
The Sinhalese people, also known as the Sinhalese or Sinhala people are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group native to the island of Sri Lanka. They are the largest ethnic group in Sri Lanka, constituting about 75% of the Sri Lankan population and number more than 15.2 million.
Theravāda is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed Theravādins, have preserved their version of Gautama Buddha's teaching or dhamma in the Pāli Canon for over two millennia.

Anuradhapura is a major city located in the north central plain of Sri Lanka. It is the capital city of North Central Province and the capital of Anuradhapura District. The city lies 205 kilometers (127 mi) north of the current capital of Colombo in the North Central Province, on the banks of the historic Malwathu Oya. The city is now a World Heritage Site famous for its well-preserved ruins of the ancient Sinhalese civilisation.

Mahāvaṃsa is the meticulously kept historical chronicle of Sri Lanka until the period of Mahasena of Anuradhapura. It was written in the style of an epic poem written in the Pali language. It relates the history of Sri Lanka from its legendary beginnings up to the reign of Mahasena of Anuradhapura covering the period between the arrival of Prince Vijaya from India in 543 BCE to his reign and later updated by different writers. It was first composed by a Buddhist monk named Mahanama at the Mahavihara temple in Anuradhapura in the 5th or 6th-century CE.

Theravada Buddhism is the largest and official religion of Sri Lanka, practiced by 70.2% of the population as of 2012. Practitioners of Sri Lankan Buddhism can be found amongst the majority Sinhalese population as well as among the minority ethnic groups. Sri Lankan Buddhists share many similarities with Southeast Asian Buddhists, specifically Myanmar Buddhists and Thai Buddhists due to traditional and cultural exchange. Sri Lanka is one of five nations with a Theravada Buddhist majority.

Jaya Sri Maha Bodhi Tree is a historical sacred bo tree in the Mahamewuna Garden in historical city of Anuradhapura, Sri Lanka. This is believed to be a tree grown from a cutting of the southern branch from the historical sacred bo tree, Sri Maha Bodhi, which was destroyed during the time of Emperor Ashoka the Great, at Buddha Gaya in India, under which Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha) attained Enlightenment. The Buddhist nun Sangamitta Maha Theri, a daughter of Indian Emperor Ashoka, in 236 BC, brought the tree cutting to Sri Lanka during the reign of Sinhalese King Devanampiya Tissa.[1] At more than 2,300 years old, it is the oldest living human-planted tree in the world with a known planting date. The Mahavamsa, or the great chronicle of the Sinhalese, provides an elaborate account of the establishment of the Jaya Sri Maha Bodhi on the Island and the subsequent development of the site as a major Buddhist pilgrimage site.

Abhayagiri Vihāra was a major monastery site of Theravada, Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhism that was situated in Anuradhapura, Sri Lanka. It is one of the most extensive ruins in the world and one of the most sacred Buddhist pilgrimage cities in the nation. Historically it was a great monastic center as well as a royal capital, with magnificent monasteries rising to many stories, roofed with gilt bronze or tiles of burnt clay glazed in brilliant colours. To the north of the city, encircled by great walls and containing elaborate bathing ponds, carved balustrades and moonstones, stood "Abhayagiri", one of seventeen such religious units in Anuradhapura and the largest of its five major viharas. One of the focal points of the complex is an ancient stupa, the Abhayagiri Dagaba. Surrounding the humped dagaba, Abhayagiri Vihara was a seat of the Northern Monastery, or Uttara Vihara and the original custodian of the Tooth relic in the island.
Atamasthana or Eight sacred places are a series of locations in Sri Lanka where the Buddha had visited during his three visits to the country. The sacred places are known as Jaya Sri Maha Bodhiya, Ruwanwelisaya, Thuparamaya, Lovamahapaya, Abhayagiri Dagaba, Jetavanarama, Mirisaveti Stupa and Lankarama. They are situated in Anuradhapura, the capital of the ancient Anuradhapura Kingdom.

The architecture of ancient Sri Lanka displays a rich diversity, varying in form and architectural style from the Anuradhapura Kingdom through the Kingdom of Kandy (1469–1815). Sinhalese architecture also displays many ancient North Indian influences. Buddhism had a significant influence on Sri Lankan architecture after it was introduced to the island in the 3rd century BC, and ancient Sri Lankan architecture was mainly religious, with more than 25 styles of Buddhist monasteries. Significant buildings include the stupas of Jetavanaramaya and Ruwanvelisaya in the Anuradhapura kingdom and further in the Polonnaruwa Kingdom. The palace of Sigiriya is considered a masterpiece of ancient architecture and ingenuity, and the fortress in Yapahuwa and the Temple of the tooth in Kandy are also notable for their architectural qualities. Ancient Sri Lankan architecture is also significant to sustainability, notably Sigiriya which was designed as an environmentally friendly structure.

Stupas, also called dagebas and cetiyas, are considered an outstanding type of architectural creation of ancient Sri Lanka. Under the influence of Buddhism, there were several changes in the field of architecture in Sri Lanka. The stupa commands a prominent place among these changes. The Stupa is also known by synonymous names such as Chaithya, Dagaba, Thupa, Seya and Vehera. Stupas designed and constructed in Sri Lanka are the largest brick structures known to the pre-modern world.
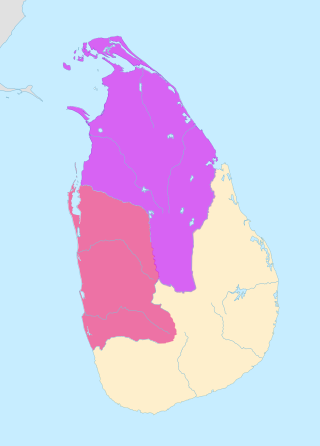
The Kingdom of Polonnaruwa was the Sinhalese kingdom that expanded across the island of Sri Lanka and several overseas territories, from 1070 until 1232. The kingdom started expanding its overseas authority during the reign of Parakramabahu the Great.

Anuradhapura Kingdom, named for its capital city, was the second established kingdom in ancient Sri Lanka related to the Sinhalese people. According to the Mahāvaṃsa, it was founded by King Pandukabhaya in 437 BC, whose authority extended throughout the country.

Sandakada Pahana, also known as Moonstone, is a unique feature of the architecture of ancient Sri Lanka. It is an elaborately carved semi-circular stone slab, usually placed at the bottom of staircases and entrances. First seen in the latter stage of the Anuradhapura period, the sandakada pahana evolved through the Polonnaruwa, Gampola and Kandyan period. According to historians, the sandakada pahana symbolises the cycle of Samsāra in Buddhism.

The Polonnaruwa Vatadage is an ancient structure dating back to the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa of Sri Lanka. It is believed to have been built during the reign of Parakramabahu I to hold the Relic of the tooth of the Buddha or during the reign of Nissanka Malla of Polonnaruwa to hold the alms bowl used by the Buddha. Both these venerated relics would have given the structure a great significance and importance at the time. Located within the ancient city of Polonnaruwa, it is the best preserved example of a vatadage in the country, and has been described as the "ultimate development" of this type of architecture. Abandoned for several centuries, excavation work at the Polonnaruwa Vatadage began in 1903.

A vaṭadāge is a type of Buddhist structure found in Sri Lanka. It also known as a dage, thupagara and a cetiyagara. Although it may have had some Indian influence, it is a structure that is more or less unique to the architecture of ancient Sri Lanka. Vatadages were built around small stupas for their protection, which often enshrined a relic or were built on hallowed ground. Circular in shape, they were commonly built of stone and brick and adorned with elaborate stone carvings. Vatadages may have also had a wooden roof, supported by a number of stone columns arranged in several concentric rows.

Ritigala is a mountain in central Sri Lanka which is home to an ancient Buddhist monastery. The ruins and rock inscriptions of the monastery date back to 1st century BCE. It is located 43 km (27 mi) away from the ancient monastic city of Anuradhapura.

Gadaladenyia Vihara is an ancient Buddhist temple situated in Pilimathalawa, Kandy, Sri Lanka. It is located on Gadaladenyia Road (B116), just up from the Gadaladeniya junction of the Colombo - Kandy Road (A1), approximately 12.5 km (7.8 mi) to the west of Kandy and 3 km (1.9 mi) from the ancient buddhist temple, Lankatilaka Vihara. It is considered one of the largest rock temples in Sri Lanka.

Muragala or muru gal, also known as a guardstone, are a unique feature of the Sinhalese architecture of ancient Sri Lanka. The muragala is a set of twin oblong slabs of stone, with a rounded top, located at the foot of the flight of steps, leading to a place of worship, situated on a higher elevation.

Korawakgala, or koravakgal (wingstones), are stone balustrades, which are located on either side of the stairs/steps leading to the entrance or door of a religious building or structure. They form one of three distinct architectural features at the entrance of most Buddhist structures in Sri Lanka, being the sandakada pahana (moonstone), muragala (guardstones) and the korawakgala (wingstones).
The history of Theravāda Buddhism begins in ancient India, where it was one of the early Buddhist schools which arose after the first schism of the Buddhist monastic community. After establishing itself in the Sri Lankan Anuradhapura Kingdom, Theravāda spread throughout mainland Southeast Asia through the efforts of missionary monks and Southeast Asian kings.
















