Related Research Articles

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. The gametes produced by an organism define its sex: males produce small gametes while females produce large gametes. Individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Gametes can be identical in form and function, but, in many cases, an asymmetry has evolved such that two different types of gametes (heterogametes) exist.

A zygote is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information necessary to form a new individual. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring.

Basidiomycota is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya within the kingdom Fungi. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and the human pathogenic yeast Cryptococcus. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores. These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by the formation of a distinctive anatomical feature, cell wall components, and definitively by phylogenetic molecular analysis of DNA sequence data.

Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the "ascus", a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewer's yeast and baker's yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens such as Cladonia belong to the Ascomycota.

In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoebulae into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula.

Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two phyla the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material. Some are parasites of plants, insects, and small animals, while others form symbiotic relationships with plants. Zygomycete hyphae may be coenocytic, forming septa only where gametes are formed or to wall off dead hyphae. Zygomycota is no longer recognised as it was not believed to be truly monophyletic.

The dictyostelids are a group of cellular slime molds, or social amoebae.

In biology, a biological life cycle is a series of changes in form that an organism undergoes, returning to the starting state. "The concept is closely related to those of the life history, development and ontogeny, but differs from them in stressing renewal." Transitions of form may involve growth, asexual reproduction, or sexual reproduction.

Karyogamy is the final step in the process of fusing together two haploid eukaryotic cells, and refers specifically to the fusion of the two nuclei. Before karyogamy, each haploid cell has one complete copy of the organism's genome. In order for karyogamy to occur, the cell membrane and cytoplasm of each cell must fuse with the other in a process known as plasmogamy. Once within the joined cell membrane, the nuclei are referred to as pronuclei. Once the cell membranes, cytoplasm, and pronuclei fuse together, the resulting single cell is diploid, containing two copies of the genome. This diploid cell, called a zygote or zygospore can then enter meiosis, or continue to divide by mitosis. Mammalian fertilization uses a comparable process to combine haploid sperm and egg cells (gametes) to create a diploid fertilized egg.

Neurospora crassa is a type of red bread mold of the phylum Ascomycota. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" in Greek, refers to the characteristic striations on the spores. The first published account of this fungus was from an infestation of French bakeries in 1843.
Heterothallic species have sexes that reside in different individuals. The term is applied particularly to distinguish heterothallic fungi, which require two compatible partners to produce sexual spores, from homothallic ones, which are capable of sexual reproduction from a single organism.
A heterokaryon is a multinucleate cell that contains genetically different nuclei. Heterokaryotic and heterokaryosis are derived terms. This is a special type of syncytium. This can occur naturally, such as in the mycelium of fungi during sexual reproduction, or artificially as formed by the experimental fusion of two genetically different cells, as e.g., in hybridoma technology.
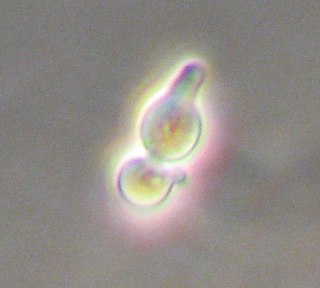
The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a simple single-celled eukaryote with both a diploid and haploid mode of existence. The mating of yeast only occurs between haploids, which can be either the a or α (alpha) mating type and thus display simple sexual differentiation. Mating type is determined by a single locus, MAT, which in turn governs the sexual behaviour of both haploid and diploid cells. Through a form of genetic recombination, haploid yeast can switch mating type as often as every cell cycle.

Saccharomycotina is a subdivision (subphylum) of the division (phylum) Ascomycota in the Kingdom Fungi. It comprises most of the ascomycete yeasts. The members of Saccharomycotina reproduce by budding and they do not produce ascocarps.

Mating in fungi is a complex process governed by mating types. Research on fungal mating has focused on several model species with different behaviour. Not all fungi reproduce sexually and many that do are isogamous; thus, the terms "male" and "female" do not apply to many members of the fungal kingdom. Homothallic species are able to mate with themselves, while in heterothallic species only isolates of opposite mating types can mate.

Phycomyces is a genus of fungus in the Zygomycota phylum. They are known for their strong phototropism response and helical growth of the sporangium. The best studied species is Phycomyces blakesleeanus.

The Mucorales is the largest and best studied order of zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds. The term mucormycosis is now preferred for infections caused by molds belonging to the order Mucorales.
Sporogenesis is the production of spores in biology. The term is also used to refer to the process of reproduction via spores. Reproductive spores were found to be formed in eukaryotic organisms, such as plants, algae and fungi, during their normal reproductive life cycle. Dormant spores are formed, for example by certain fungi and algae, primarily in response to unfavorable growing conditions. Most eukaryotic spores are haploid and form through cell division, though some types are diploid or dikaryons and form through cell fusion.
The parasexual cycle, a process peculiar to fungi and single-celled organisms, is a nonsexual mechanism of parasexuality for transferring genetic material without meiosis or the development of sexual structures. It was first described by Italian geneticist Guido Pontecorvo in 1956 during studies on Aspergillus nidulans. A parasexual cycle is initiated by the fusion of hyphae (anastomosis) during which nuclei and other cytoplasmic components occupy the same cell. Fusion of the unlike nuclei in the cell of the heterokaryon results in formation of a diploid nucleus (karyogamy), which is believed to be unstable and can produce segregants by recombination involving mitotic crossing-over and haploidization. Mitotic crossing-over can lead to the exchange of genes on chromosomes; while haploidization probably involves mitotic nondisjunctions which randomly reassort the chromosomes and result in the production of aneuploid and haploid cells. Like a sexual cycle, parasexuality gives the species the opportunity to recombine the genome and produce new genotypes in their offspring. Unlike a sexual cycle, the process lacks coordination and is exclusively mitotic.
Homothallic refers to the possession, within a single organism, of the resources to reproduce sexually; i.e., having male and female reproductive structures on the same thallus. The opposite sexual functions are performed by different cells of a single mycelium.
References
- ↑ David Moore; Geoffrey D. Robson; Anthony P. J. Trinci (14 July 2011). 21st Century Guidebook to Fungi with CD. Cambridge University Press. p. 52. ISBN 978-1-107-00676-8.