Protein disulfide isomerase, or PDI, is an enzyme in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in eukaryotes and the periplasm of bacteria that catalyzes the formation and breakage of disulfide bonds between cysteine residues within proteins as they fold. This allows proteins to quickly find the correct arrangement of disulfide bonds in their fully folded state, and therefore the enzyme acts to catalyze protein folding.

Tissue transglutaminase is a 78-kDa, calcium-dependent enzyme of the protein-glutamine γ-glutamyltransferases family. Like other transglutaminases, it crosslinks proteins between an ε-amino group of a lysine residue and a γ-carboxamide group of glutamine residue, creating an inter- or intramolecular bond that is highly resistant to proteolysis. Aside from its crosslinking function, tTG catalyzes other types of reactions including deamidation, GTP-binding/hydrolyzing, and isopeptidase activities. Unlike other members of the transglutaminase family, tTG can be found both in the intracellular and the extracellular spaces of various types of tissues and is found in many different organs including the heart, the liver, and the small intestine. Intracellular tTG is abundant in the cytosol but smaller amounts can also be found in the nucleus and the mitochondria. Intracellular tTG is thought to play an important role in apoptosis. In the extracellular space, tTG binds to proteins of the extracellular matrix (ECM), binding particularly tightly to fibronectin. Extracellular tTG has been linked to cell adhesion, ECM stabilization, wound healing, receptor signaling, cellular proliferation, and cellular motility.

ER oxidoreductin 1 (Ero1) is an oxidoreductase enzyme that catalyses the formation and isomerization of protein disulfide bonds in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of eukaryotes. ER Oxidoreductin 1 (Ero1) is a conserved, luminal, glycoprotein that is tightly associated with the ER membrane, and is essential for the oxidation of protein dithiols. Since disulfide bond formation is an oxidative process, the major pathway of its catalysis has evolved to utilise oxidoreductases, which become reduced during the thiol-disulfide exchange reactions that oxidise the cysteine thiol groups of nascent polypeptides. Ero1 is required for the introduction of oxidising equivalents into the ER and their direct transfer to protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), thereby ensuring the correct folding and assembly of proteins that contain disulfide bonds in their native state.

Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 (PDIA3), also known as glucose-regulated protein, 58-kD (GRP58), is an isomerase enzyme encoded by the autosomal gene PDIA3 in humans. This protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and interacts with lectin chaperones calreticulin and calnexin (CNX) to modulate folding of newly synthesized glycoproteins. It is thought that complexes of lectins and this protein mediate protein folding by promoting formation of disulfide bonds in their glycoprotein substrates.

Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B is an enzyme that is encoded by the PPIB gene. As a member of the peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) family, this protein catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds, which allows it to regulate protein folding of type I collagen. Generally, PPIases are found in all eubacteria and eukaryotes, as well as in a few archaebacteria, and thus are highly conserved.

Activating transcription factor 6, also known as ATF6, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ATF6 gene and is involved in the unfolded protein response.

Protein disulfide-isomerase, also known as the beta-subunit of prolyl 4-hydroxylase (P4HB), is an enzyme that in humans encoded by the P4HB gene. The human P4HB gene is localized in chromosome 17q25. Unlike other prolyl 4-hydroxylase family proteins, this protein is multifunctional and acts as an oxidoreductase for disulfide formation, breakage, and isomerization. The activity of P4HB is tightly regulated. Both dimer dissociation and substrate binding are likely to enhance its enzymatic activity during the catalysis process.

Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein large subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTTP, also known as MTP, gene.

Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP2A3 gene.

Endoplasmic reticulum protein 29 (ERp29) is a chaperone protein that in humans is encoded by the ERP29 gene.

ERO1-like protein alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ERO1L gene.

15 kDa selenoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEP15 gene. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene.

Endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 44 (ERp44) also known as thioredoxin domain-containing protein 4 (TXNDC4) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ERP44 gene.

Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TXNDC12 gene.

ERO1-like protein beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ERO1LB gene.

DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAJC10 gene.

Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TXNDC5 gene.

Protein disulfide-isomerase TMX3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TMX3 gene.
Thioredoxins are small disulfide-containing redox proteins that have been found in all the kingdoms of living organisms. Thioredoxin serves as a general protein disulfide oxidoreductase. It interacts with a broad range of proteins by a redox mechanism based on reversible oxidation of 2 cysteine thiol groups to a disulfide, accompanied by the transfer of 2 electrons and 2 protons. The net result is the covalent interconversion of a disulfide and a dithiol.
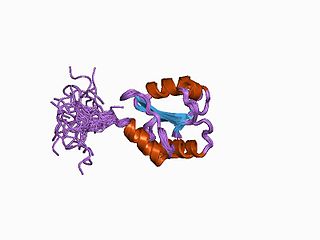
ERp27 is a homologue of PDI, localised to the Endoplasmic Reticulum. The structure of ERp27 has been solved by both X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy, showing it to be composed of two thioredoxin-like domains with homology to the non-catalytic b and b' domains of PDI. The function of ERp27 is unknown, but on the basis of its homology with PDI it is thought to possess chaperone activity.



















