
Eurotiomycetes is a large class of ascomycetes with cleistothecial ascocarps within the subphylum Pezizomycotina, currently containing around 3810 species according to the Catalogue of Life. It is the third largest lichenized class, with more than 1200 lichen species that are mostly bitunicate in the formation of asci. It contains most of the fungi previously known morphologically as "Plectomycetes".

Dothideomycetes is the largest and most diverse class of ascomycete fungi. It comprises 11 orders 90 families, 1,300 genera and over 19,000 known species. Wijayawardene et al. in 2020 added more orders to the class.

The Nectriaceae comprise a family of fungi in the order Hypocreales. It was circumscribed by brothers Charles and Louis René Tulasne in 1865. In 2020, an Outline of fungi was produced and listed 70 genera and about 1,336 species.

The Chaetothyriales are an order of ascomycetous fungi in the class Eurotiomycetes and within the subclass Chaetothyriomycetidae. The order was circumscribed in 1987 by mycologist Margaret Elizabeth Barr-Bigelow.

The Botryosphaeriaceae are a family of sac fungi (Ascomycetes), which is the type representative of the order Botryosphaeriales. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contains 26 genera and over 1500 species. Members of this order include notable plant pathogens.

Phyllachoraceae is a family of sac fungi.

The Massarinaceae are a family of fungi in the order Pleosporales. Although taxa have a cosmopolitan distribution, they are better-known in temperate regions. They are thought to be saprobic in wood and bark; some species are weak pathogens.

The Dactylosporaceae or Sclerococcaceae are a family of lichen-forming fungi in the class Eurotiomycetes. It is the only family of the order Sclerococcales and subclass Sclerococcomycetidae.

The Pyrenulales are an order of ascomycetous fungi within the class Eurotiomycetes and within the subphylum Pezizomycotina.
Montagnula is a genus of fungi in the family Didymosphaeriaceae. The genus, circumscribed by mycologist Augusto Napoleone Berlese in 1896, contains an estimated 24 species in 2008, but is probably polyphyletic as currently circumscribed. It was originally placed in family Montagnulaceae, before that family was dissolved and it was later placed in family Didymosphaeriaceae, with 34 species.

Herpotrichiellaceae is a family of ascomycetous fungi within the order Chaetothyriales and within the class Eurotiomycetes. It contains 16 genera and about 270 species. The type genus of the family, Herpotrichiella, is now synonymous with Capronia.
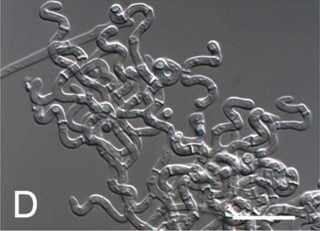
Arachnomyces is a genus of cleistothecial ascomycete fungi described in 1902, of which the anamorph (asexual) stage is the genus Onychocola. Although morphologically similar to members of other families, the fungus now belongs to its own monotypic family Arachnomycetaceae, which is the only family in the monotypic order Arachnomycetales.

The Anthracoideaceae are a family of smut fungi in the order Ustilaginales. Collectively, the family contains 20 genera and 198 species. Anthracoideaceae was circumscribed by the Bulgarian mycologist Cvetomir M. Denchev in 1997.

Job Bicknell Ellis was a pioneering North American mycologist known for his study of ascomycetes, especially the grouping of fungi called the Pyrenomycetes. Born and raised in New York, he worked as a teacher and farmer before developing an interest in mycology. He collected specimens extensively, and together with his wife, prepared 200,000 sets of dried fungal samples that were sent out to subscribers in series between 1878 and 1894. Together with colleagues William A. Kellerman and Benjamin Matlack Everhart, he founded the Journal of Mycology in 1885, forerunner to the modern journal Mycologia. He described over 4000 species of fungi, and his collection of over 100,000 specimens is currently housed at the herbarium of the New York Botanical Gardens. Ellis had over 100 taxa of fungi named in his honor.

Geoglossum is a genus of fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. They are commonly called earth tongues. The type species is Geoglossum glabrum. Geoglossum species are distinguished from the related genus Trichoglossum by the lack of setae on the spore bearing surface. Geoglossum species are characterized by dark, club-shaped, terrestrial ascocarps with a fertile hymenium continuing downward from the apex of the ascocarp along the stipe, eventually intergrading with a sterile stipe. The ascospores of Geoglossum range from translucent to dark brown, and are fusiform, and multiseptate. Identification of species is based on the gross morphology of the ascocarp, color and septation of the ascospores, and shape and ornamentation of the paraphyses.
Harry Morton Fitzpatrick, was an American mycologist. He was professor of mycology at Cornell. He is known for his work on the Phycomycetes. His book on the Lower Fungi was the standard text and reference work on the Phycomycetes. He trained Clark Thomas Rogerson and Richard P. Korf, two prominent mycologists.

Cordieritidaceae is a family of fungi in the order Cyttariales. Species in this family are saprobes or lichenicolous.
Aposphaeria is a genus of fungi in the family Melanommataceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1880 by Pier Andrea Saccardo, with Aposphaeria pulviscula selected as the type species.
Brachysporium is a genus of anamorphic fungi in the family Trichosphaeriaceae. It has 25 species. The genus was circumscribed in 1886 by Pier Andrea Saccardo, with Brachysporium obovatum assigned as the type species. The genus Cryptadelphia, circumscribed in 2004 to contain six presumed teleomorphs of Brachysporium, has since been placed in synonymy with Brachysporium.
Epibryon is a genus of fungi, and the sole genus in the monogeneric family Epibryaceae. It has about 40 species. Many of the species grow parasitically on bryophytes. The genus was circumscribed by mycologist Peter Döbbeler in 1978; the family by Soili Stenroos and Cécile Gueidan in 2014.















