Related Research Articles

A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. Toadstool generally denotes one poisonous to humans.

Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis. Infection typically occurs by contact with the skin, inhalation, or intestinal absorption. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The skin form presents with a small blister with surrounding swelling that often turns into a painless ulcer with a black center. The inhalation form presents with fever, chest pain and shortness of breath. The intestinal form presents with diarrhea, abdominal pains, nausea and vomiting.

An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form, but it is not a true spore. It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce itself. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries. There are many reports of spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been claimed. There is one report of viable spores of Bacillus marismortui in salt crystals approximately 25 million years old. When the environment becomes more favorable, the endospore can reactivate itself into a vegetative state. Most types of bacteria cannot change to the endospore form. Examples of bacterial species that can form endospores include Bacillus cereus, Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus thuringiensis, Clostridium botulinum, and Clostridium tetani. Endospore formation is not found among Archaea.

Basidiomycota is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: agarics, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and Cryptococcus, the human pathogenic yeast.

Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the "ascus", a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of Ascomycota are asexual and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens such as Cladonia belong to the Ascomycota.

A mold or mould is one of the structures that certain fungi can form. The dust-like, colored appearance of molds is due to the formation of spores containing fungal secondary metabolites. The spores are the dispersal units of the fungi. Not all fungi form molds. Some fungi form mushrooms; others grow as single cells and are called microfungi.

In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. They were thought to have appeared as early as the mid-late Ordovician period as an adaptation of early land plants.

Rusts are fungal plant pathogens of the order Pucciniales causing plant fungal diseases.

A sporangium ; pl.: sporangia) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other groups form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in land plants and many fungi, sporangia produce genetically distinct haploid spores by meiosis.

A basidium is a microscopic spore-producing structure found on the hymenophore of reproductive bodies of basidiomycete fungi. These bodies also called tertiary mycelia, which are highly coiled versions of secondary mycelia. The presence of basidia is one of the main characteristic features of the genus. A basidium usually bears four sexual spores called basidiospores. Occasionally the number may be two or even eight. Each reproductive spore is produced at the tip of a narrow prong or horn called a sterigma (pl. sterigmata), and is forcefully expelled at full growth.
An ascocarp, or ascoma, is the fruiting body (sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia).
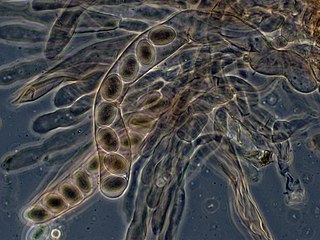
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores, produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one, two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some Cordyceps, also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic, and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm that is surrounded by the "bourrelet".

The spore print is the powdery deposit obtained by allowing spores of a fungal fruit body to fall onto a surface underneath. It is an important diagnostic character in most handbooks for identifying mushrooms. It shows the colour of the mushroom spores if viewed en masse.

A basidiospore is a reproductive spore produced by basidiomycete fungi, a grouping that includes mushrooms, shelf fungi, rusts, and smuts. Basidiospores typically each contain one haploid nucleus that is the product of meiosis, and they are produced by specialized fungal cells called basidia. Typically, four basidiospores develop on appendages from each basidium, of which two are of one strain and the other two of its opposite strain. In gills under a cap of one common species, there exist millions of basidia. Some gilled mushrooms in the order Agaricales have the ability to release billions of spores. The puffball fungus Calvatia gigantea has been calculated to produce about five trillion basidiospores. Most basidiospores are forcibly discharged, and are thus considered ballistospores. These spores serve as the main air dispersal units for the fungi. The spores are released during periods of high humidity and generally have a night-time or pre-dawn peak concentration in the atmosphere.
A spore is an asexual biological reproductive mechanism.

The Mucorales is the largest and best-studied order of zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds. The term mucormycosis is now preferred for infections caused by molds belonging to the order Mucorales.
Paenibacillus popilliae is a soil-dwelling, Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium. It is responsible for a disease of the white grubs of Japanese beetles.

Spore is a 2008 life simulation real-time strategy god game developed by Maxis and published by Electronic Arts for Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X. Designed by Will Wright, it covers many genres including action, real-time strategy, and role-playing games. Spore allows a player to control the development of a species from its beginnings as a microscopic organism, through development as an intelligent and social creature, to interstellar exploration as a spacefaring culture. It has drawn wide attention for its massive scope, and its use of open-ended gameplay and procedural generation. Throughout each stage, players are able to use various creators to produce content for their games. These are then automatically uploaded to the online Sporepedia and are accessible by other players for download.

Pycniospores are a type of spore found in certain species of rust fungi. They are produced in special cup-like structures called pycnia or pynidia. Almost all fungi reproduce asexually with the production of spores. Spores may be colorless, green, yellow, orange, red, brown or black.

Amylostereum is the single genus in the fungal family Amylostereaceae. The genus currently comprises four saprotrophic and parasitic species, which live off living or dead wood. The Amylostereaceae cause white rot in the wood by disintegrating the tissue component lignin. They produce crust-like, partially wavy fruit bodies on the surface of infested trees, which are similar to those produced by Stereum species.
References
- Illinois Mycological Association glossary