
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans as a source for tinder, traditional medicine, food, and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as toxicity or infection.
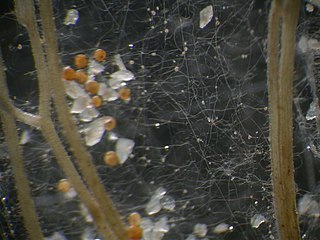
Glomeromycota are one of eight currently recognized divisions within the kingdom Fungi, with approximately 230 described species. Members of the Glomeromycota form arbuscular mycorrhizas (AMs) with the thalli of bryophytes and the roots of vascular land plants. Not all species have been shown to form AMs, and one, Geosiphon pyriformis, is known not to do so. Instead, it forms an endocytobiotic association with Nostoc cyanobacteria. The majority of evidence shows that the Glomeromycota are dependent on land plants for carbon and energy, but there is recent circumstantial evidence that some species may be able to lead an independent existence. The arbuscular mycorrhizal species are terrestrial and widely distributed in soils worldwide where they form symbioses with the roots of the majority of plant species (>80%). They can also be found in wetlands, including salt-marshes, and associated with epiphytic plants.

Lewis David de Schweinitz was a German-American botanist and mycologist. He is considered by some the "Father of North American Mycology", but also made significant contributions to botany.
Glomus aggregatum is an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus used as a soil inoculant in agriculture and horticulture. Like other species in this phylum it forms obligate symbioses with plant roots, where it obtains carbon (photosynthate) from the host plant in exchange for nutrients and other benefits.
Glomus is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi, and all species form symbiotic relationships (mycorrhizae) with plant roots. Glomus is the largest genus of AM fungi, with ca. 85 species described, but is currently defined as non-monophyletic.
The New York Mycological Society is a nonprofit organization of people who share an interest in mycology as well as in mycophagy. The present NYMS was reincarnated in 1962 by the composer John Cage and a small group of other mushroom lovers and students, including illustrator Lois Long and noted mycologist Guy Nearing.

Geosiphon is a genus of fungus in the family Geosiphonaceae. The genus is monotypic, containing the single species Geosiphon pyriformis, first described by Kützing in 1849 as Botrydium pyriforme. In 1915, Von Wettstein characterized Geosiphon pyriforme as a multinucleate alga containing endosymbiotic cyanobacteria, although he also noted the presence of chitin, a component of fungal cell walls. In 1933, Knapp was the first to suggest the fungal origin of the species and described it as a lichen with endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. It is the only member of the Glomeromycota known to not form a symbiosis with terrestrial plants in the form of arbuscular mycorrhiza.

The British Mycological Society is a learned society established in 1896 to promote the study of fungi.

William Alphonso Murrill was an American mycologist, known for his contributions to the knowledge of the Agaricales and Polyporaceae. In 1904, he became the assistant Curator at the New York Botanical Garden (NYBG). He, along with the NYBG, founded the journal Mycologia and was its first editor for 16 years. Murrill was known to travel extensively to describe the mycota of Europe and the Americas. He traveled along the East Coast, Pacific Coast, Mexico and the Caribbean. Although Murrill was a very influential person at the NYBG, having worked his way up to become assistant director in 1908, his rather eccentric personality caused problems with his job. He went on annual collecting trips to Mexico, the Caribbean, Europe, and South America, sometimes, without informing any of his colleagues prior. These trips resulted in a cumulative total of 70,000 specimens, 1,400 of which are deposited in the NYBG.
MycoBank is an online database, documenting new mycological names and combinations, eventually combined with descriptions and illustrations. It is run by the Westerdijk Fungal Biodiversity Institute in Utrecht.

Charles Horton Peck was an American mycologist of the 19th and early 20th centuries. He was the New York State Botanist from 1867 to 1915, a period in which he described over 2,700 species of North American fungi.

Lucien Quélet was a French naturalist and mycologist. Quélet discovered several species of fungi and was the founder of the Société mycologique de France, a society devoted to mycological studies.

Glomerales is an order of symbiotic fungi within the phylum Glomeromycota.
The Botanical Society of America (BSA) represents professional and amateur botanists, researchers, educators and students in over 80 countries of the world. It functions as a United States nonprofit 501(c)(3) membership society.

A fungus is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista.

Mycologia is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes papers on all aspects of the fungi, including lichens. It first appeared as a bimonthly journal in January 1909, published by the New York Botanical Garden under the editorship of William Murrill. It became the official journal of the Mycological Society of America, which still publishes it today. It was formed as a merger of the Journal of Mycology and the Mycological Bulletin. The Mycological Bulletin was known as the Ohio Mycological Bulletin in its first volume.
The mycorrhizosphere is the region around a mycorrhizal fungus in which nutrients released from the fungus increase the microbial population and its activities. The roots of most terrestrial plants, including most crop plants and almost all woody plants, are colonized by mycorrhiza-forming symbiotic fungi. In this relationship, the plant roots are infected by a fungus, but the rest of the fungal mycelium continues to grow through the soil, digesting and absorbing nutrients and water and sharing these with its plant host. The fungus in turn benefits by receiving photosynthetic sugars from its host. The mycorrhizosphere consists of roots, hyphae of the directly connected mycorrhizal fungi, associated microorganisms, and the soil in their direct influence.
Olpidium is a fungal genus in the family Olpidiaceae. Members of Olpidium are zoosporic pathogens of plants, animals, fungi, and oomycetes.
Yolande Dalpé is a former Research Scientist with Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada. She became the first mycologist in Ottawa to study the taxonomy of mycorrhizal fungi. Her research focuses on developing new information on taxonomy, phylogeny, distribution and biology of fungi, including systematic research related to biosecurity/alien invasive species as well as species involved in the development of bioproducts. She was awarded the Lawson Medal by the Canadian Botanical Association for her "cumulative, lifetime contributions to Canadian botany, for the research she has performed in mycology, and has been recognized nationally and internationally." The standard author abbreviation Dalpé is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.

Constantine John Alexopoulos was an American mycologist. He was the main author of the landmark book Introductory Mycology, commonly used in mycology and mycology-related courses in undergrad and grad schools around the globe. Introductory Mycology was translated into five languages.












