Related Research Articles

Dothideomycetes is the largest and most diverse class of ascomycete fungi. It comprises 11 orders 90 families, 1,300 genera and over 19,000 known species. Wijayawardene et al. in 2020 added more orders to the class.

Pezizomycetes are a class of fungi within the division Ascomycota.

The Agaricomycetes are a class of fungi in the division Basidiomycota. The taxon is roughly identical to that defined for the Homobasidiomycetes by Hibbett & Thorn, with the inclusion of Auriculariales and Sebacinales. It includes not only mushroom-forming fungi, but also most species placed in the deprecated taxa Gasteromycetes and Homobasidiomycetes. Within the subdivision Agaricomycotina, which already excludes the smut and rust fungi, the Agaricomycetes can be further defined by the exclusion of the classes Tremellomycetes and Dacrymycetes, which are generally considered to be jelly fungi. However, a few former "jelly fungi", such as Auricularia, are classified in the Agaricomycetes. According to a 2008 estimate, Agaricomycetes include 17 orders, 100 families, 1147 genera, and about 21000 species. Modern molecular phylogenetic analyses have been since used to help define several new orders in the Agaricomycetes: Amylocorticiales, Jaapiales, Stereopsidales, and Lepidostromatales.

The Ustilaginomycotina is a subdivision within the division Basidiomycota of the kingdom Fungi. It consists of the classes Ustilaginomycetes and Exobasidiomycetes, and in 2014 the subdivision was reclassified and the two additional classes Malasseziomycetes and Monilielliomycetes added. The name was first published by Doweld in 2001; Bauer and colleagues later published it in 2006 as an isonym. Ustilagomycotina and Agaricomycotina are considered to be sister groups, and they are in turn sister groups to the subdivision Pucciniomycotina.

Blastocladiomycota is one of the currently recognized phyla within the kingdom Fungi. Blastocladiomycota was originally the order Blastocladiales within the phylum Chytridiomycota until molecular and zoospore ultrastructural characters were used to demonstrate it was not monophyletic with Chytridiomycota. The order was first erected by Petersen for a single genus, Blastocladia, which was originally considered a member of the oomycetes. Accordingly, members of Blastocladiomycota are often referred to colloquially as "chytrids." However, some feel "chytrid" should refer only to members of Chytridiomycota. Thus, members of Blastocladiomycota are commonly called "blastoclads" by mycologists. Alternatively, members of Blastocladiomycota, Chytridiomycota, and Neocallimastigomycota lumped together as the zoosporic true fungi. Blastocladiomycota contains 5 families and approximately 12 genera. This early diverging branch of kingdom Fungi is the first to exhibit alternation of generations. As well, two (once) popular model organisms—Allomyces macrogynus and Blastocladiella emersonii—belong to this phylum.

Pucciniomycotina is a subdivision of fungus within the division Basidiomycota. The subdivision contains 10 classes, 21 orders, and 38 families. Over 8400 species of Pucciniomycotina have been described - more than 8% of all described fungi. The subdivision is considered a sister group to Ustilaginomycotina and Agaricomycotina, which may share the basal lineage of Basidiomycota, although this is uncertain due to low support for placement between the three groups. The group was known as Urediniomycetes until 2006, when it was elevated from a class to a subdivision and named after the largest order in the group, Pucciniales.

The Gomphales are an order of basidiomycete fungi. Some or all families belonging to Gomphales have been sometimes included in the order Phallales, the now-obsolete Ramariaceae was also previously included in Cantharellales. Recent phylogenetic analyses include in Gomphales the families of the original description of the order by Walter Jülich, with addition of Clavariadelphaceae. According to one 2008 estimate, the Gomphales contain 18 genera and 336 species.

Gloeophyllum is a genus of fungus in the class Agaricomycetes. It is characterized by the production of leathery to corky tough, brown, shaggy-topped, revivable fruitbodies lacking a stipe and with a lamellate to daedaleoid or poroid fertile hymenial surfaces. The hyphal system is dimitic to trimitic. The genus is further characterized by the production of a brown rot of wood. Phylogenetically, it along with several other brown rot Basidiomycota, Neolentinus, Heliocybe, and Veluticeps form an order called the Gloeophyllales.

Erast Parmasto was a noted Estonian mycologist, bioscientist and botanist and onetime director of the Estonian Institute of Zoology and Botany.

Kickxellomycotina is a fungus grouping. In the subkingdom of Zoopagomyceta Benny, 2007.
The Doassansiales are an order of fungi in the class Exobasidiomycetes. The order consist of three families: the Doassansiaceae, the Melaniellaceae, and the Rhamphosporaceae.

The Entylomatales are an order of smut fungi in the class Exobasidiomycetes. A monotypic order, it consists of a single family, the Entylomataceae. Both the family and order were circumscribed in 1997.

The Georgefischeriales are an order of smut fungi in the class Exobasidiomycetes. The order consists of four families, the Eballistraceae, the Georgefischeriaceae, the Gjaerumiaceae, and the Tilletiariaceae.

The Microstromatales are order of fungi in the class Exobasidiomycetes. The order consists of three families: the Microstromataceae, the Quambalariaceae, and the Volvocisporiaceae.
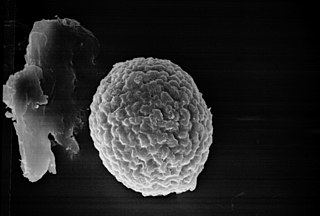
The Tilletiales are an order of smut fungi in the class Exobasidiomycetes. It is a monotypic order, consisting of a single family, the Tilletiaceae, which contains seven genera. The roughly 150 species in the Tilletiales all infect hosts of the grass family, except for species of Erratomyces, which occur on legumes.

Entorrhizomycetes is the sole class in the phylum Entorrhizomycota, within the Fungi subkingdom Dikarya along with Basidiomycota and Ascomycota. It contains three genera and is a small group of teliosporic root parasites that form galls on plants in the Juncaceae (rush) and Cyperaceae (sedge) families. Prior to 2015 this phylum was placed under the subdivision Ustilaginomycotina. A 2015 study did a "comprehensive five-gene analyses" of Entorrhiza and concluded that the former class Entorrhizomycetes is possibly either a close sister group to the rest of Dikarya or Basidiomycota.

The Agaricostilbomycetes are a class of fungi in the subdivision Pucciniomycotina of the Basidiomycota. The class consists of a single order, six families, and 15 genera. Its type genus, Agaricostilbum was originally placed in Ascomycota, and later, Agaricomycotina, before being placed in Pucinniomycotina.

The Urocystidales are an order of fungi within the class Ustilaginomycetes. The order contains 6 families and about 400 genera. They are a sister order to Ustilaginales.
Claude Roux is a French lichenologist, mycologist and Esperantist. He has co-authored books about the identification of lichens written in Esperanto.
The Spiculogloeomycetes are a class of fungi in the subdivision Pucciniomycotina of the Basidiomycota. The class consists of a single order, the Spiculogloeales, together with an additional, unassigned genus, Meniscomyces. Many species are currently known only from their yeast states. Species in the genus Spiculogloea form hyphal states that produce auricularioid basidia and are parasitic on other fungi.
References
- ↑ Silar, Philippe (2016). Protistes Eucaryotes : Origine, Evolution et Biologie des Microbes Eucaryotes. HAL. p. 462. ISBN 978-2-9555841-0-1.
- ↑ Esser, Karl (2014). The Mycota VII A: Systematics and Evolution (2nd ed.). Springer. p. 461. ISBN 978-3-642-55317-2.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Wijayawardene NN, Hyde KD, Al-Ani LK, Tedersoo L, Haelewaters D, Rajeshkumar KC, et al. (2020). "Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa" (PDF). Mycosphere. 11 (1): 1060–1456. doi: 10.5943/mycosphere/11/1/8 . ISSN 2077-7019.