
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the late 16th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means to combat the Reformation and the Protestant church with a new architecture that inspired surprise and awe. It reached its peak in the High Baroque (1625–1675), when it was used in churches and palaces in Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, Bavaria and Austria. In the Late Baroque period (1675–1750), it reached as far as Russia, the Ottoman Empire and the Spanish and Portuguese colonies in Latin America. In about 1730, an even more elaborately decorative variant called Rococo appeared and flourished in Central Europe.
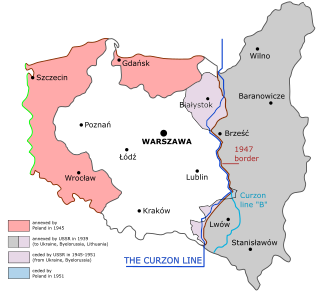
Eastern Borderlands or simply Borderlands was a term coined for the eastern part of the Second Polish Republic during the interwar period (1918–1939). Largely agricultural and extensively multi-ethnic with a Polish minority, it amounted to nearly half of the territory of interwar Poland. Historically situated in the eastern Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, following the 18th-century foreign partitions it was divided between the Empires of Russia and Austria-Hungary, and ceded to Poland in 1921 after the Treaty of Riga. As a result of the post-World War II border changes, all of the territory was ceded to the USSR, and none of it is in modern Poland.

Palace of Culture or House of Culture is a common name for major club-houses in the former Soviet Union and the rest of the Eastern bloc.
Palais des Sports is a generic name of comprehensive indoors sports venue, mostly in the French-speaking world, including:

Palacio de los Deportes is an indoor arena located in Mexico City, Mexico. It is within the Magdalena Mixhuca Sports City complex, near the Mexico City International Airport and in front of the Foro Sol, in which sports and artistic events are also celebrated. It is operated by Grupo CIE. The palace is named after Mexican military official Juan Escutia, although it is rarely referred to in its full name.
The 2002 Fed Cup was the 40th edition of the most important competition between national teams in women's tennis.
The Soviet Top League, known after 1970 as the Higher League, served as the top division (tier) of Soviet Union football from 1936 until 1991. The league's name was a conditional designation used for brevity since being completely owned and governed by the Football Federation of the Soviet Union. The full official name was the USSR Championship in football: Top League. An attempt to create an independent league as autonomously governed organization during "perestroika" period was denied by the Federation due to political culture in the Soviet Union.

Palacio de Deportes de la Comunidad de Madrid, officially WiZink Center since November 2016 for sponsorship reasons, is an indoor sporting arena located in Madrid, Spain.

The Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania is a palace in Vilnius, Lithuania. It was originally constructed in the 15th century for the rulers of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the future Kings of Poland. The palace, located in the lower castle of Vilnius, evolved over the years and prospered during the 16th and mid-17th centuries. For four centuries the palace was the political, administrative and cultural centre of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was demolished in 1801.

Vilnius Palace of Concerts and Sports is an indoor arena in Vilnius, Lithuania. The venue was opened in 1971. It was deemed unsafe and closed in 2004. Plans to reconstruct the venue received significant opposition from the Jewish community as the site is located on the grounds of the oldest Jewish cemetery in Vilnius.

The Polish population transfers in 1944–1946 from the eastern half of prewar Poland, were the forced migrations of Poles toward the end and in the aftermath of World War II. These were the result of a Soviet Union policy that had been ratified by the main Allies of World War II. Similarly, the Soviet Union had enforced policies between 1939 and 1941 which targeted and expelled ethnic Poles residing in the Soviet zone of occupation following the Nazi-Soviet invasion of Poland. The second wave of expulsions resulted from the retaking of Poland from the Wehrmacht by the Red Army. The USSR took over territory for its western republics.

The Archdiocese of Mohilev was a territorial Latin rite division of the Catholic Church, covering the greater part of the territory of the Tsarist Russian empire. The Cathedral was the Church of the Assumption of the Virgin.
The 2013 FIVB Volleyball World Grand Prix was the 21st edition of the annual women's international volleyball tournament played by 20 countries from 2 August to 1 September 2013.
The UEFA Futsal Euro 2018 qualifying competition was a men's futsal competition that determined the 11 teams joining the automatically qualified hosts Slovenia in the UEFA Futsal Euro 2018 final tournament.
The 2017 Women's European Volleyball League was the ninth edition of the annual Women's European Volleyball League, which features women's national volleyball teams from twelve European countries.
The football tournament at the 1956 Spartakiad of Peoples of the USSR was a preparatory competition for the Soviet Union national football team for the upcoming 1956 Summer Olympics. The competition took place on August 2 – 16, 1956 as part of the Spartakiad of Peoples of the USSR. The Soviet team has already qualified for the Olympic tournament by winning a play-off match up against Israel national football team earlier in July 1956. The Soviet team competed under the name of the Moscow city team.











