paraíso on the border with Argentina.

In Brazil, the lords of Casa da Torre de Garcia d'Avila pioneered the livestock industry, often using indigenous labor as cowboys. However, a great drought in the Northeast and the discovery of precious minerals in Minas Gerais at the end of the 18th century moved the cattle ranch in Brazil to the Southeast and South, more specifically São Paulo and Rio Grande do Sul.





















