Related Research Articles

Archaeoglobaceae are a family of the Archaeoglobales. All known genera within the Archaeoglobaceae are hyperthermophilic and can be found near undersea hydrothermal vents. Archaeoglobaceae are the only family in the order Archaeoglobales, which is the only order in the class Archaeoglobi.
In taxonomy, the Thermoplasmata are a class of the Euryarchaeota.
In taxonomy, the Thermoplasmatales are an order of the Thermoplasmata. All are acidophiles, growing optimally at pH below 2. Picrophilus is currently the most acidophilic of all known organisms, being capable of growing at a pH of -0.06. Many of these organisms do not contain a cell wall, although this is not true in the case of Picrophilus. Most members of the Thermotoplasmata are thermophilic.
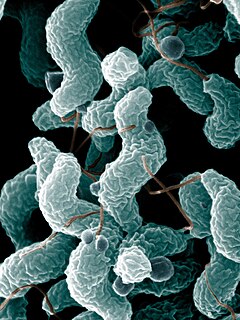
Epsilonproteobacteria are a class of Proteobacteria. All species of this class are, like all Proteobacteria, Gram-negative.
Chryseobacterium greenlandense is an ultramicrobacteria species, of bacteria that is able to live for long periods of time in low-temperature, high-pressure, reduced-oxygen and nutrient-poor habitats. It is known to have survived for more than 120,000 years in an ice block in Greenland, at a depth of 3,000 metres (1.9 mi).
The Negativicutes are a class of bacteria in the phylum Firmicutes, whose members have a peculiar cell wall with a lipopolysaccharide outer membrane which stains gram-negative, unlike most other members of the Firmicutes. Although several neighbouring Clostridia species also stain gram-negative, the proteins responsible for the unusual diderm structure of the Negativicutes may have actually been laterally acquired from Proteobacteria. Additional research is required to confirm the origin of the diderm cell envelope in the Negativicutes.
Psychrobacter is a genus of Gram-negative, osmotolerant, oxidase-positive, psychrophilic or psychrotolerant, aerobic bacteria which belong to the family Moraxellaceae and the class Gammaproteobacteria. The shape is typically cocci or coccobacilli. Some of those bacteria were isolated from humans and can cause humans infections such as endocarditis and peritonitis. This genus of bacteria is able to grow at temperatures between −10 and 42 °C. Rudi Rossau found through DNA-rRNA hybridization analysis that Psychrobacter belongs to the Moraxellaceae. The first species was described by Juni and Heym. Psychrobacter occur in wide range of moist, cold saline habitats, but they also occur in warm and slightly saline habitats.
Virgibacillus is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped (bacillus) bacteria and a member of the phylum Firmicutes. Virgibacillus species can be obligate aerobes, or facultative anaerobes and catalase enzyme positive. Under stressful environmental conditions, the bacteria can produce oval or ellipsoidal endospores in terminal, or sometimes subterminal, swollen sporangia. The genus was recently reclassified from the genus Bacillus in 1998 following an analysis of the species V. pantothenticus. Subsequently, a number of new species have been discovered or reclassified as Virgibacillus species.
Phyllobacterium is a genus of Gram-negative, oxidase- and catalase-positive, aerobic bacteria.
Paenochrobactrum gallinarii is a bacterium of the genus Paenochrobactrum which was isolated from air of a duck barn in Berlin.
Paenochrobactrum glaciei is a bacterium of the genus Paenochrobactrum reclassified from Pseudochrobactrum glaciei.
Paenochrobactrum pullorum is a Gram-negative, oxidase-positive, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped, nonmotile bacterium of the genus Paenochrobactrum, which was isolated from faeces of a chicken in Germany
Pseudochrobactrum asaccharolyticum is a Gram-negative, oxidase-positive, non-spore-forming, nonmotile bacterium of the genus Paenochrobactrum.
Pseudochrobactrum kiredjianiae is a bacterium from the genus of Paenochrobactrum which was isolated in Nelson in New Zealand.
Pseudochrobactrum lubricantis is a Gram-negative, oxidase-positive, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped, nonmotile bacterium of the genus Paenochrobactrum, which was isolated from water mixed metal-working fluid in Germany.
Pseudochrobactrum saccharolyticum is a bacterium from the genus of Paenochrobactrum which was isolated from industrial glue.
Erythrobacteraceae is a bacterium family in the order of Sphingomonadales.
Psychrobacter glaciei is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming and non-motile bacterium of the genus Psychrobacter which has been isolated from the ice core of an arctic glacier from Austre Lovénbreen in Svalbard.
Chryseobacterium glaciei is a Gram-negative, aerobic and non-spore-forming bacteria from the genus of Chryseobacterium which has been isolated from the surface of a glacier near the Kunzum Pass in India.
Aureimonas glaciei is a Gram-negative, aerobic, short rod-shaped and motile bacteria from the genus of Aurantimonas which has been isolated from the Muztagh Glacier in China.
References
- 1 2 LPSN lpsn.dsmz.de
- ↑ UniProt
- ↑ Kampfer, P.; Martin, E.; Lodders, N.; Jackel, U.; Huber, B. E.; Schumann, P.; Langer, S.; Busse, H. -J.; Scholz, H. (2009). "Paenochrobactrum gallinarii gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from air of a duck barn, and reclassification of Pseudochrobactrum glaciei as Paenochrobactrum glaciei comb. nov". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 60 (7): 1493–8. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.015842-0 . PMID 19684318.