In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and in most Archaeal phyla. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30-nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones prevent DNA from becoming tangled and protect it from DNA damage. In addition, histones play important roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. Without histones, unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long. For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA if completely stretched out; however, when wound about histones, this length is reduced to about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of 30 nm diameter chromatin fibers.
Histone methylation is a process by which methyl groups are transferred to amino acids of histone proteins that make up nucleosomes, which the DNA double helix wraps around to form chromosomes. Methylation of histones can either increase or decrease transcription of genes, depending on which amino acids in the histones are methylated, and how many methyl groups are attached. Methylation events that weaken chemical attractions between histone tails and DNA increase transcription because they enable the DNA to uncoil from nucleosomes so that transcription factor proteins and RNA polymerase can access the DNA. This process is critical for the regulation of gene expression that allows different cells to express different genes.

Citrullination or deimination is the conversion of the amino acid arginine in a protein into the amino acid citrulline. Citrulline is not one of the 20 standard amino acids encoded by DNA in the genetic code. Instead, it is the result of a post-translational modification. Citrullination is distinct from the formation of the free amino acid citrulline as part of the urea cycle or as a byproduct of enzymes of the nitric oxide synthase family.

Histone-modifying enzymes are enzymes involved in the modification of histone substrates after protein translation and affect cellular processes including gene expression. To safely store the eukaryotic genome, DNA is wrapped around four core histone proteins, which then join to form nucleosomes. These nucleosomes further fold together into highly condensed chromatin, which renders the organism's genetic material far less accessible to the factors required for gene transcription, DNA replication, recombination and repair. Subsequently, eukaryotic organisms have developed intricate mechanisms to overcome this repressive barrier imposed by the chromatin through histone modification, a type of post-translational modification which typically involves covalently attaching certain groups to histone residues. Once added to the histone, these groups elicit either a loose and open histone conformation, euchromatin, or a tight and closed histone conformation, heterochromatin. Euchromatin marks active transcription and gene expression, as the light packing of histones in this way allows entry for proteins involved in the transcription process. As such, the tightly packed heterochromatin marks the absence of current gene expression.
Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRMT1 gene. The HRMT1L2 gene encodes a protein arginine methyltransferase that functions as a histone methyltransferase specific for histone H4.

Histone H2A type 2-C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST2H2AC gene.

Histone H2A type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST1H2AM gene.
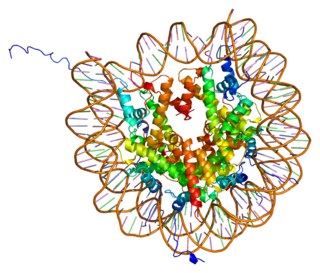
Histone H2A type 1-B/E is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST1H2AE gene.

Histone H2A type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST1H2AK gene.

Histone H2A type 1-H is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST1H2AH gene.

Histone H2A type 1-B/E is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST1H2AB gene.

Histone H2A type 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST3H2A gene.

Protein-arginine deiminase type-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PADI2 gene.

Peptidyl arginine deiminase, type III, also known as PADI3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PADI3 gene.

Peptidyl arginine deiminase, type I, also known as PADI1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PADI1 gene.

Histone H2A type 2-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST2H2AB gene.
H3K4me3 is an epigenetic modification to the DNA packaging protein Histone H3 that indicates tri-methylation at the 4th lysine residue of the histone H3 protein and is often involved in the regulation of gene expression. The name denotes the addition of three methyl groups (trimethylation) to the lysine 4 on the histone H3 protein.
H3R17me2 is an epigenetic modification to the DNA packaging protein histone H3. It is a mark that indicates the di-methylation at the 17th arginine residue of the histone H3 protein. In epigenetics, arginine methylation of histones H3 and H4 is associated with a more accessible chromatin structure and thus higher levels of transcription. The existence of arginine demethylases that could reverse arginine methylation is controversial.
H3R2me2 is an epigenetic modification to the DNA packaging protein histone H3. It is a mark that indicates the di-methylation at the 2nd arginine residue of the histone H3 protein. In epigenetics, arginine methylation of histones H3 and H4 is associated with a more accessible chromatin structure and thus higher levels of transcription. The existence of arginine demethylases that could reverse arginine methylation is controversial.
Epigenetics of autoimmune disorders is the role that epigenetics play in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune disorders are a diverse class of diseases that share a common origin. These diseases originate when the immune system becomes dysregulated and mistakenly attacks healthy tissue rather than foreign invaders. These diseases are classified as either local or systemic based upon whether they affect a single body system or if they cause systemic damage.