| Pneumocystidomycetes | |
|---|---|
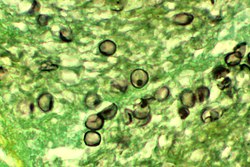 | |
| Pneumocystis jirovecii in tissue | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Subdivision: | Taphrinomycotina |
| Class: | Pneumocystidomycetes O.E.Erikss. & Winka (1997) |
| Order: | Pneumocystidales O.E.Erikss. (1994) |
| Family: | Pneumocystidaceae O.E.Erikss. (1994) |
| Genus: | Pneumocystis P.Delanoë & Delanoë (1912) |
| Type species | |
| Pneumocystis carinii P.Delanoë & Delanoë (1912) | |
| Species | |
| Synonyms | |
Pneumocystomycetes [1] | |
The Pneumocystidomycetes are a class of ascomycete fungi. It includes the single order Pneumocystidales, which contains the single monotypic family Pneumocystidaceae, which in turn contains the genus Pneumocystis, causative agent of Pneumocystis pneumonia.