The search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) is a collective term for scientific searches for intelligent extraterrestrial life, for example, monitoring electromagnetic radiation for signs of transmissions from civilizations on other planets.

A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by astronomical objects, just as optical telescopes are the main observing instrument used in traditional optical astronomy which studies the light wave portion of the spectrum coming from astronomical objects. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night.

Frank Donald Drake was an American astrophysicist and astrobiologist.
Project Phoenix was a SETI project to search for extraterrestrial intelligence by analyzing patterns in radio signals. It was run by the independently funded SETI Institute of Mountain View, California, U.S.

The SETI Institute is a not-for-profit research organization incorporated in 1984 whose mission is to explore, understand, and explain the origin and nature of life in the universe, and to use this knowledge to inspire and guide present and future generations, sharing knowledge with the public, the press, and the government. SETI stands for the "search for extraterrestrial intelligence".

Project Ozma was a search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) experiment started in 1960 by Cornell University astronomer Frank Drake, at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Green Bank at Green Bank, West Virginia. The object of the experiment was to search for signs of life in distant planetary systems through interstellar radio waves. The program was named after Princess Ozma, ruler of the fictional land of Oz, inspired by L. Frank Baum's supposed communication with Oz by radio to learn of the events in the books taking place after The Emerald City of Oz. The search was publicized in articles in the popular media of the time, such as Time magazine and was described as the first modern SETI experiment.

The Wow! signal was a strong narrowband radio signal detected on August 15, 1977, by Ohio State University's Big Ear radio telescope in the United States, then used to support the search for extraterrestrial intelligence. The signal appeared to come from the direction of the constellation Sagittarius and bore expected hallmarks of extraterrestrial origin.

Perkins Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Delaware, Ohio. It is owned and operated by Ohio Wesleyan University.

The Allen Telescope Array (ATA), formerly known as the One Hectare Telescope (1hT), is a radio telescope array dedicated to astronomical observations and a simultaneous search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI). The array is situated at the Hat Creek Radio Observatory in Shasta County, 290 miles (470 km) northeast of San Francisco, California.

The RATAN-600 is a radio telescope in Zelenchukskaya, Karachay–Cherkess Republic, Russia. It comprises a 576 m diameter circle of rectangular radio reflectors and a set of secondary reflectors and receivers, based at an altitude of 970 m. Each of the 895 2×7.4 m reflectors can be angled to reflect incoming radio waves towards a central conical secondary mirror, or to one of five parabolic cylinders. Each secondary reflector is combined with an instrumentation cabin containing various receivers and instruments. The overall effect is that of a partially steerable antenna with a maximum resolving power of a nearly 600 m diameter dish, when using the central conical receiver, making it the world's largest-diameter individual radio telescope.
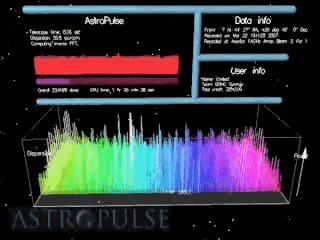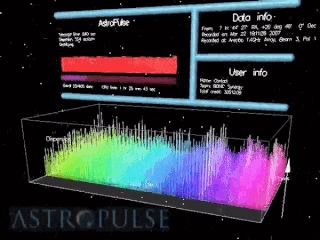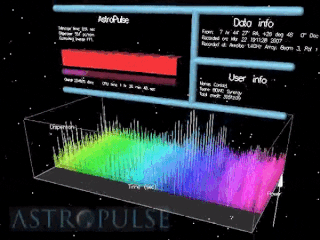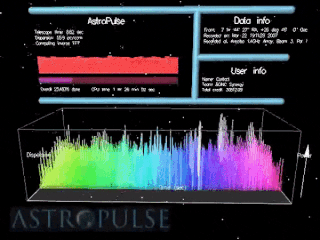
Astropulse is a volunteer computing project to search for primordial black holes, pulsars, and extraterrestrial intelligence (ETI). Volunteer resources are harnessed through Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing (BOINC) platform. In 1999, the Space Sciences Laboratory launched SETI@home, which would rely on massively parallel computation on desktop computers scattered around the world. SETI@home utilizes recorded data from the Arecibo radio telescope and searches for narrow-bandwidth radio signals from space, signifying the presence of extraterrestrial technology. It was soon recognized that this same data might be scoured for other signals of value to the astronomy and physics community.
John Daniel Kraus was an American physicist and electrical engineer known for his contributions to electromagnetics, radio astronomy, and antenna theory. His inventions included the helical antenna, the corner reflector antenna, and several other types of antennas. He designed the Big Ear radio telescope at Ohio State University, which was constructed mostly by a team of OSU students and was used to carry out the Ohio Sky Survey. Kraus held a number of patents and published widely.
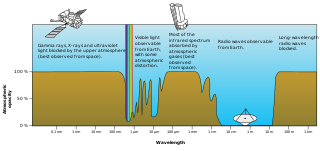
The waterhole, or water hole, is an especially quiet band of the electromagnetic spectrum between 1420 and 1662 megahertz, corresponding to wavelengths of 18–21 centimeters. It is a popular observing frequency used by radio telescopes in radio astronomy.
SERENDIP is a Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence (SETI) program originated by the Berkeley SETI Research Center at the University of California, Berkeley.

The Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope, nicknamed Tianyan, is a radio telescope located in the Dawodang depression (大窝凼洼地), a natural basin in Pingtang County, Guizhou, southwest China. FAST has a 500 m (1,640 ft) diameter dish constructed in a natural depression in the landscape. It is the world's largest filled-aperture radio telescope and the second-largest single-dish aperture, after the sparsely-filled RATAN-600 in Russia.

The Arecibo Telescope was a 305 m (1,000 ft) spherical reflector radio telescope built into a natural sinkhole at the Arecibo Observatory located near Arecibo, Puerto Rico. A cable-mount steerable receiver and several radar transmitters for emitting signals were mounted 150 m (492 ft) above the dish. Completed in November 1963, the Arecibo Telescope was the world's largest single-aperture telescope for 53 years, until it was surpassed in July 2016 by the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST) in Guizhou, China.

Robert Hansen Gray was an American data analyst, author, and astronomer, and author of The Elusive Wow: Searching for Extraterrestrial Intelligence.
The Xinjiang Qitai 110m Radio Telescope (QTT) is a planned radio telescope to be built in Qitai County in Xinjiang, China. Upon completion, which is scheduled for 2028, it will be the world's largest fully steerable single-dish radio telescope. It is intended to operate at 150 MHz to 115 GHz. The construction of the antenna project is under the leadership of the Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.

Breakthrough Listen is a project to search for intelligent extraterrestrial communications in the Universe. With $100 million in funding and thousands of hours of dedicated telescope time on state-of-the-art facilities, it is the most comprehensive search for alien communications to date. The project began in January 2016, and is expected to continue for 10 years. It is a component of Yuri Milner's Breakthrough Initiatives program. The science program for Breakthrough Listen is based at Berkeley SETI Research Center, located in the Astronomy Department at the University of California, Berkeley.

The Berkeley SETI Research Center (BSRC) conducts experiments searching for optical and electromagnetic transmissions from intelligent extraterrestrial civilizations. The center is based at the University of California, Berkeley.

















